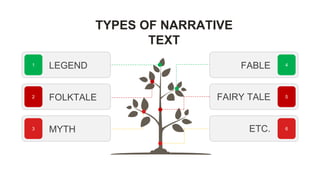
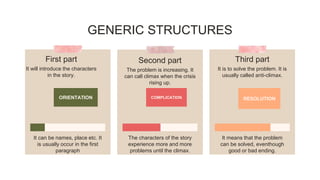
The document discusses narrative text, emphasizing its purpose to entertain and teach moral lessons through imaginative storytelling. Various types of narrative texts such as legends, folktales, myths, fables, and fairy tales are highlighted, along with their generic structures: orientation, complication, and resolution. An example is provided through the story of 'the legend of rawa pening,' illustrating how narrative elements come together.