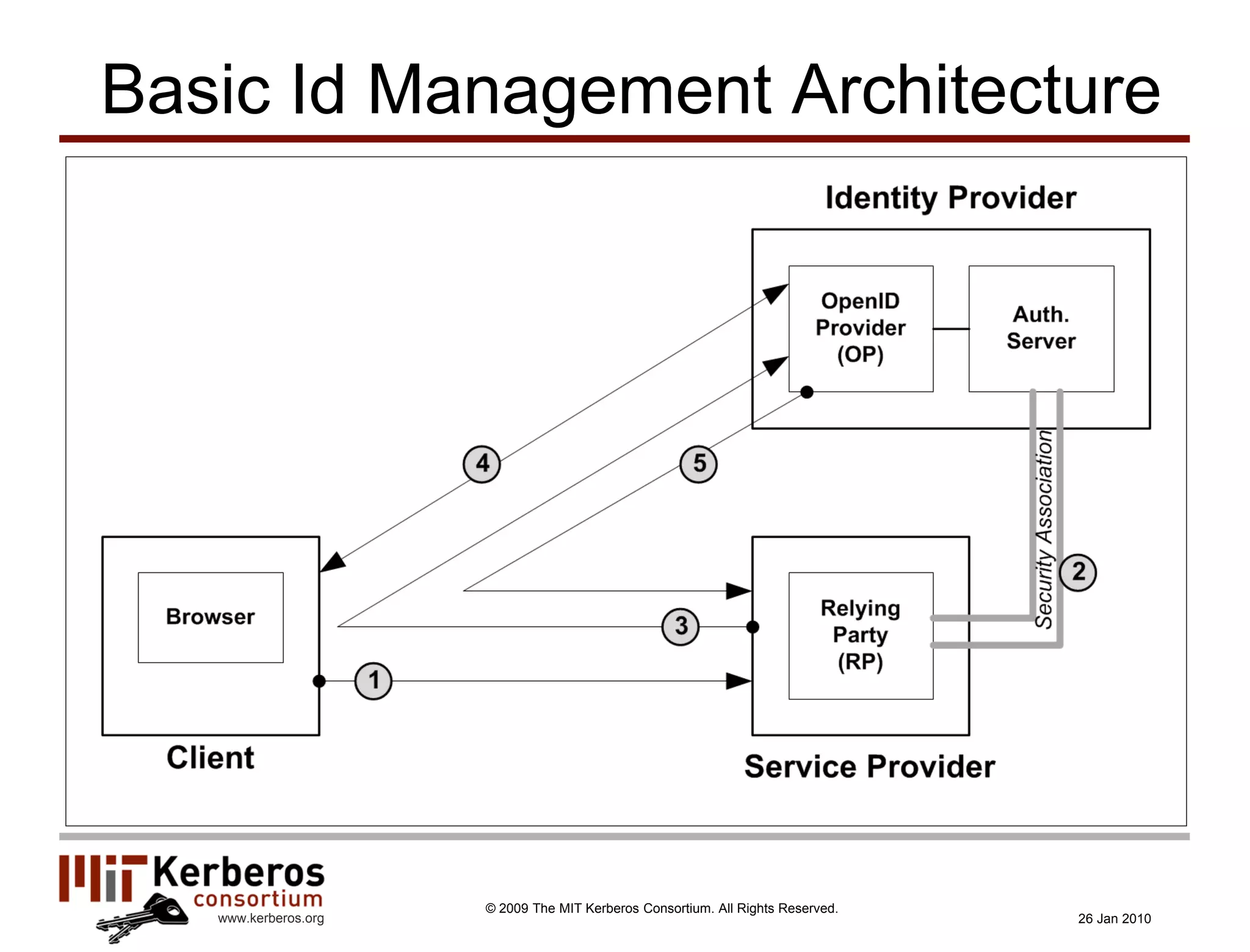
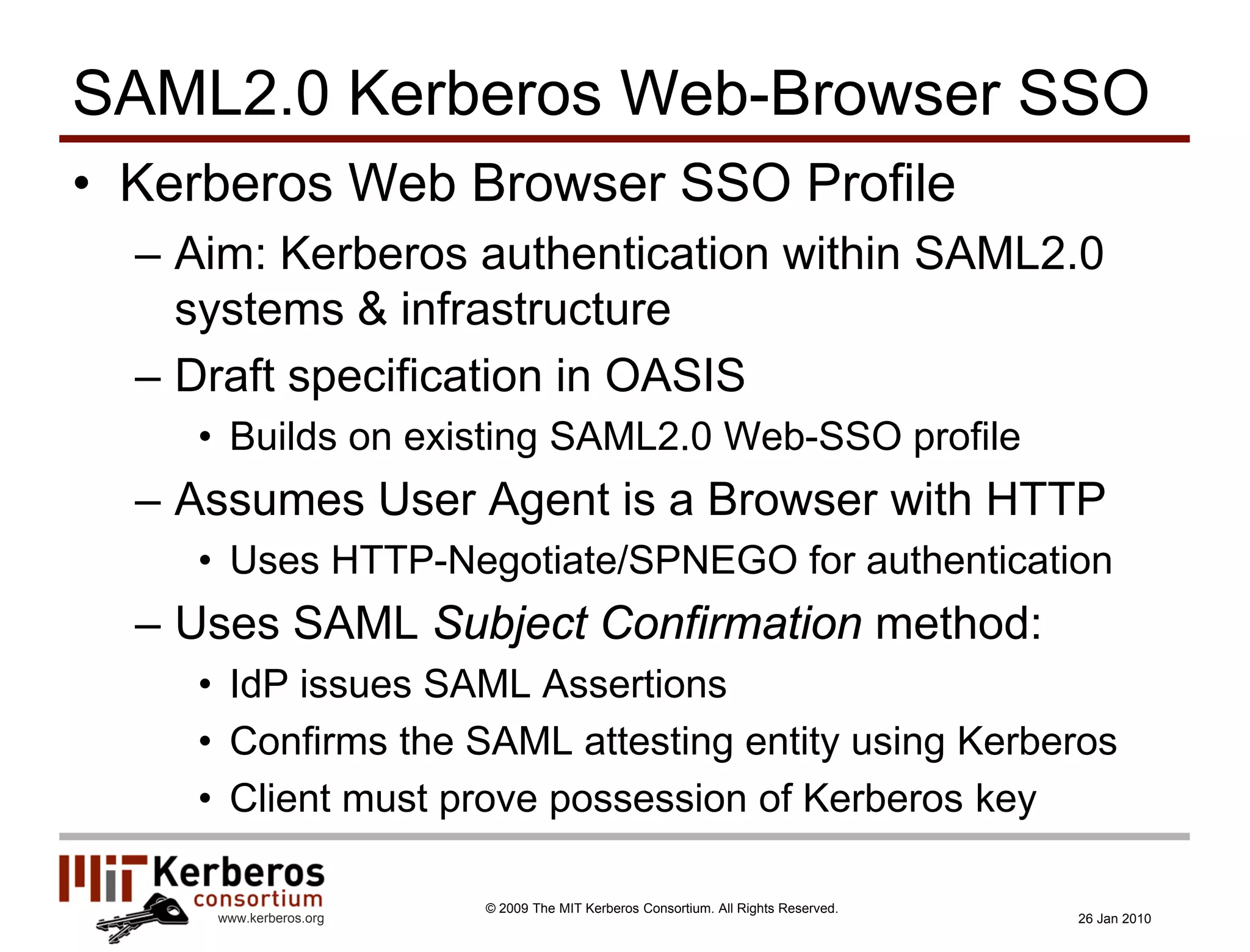
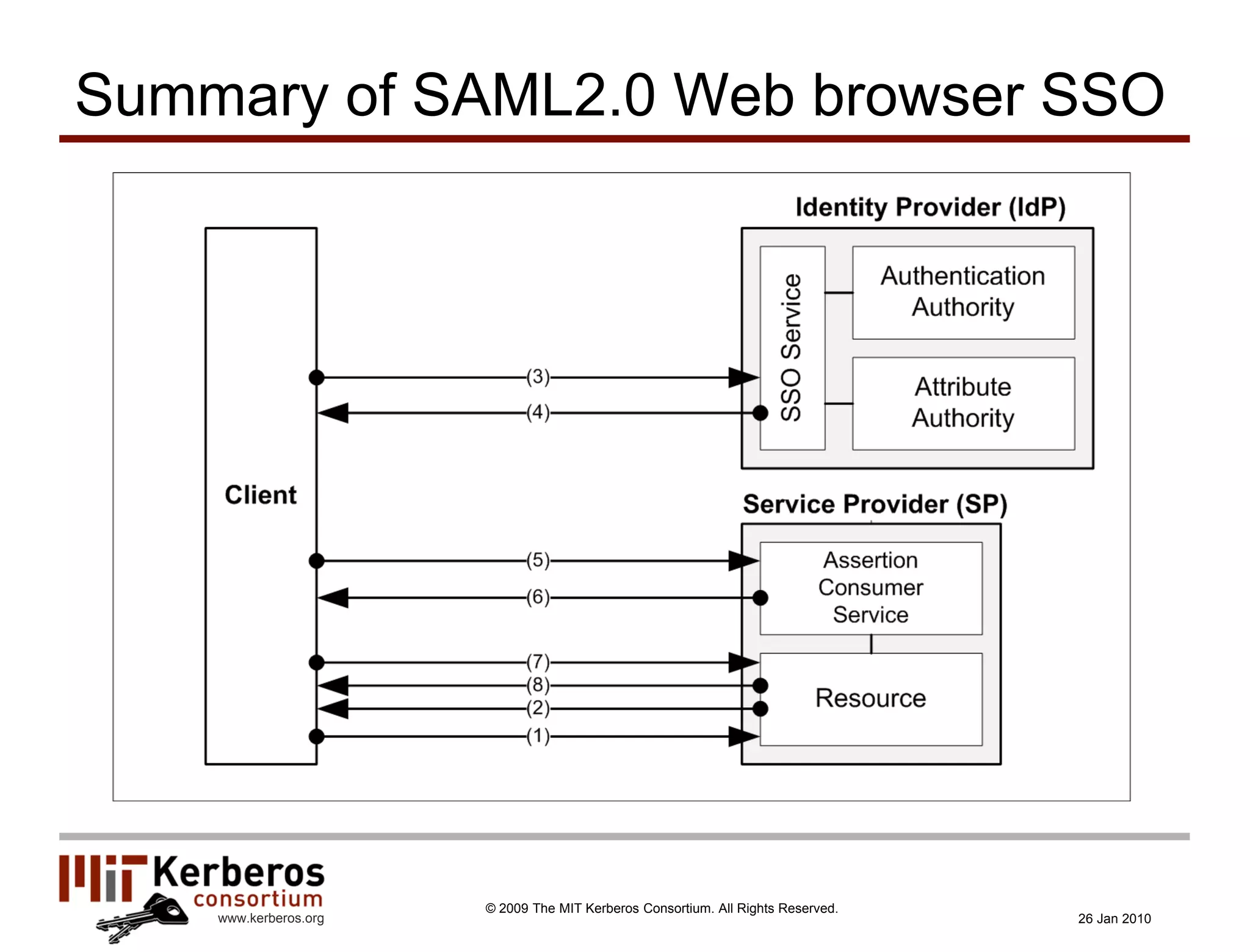
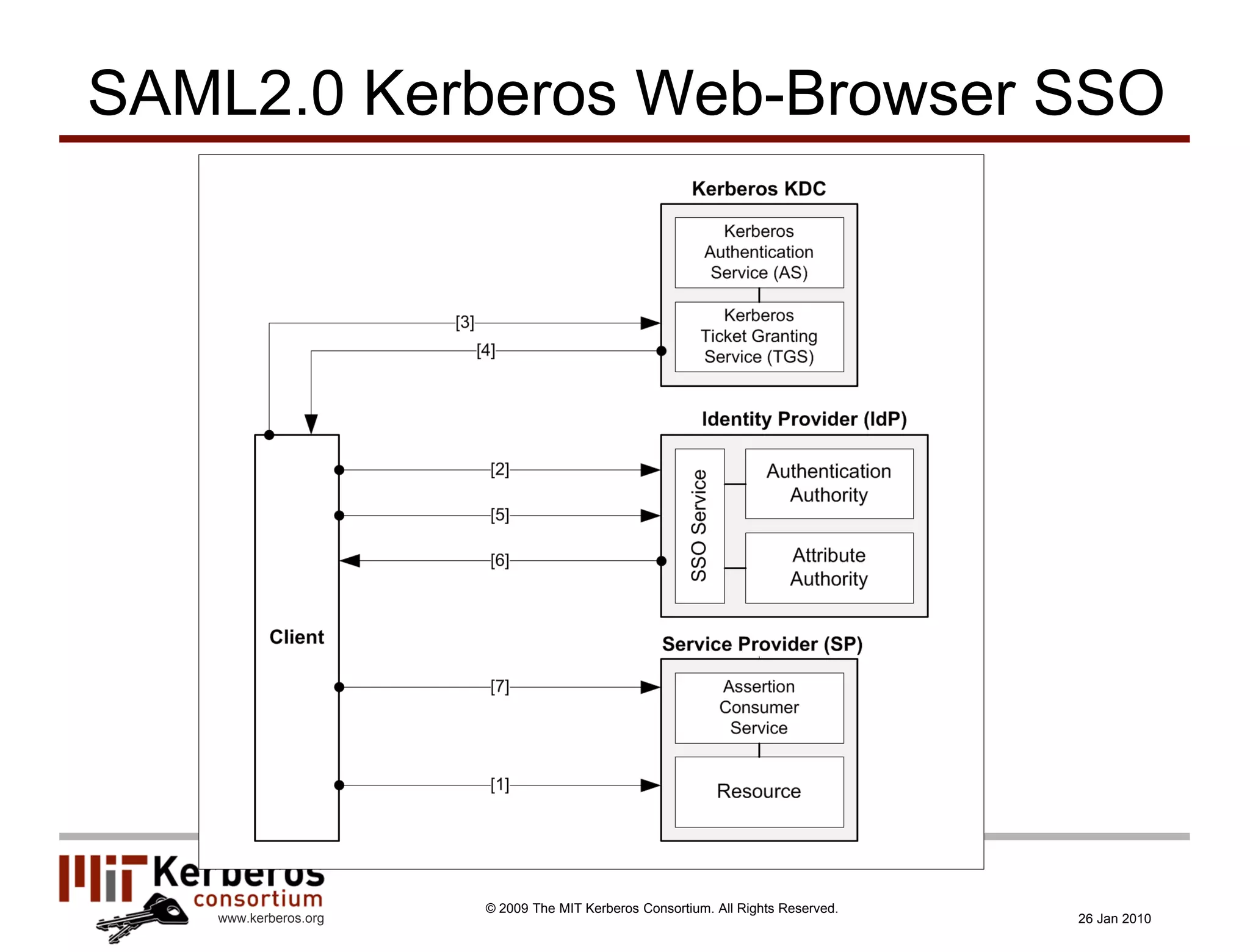
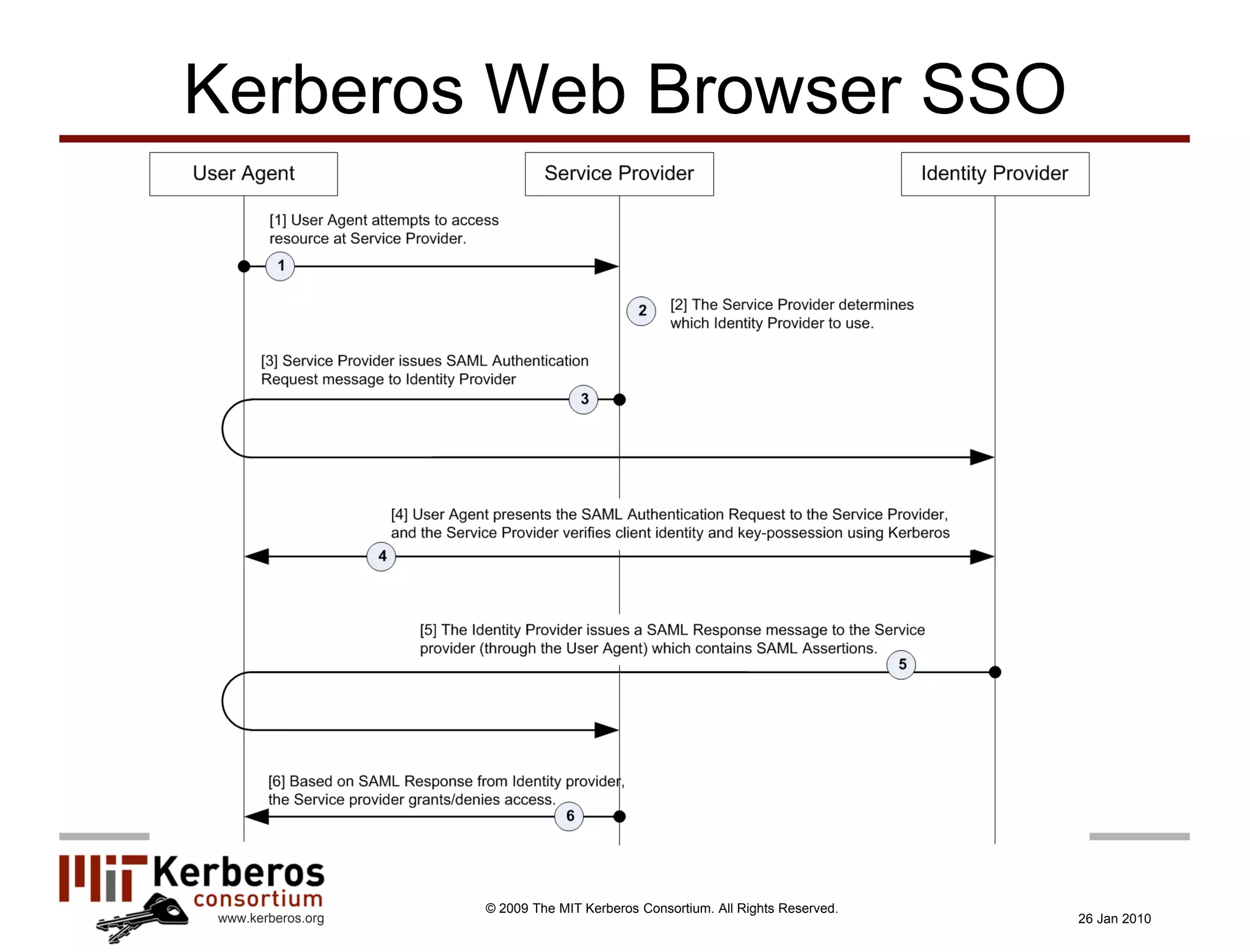
The document is a presentation about Kerberos and identity management given by Thomas Hardjono of the MIT Kerberos Consortium. It provides an overview of Kerberos' history and role in authentication, describes the Kerberos protocol, and discusses how Kerberos can be used for identity management including in SAML single sign-on systems on the web.