This document provides an overview of SQL concepts for an exam on business intelligence. It covers topics like SELECT statements, filtering data, joining tables, and ordering results. Examples are provided using databases that contain data on film information, the Eurovision song contest, and telecom customer transactions. The last section provides sample exam questions focusing on analyzing and aggregating data from the transaction database to answer business questions.



![#
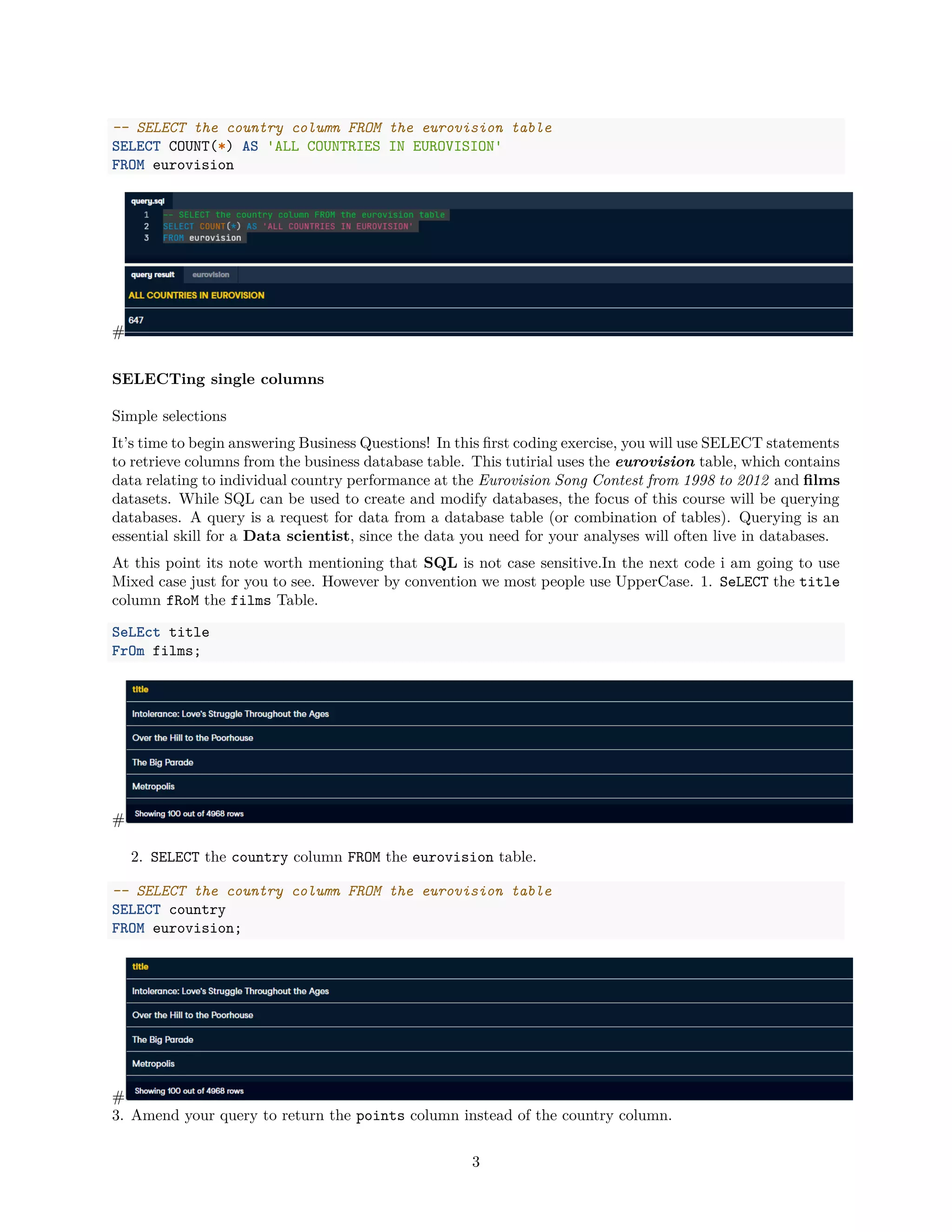
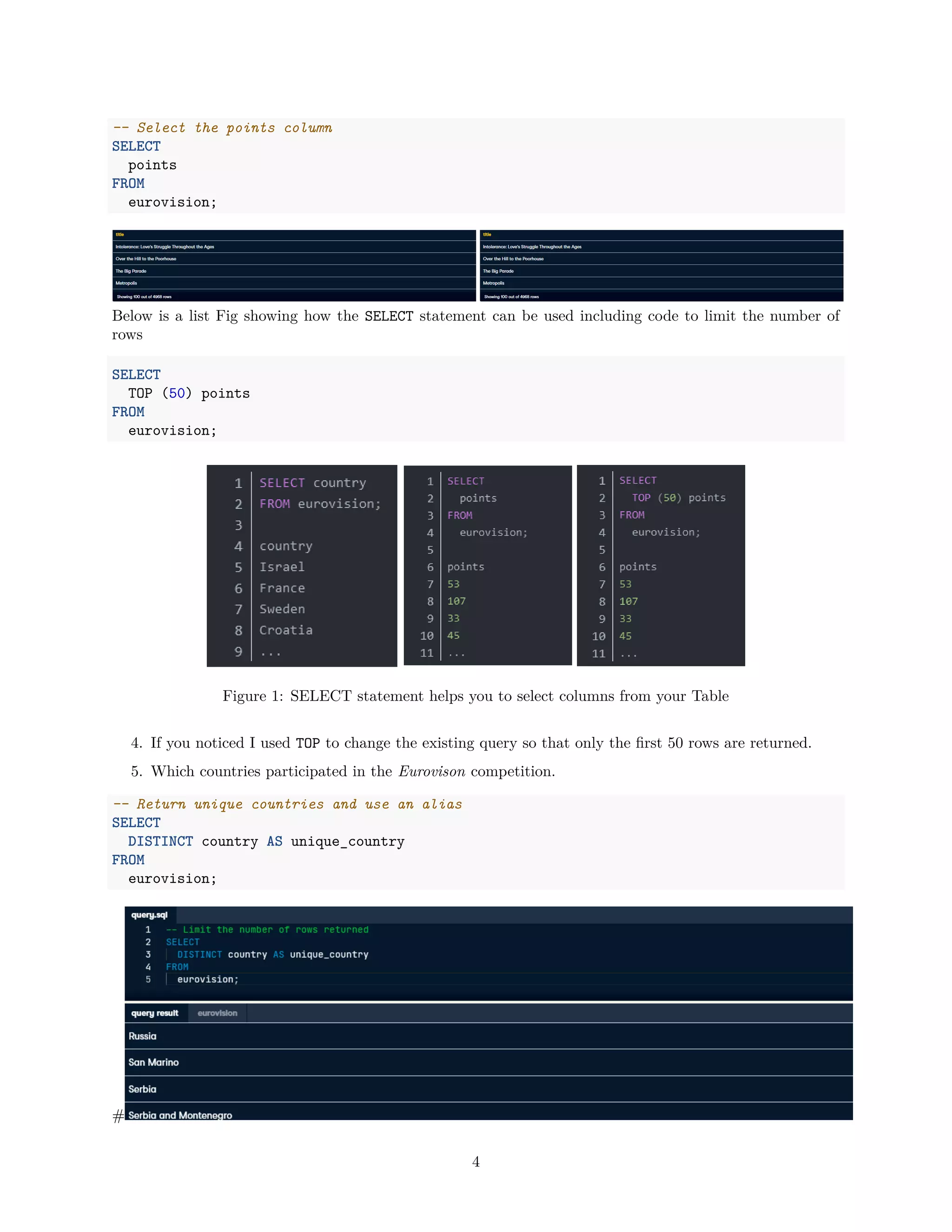
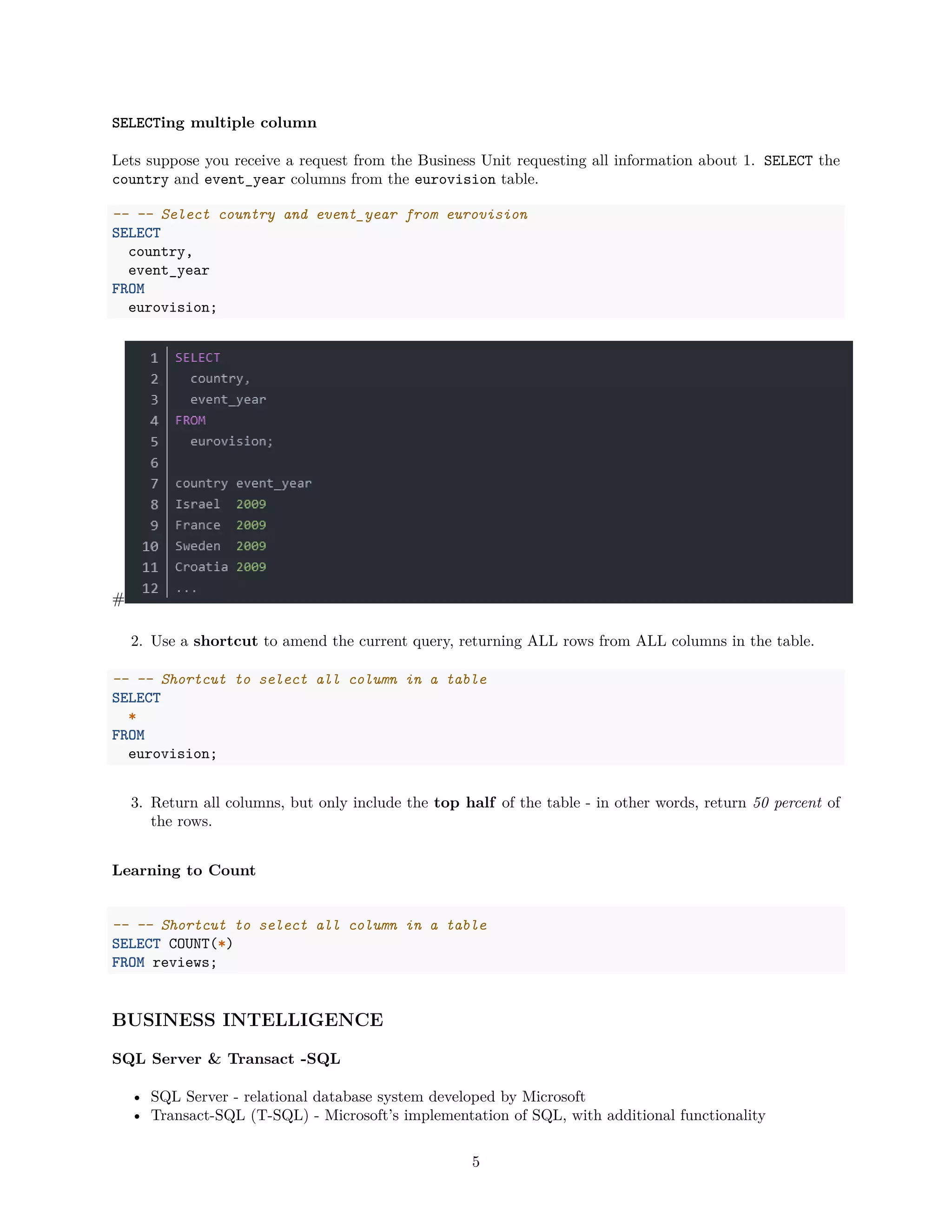
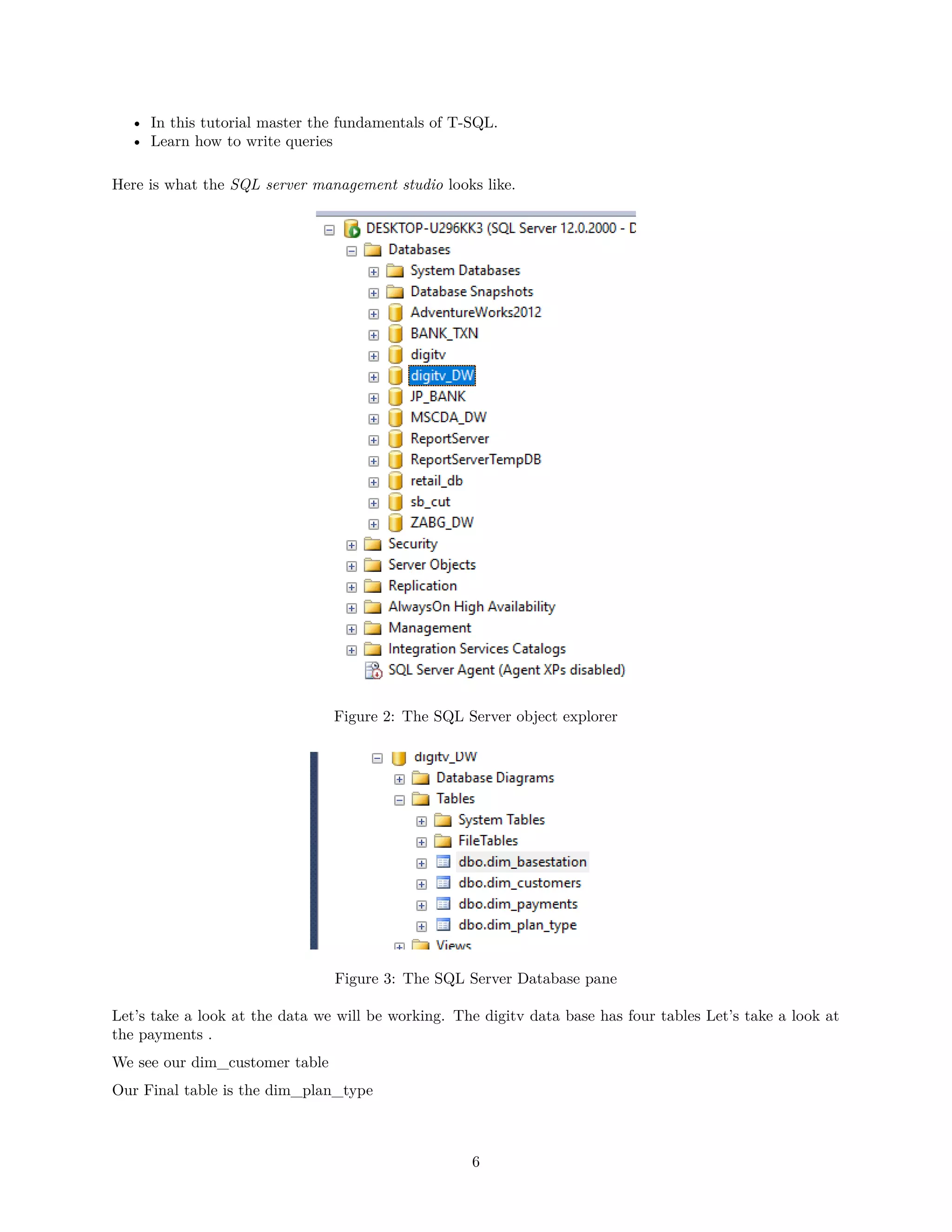
Where Clause
I am about to show you a beginers error. In SQL date is a reserved word so when you want to query the
column you will get an error.select [date] from dim_payments.Don‘t do that. Use Square brackets to
escape preserved word
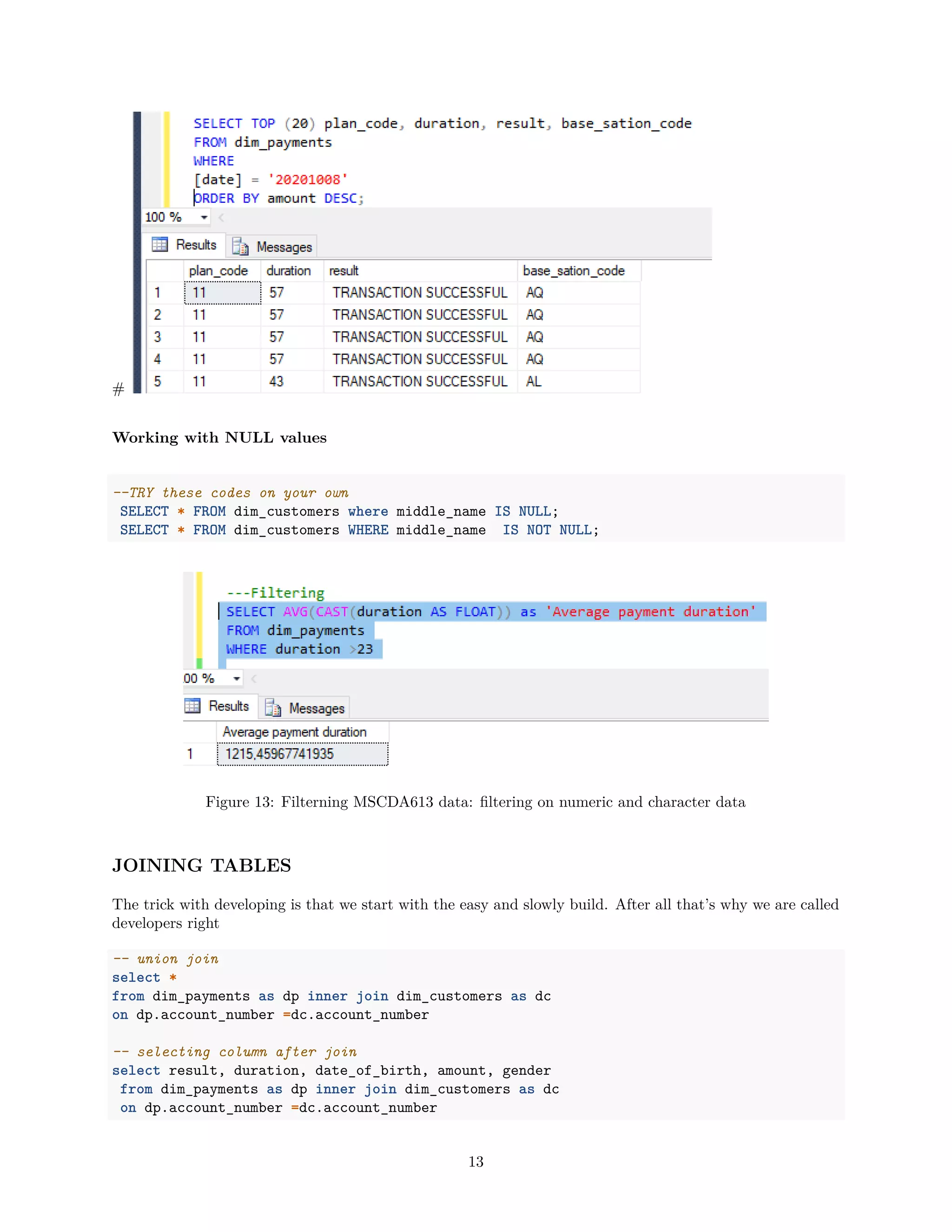
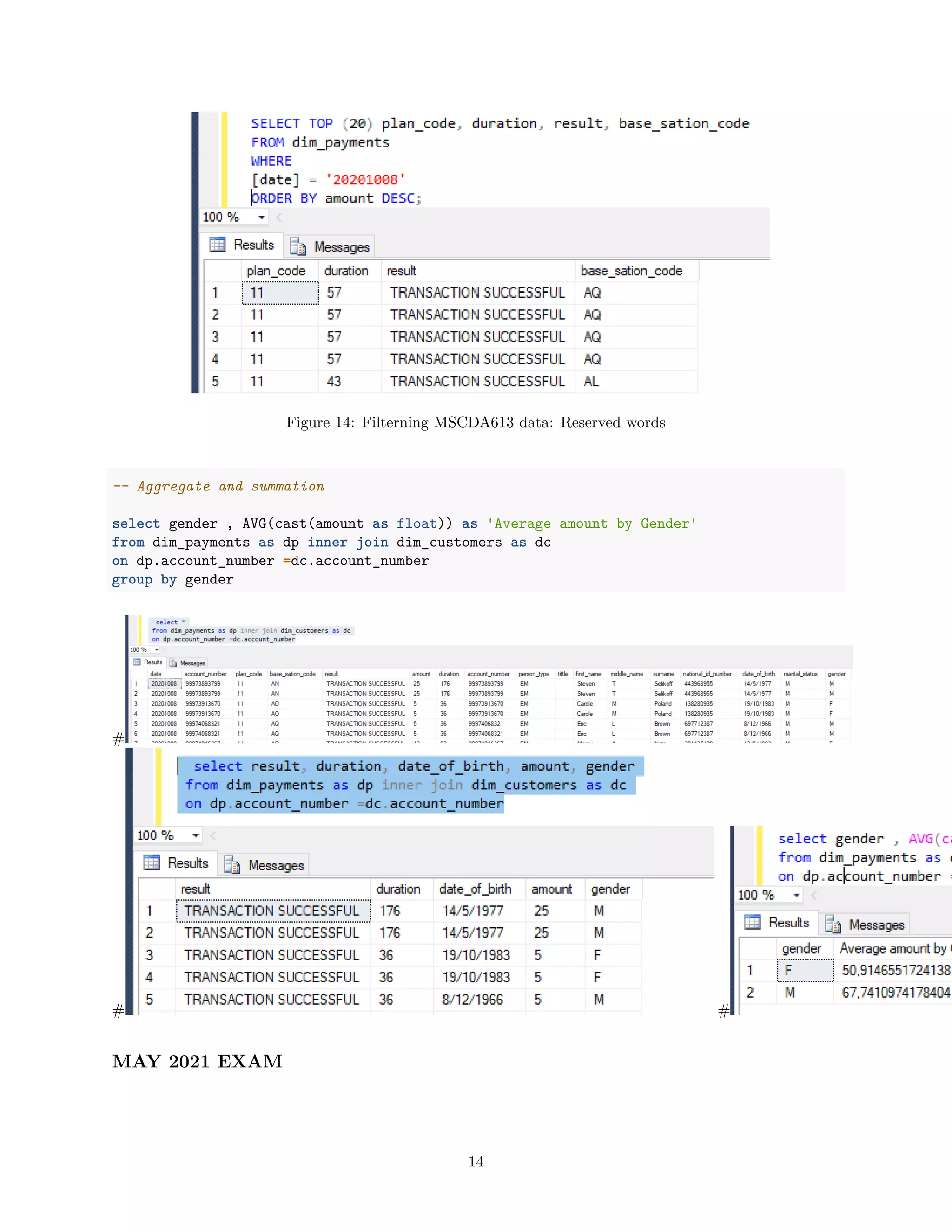
SELECT TOP (20) plan_code, duration, result, base_sation_code
FROM dim_payments
WHERE
[date] = '20201008';
SELECT TOP (20) plan_code, duration, result, base_sation_code
FROM dim_payments
WHERE
[date] = '20201008'
ORDER BY amount DESC;
-- BETWEEN
SELECT TOP (20) plan_code, duration, result, base_sation_code
FROM dim_payments
WHERE
[date] BETWEEN '20201008' AND '20201017'
ORDER BY amount DESC;
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/the-ultimate-guide-to-sql-210604064838/75/The-ultimate-guide-to-sql-12-2048.jpg)