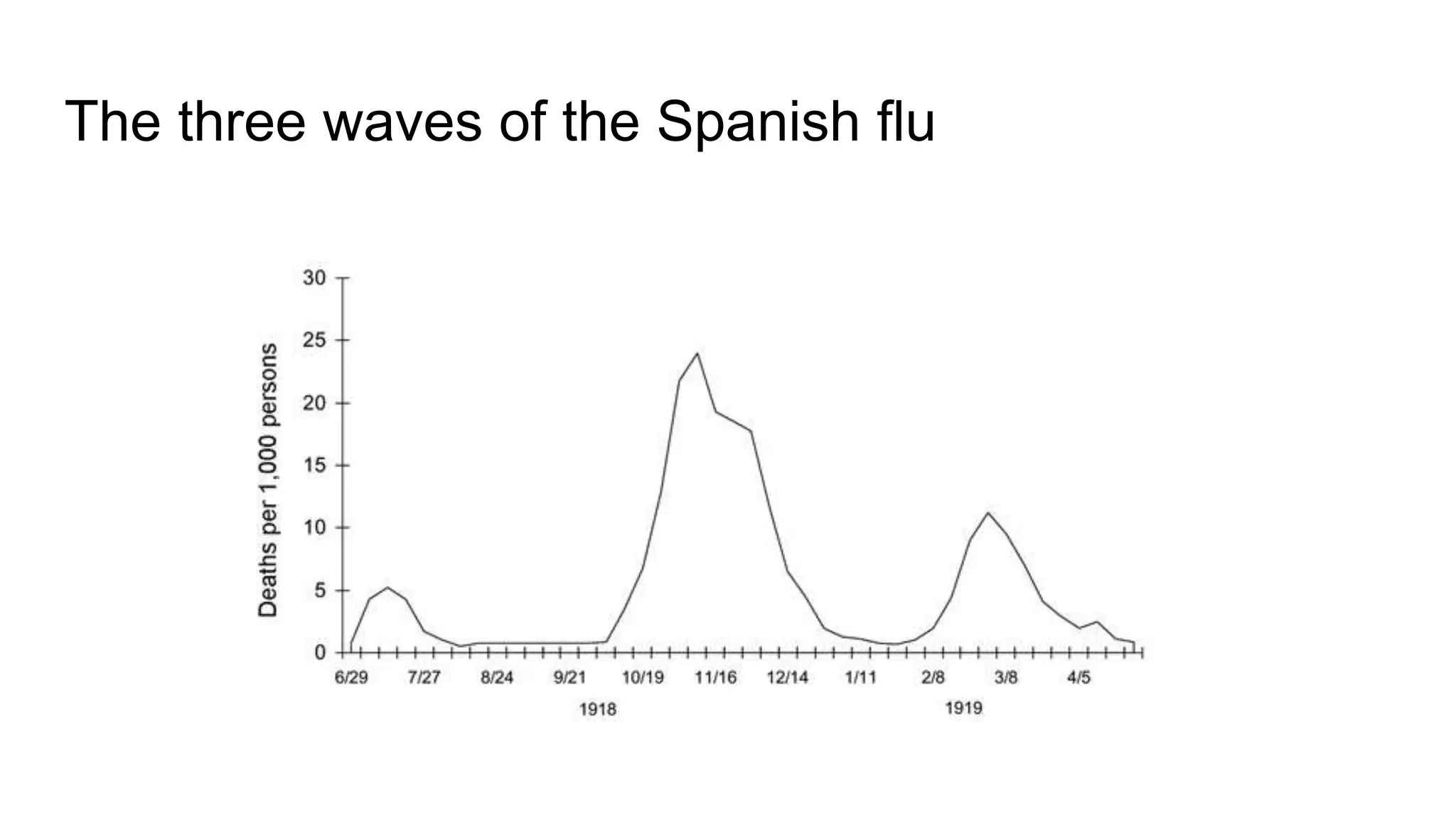
The Spanish flu pandemic of 1918-1919 was one of the deadliest in history, killing an estimated 20-50 million people globally, with significant mortality in India and the U.S. The pandemic's origin is uncertain, but theories suggest it may have started in China, France, or the U.S., exacerbated by troop movements during World War I. With no vaccine available, public health measures like social distancing, isolation, and hygiene were implemented until the pandemic ended in 1919, either through immunity or lesser virus mutation.