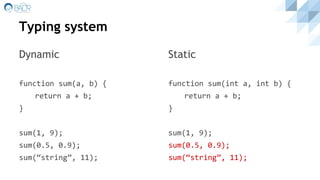
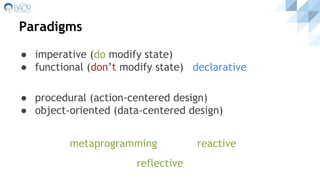
A programming language is defined by its syntax, semantics, paradigms, typing system, translation scheme, and memory management. There are many programming languages because each has a different focus, like being imperative, functional, procedural, or object-oriented. Languages get translated via compilation, interpretation, or a hybrid approach, and are typed statically or dynamically. Popular examples include C, Java, Lisp, and Smalltalk.




![What defines a programming language?
Syntax
Semantics
Paradigm[s]
Typing system
Translation scheme / Execution model
Memory management
….](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thereandbackagain-ataleofprogramminglanguages-161229133419/85/There-and-Back-Again-A-Tale-of-Programming-Languages-6-320.jpg)
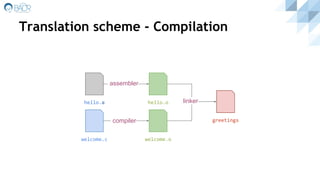
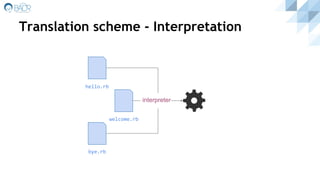
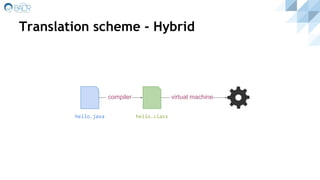
![Translation scheme - Hybrid [enhanced]
compiler
hello.java hello.class
JIT
010101001110
010001000100
010010000101](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thereandbackagain-ataleofprogramminglanguages-161229133419/85/There-and-Back-Again-A-Tale-of-Programming-Languages-10-320.jpg)