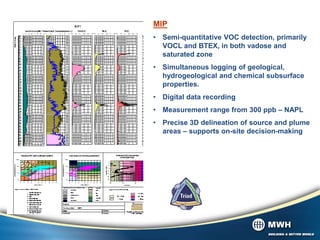
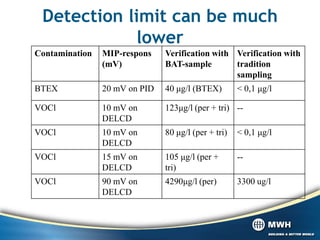
The document discusses the Membrane Interface Probe (MIP) technique for semi-quantitative detection of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and benzene, toluene, ethylbenzene, and xylenes (BTEX) in both the vadose and saturated zones. It describes the standard operating procedure, components of an MIP system including detectors, detection limits, factors that can influence results, and developments that have improved the technique over the past 15 years including a heated trunk line and more stable detectors. It emphasizes that MIP provides a screening rather than definitive identification of contamination and that samples should be taken for verification.