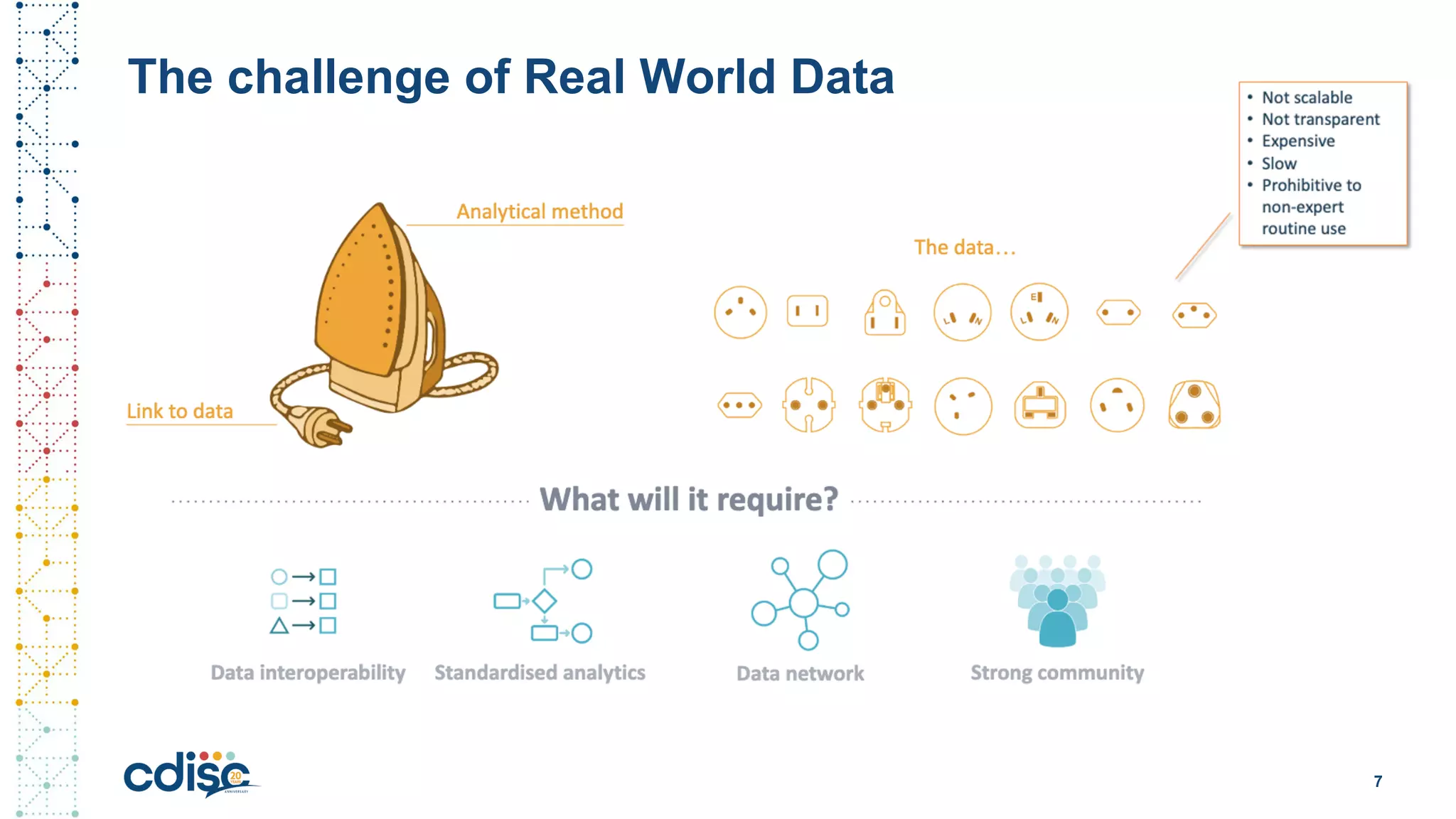
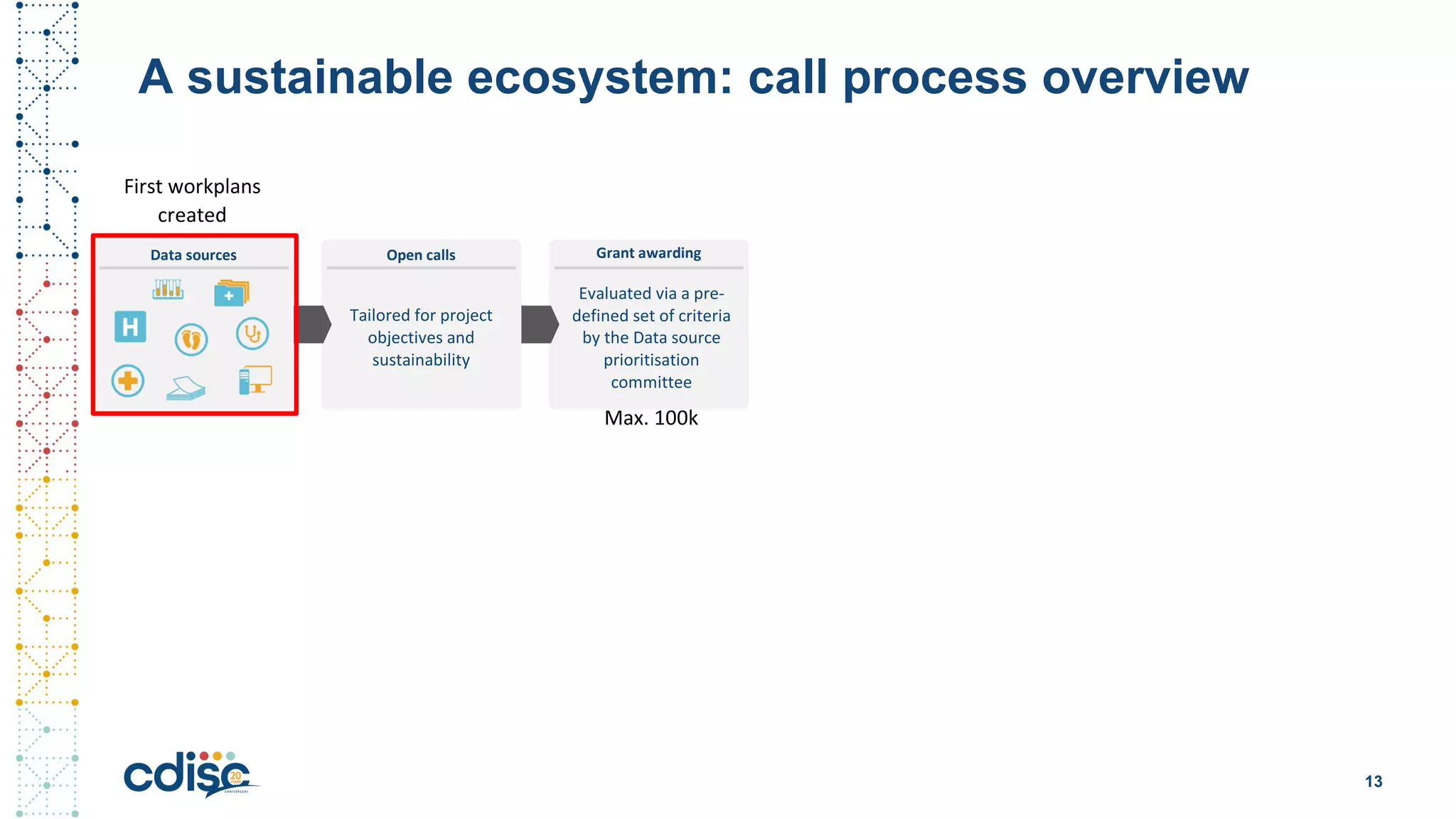
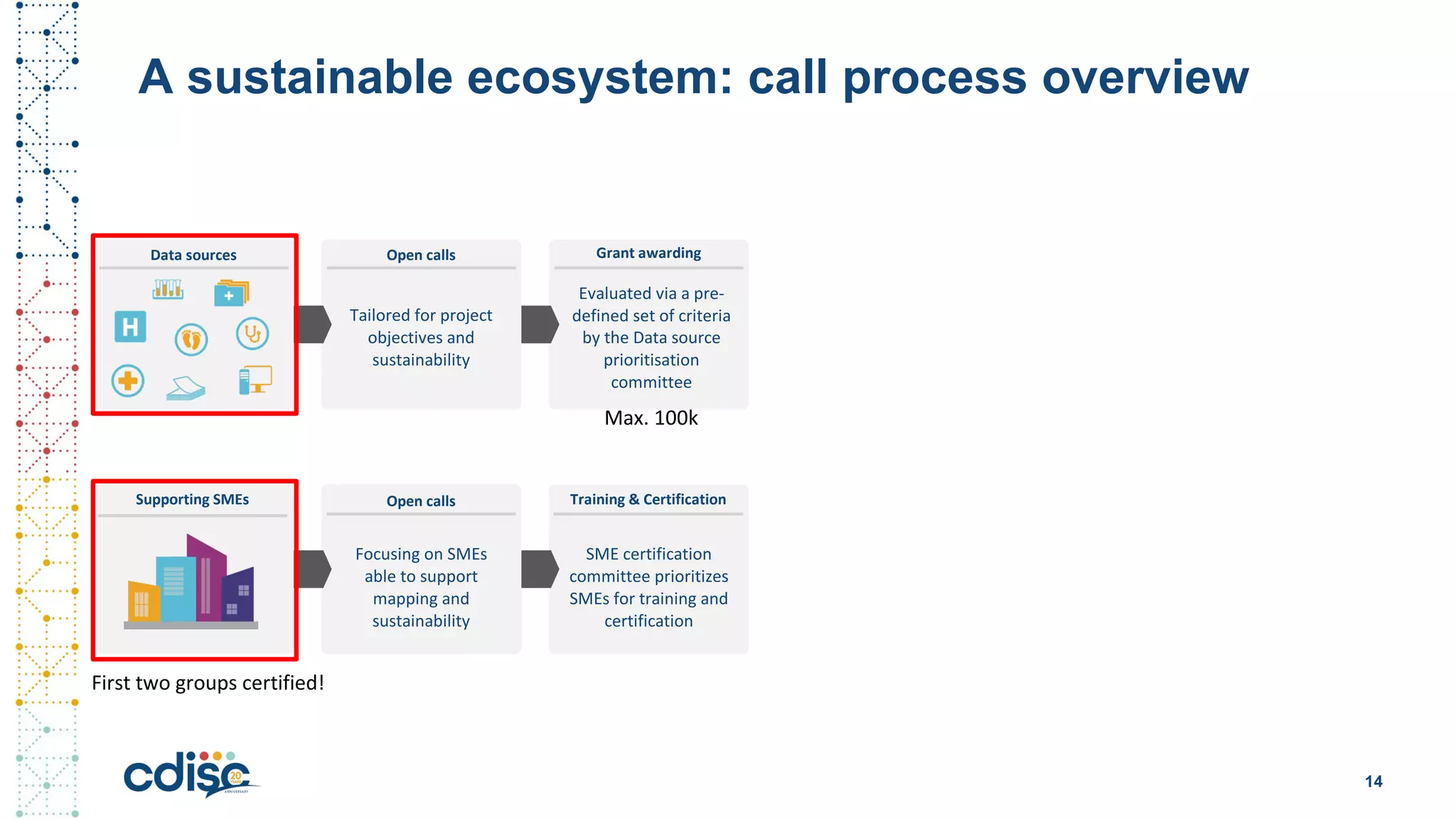
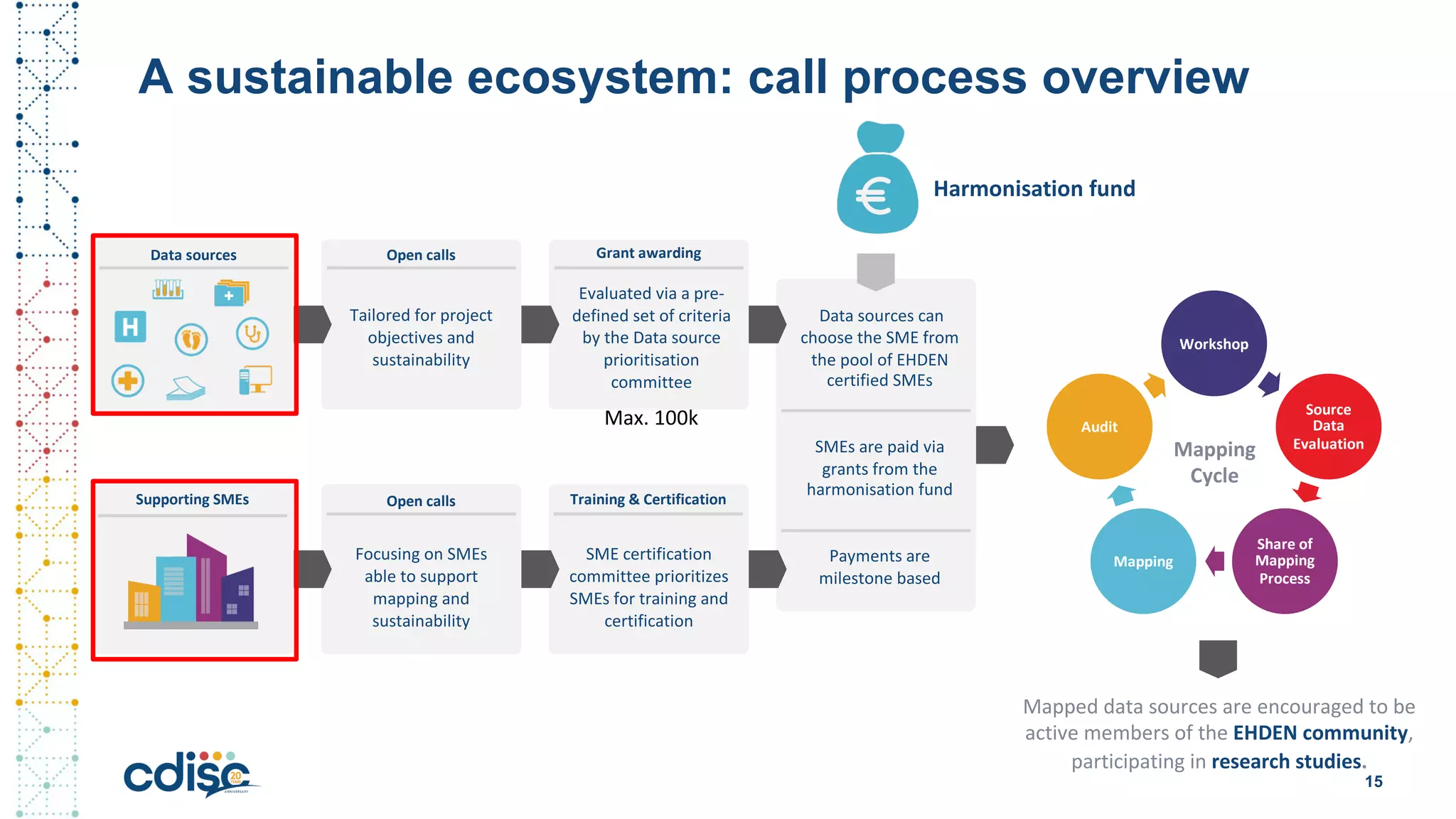
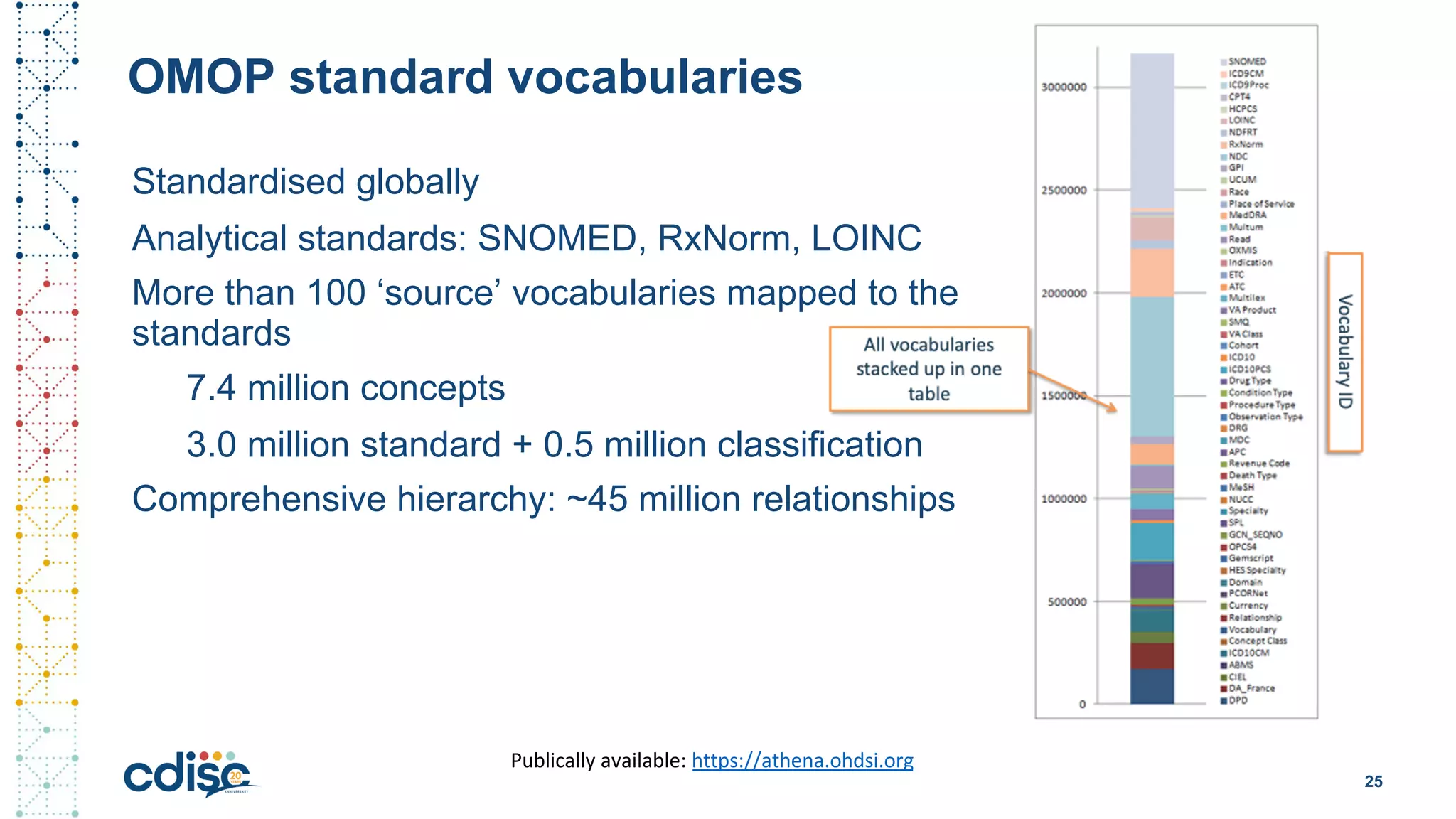
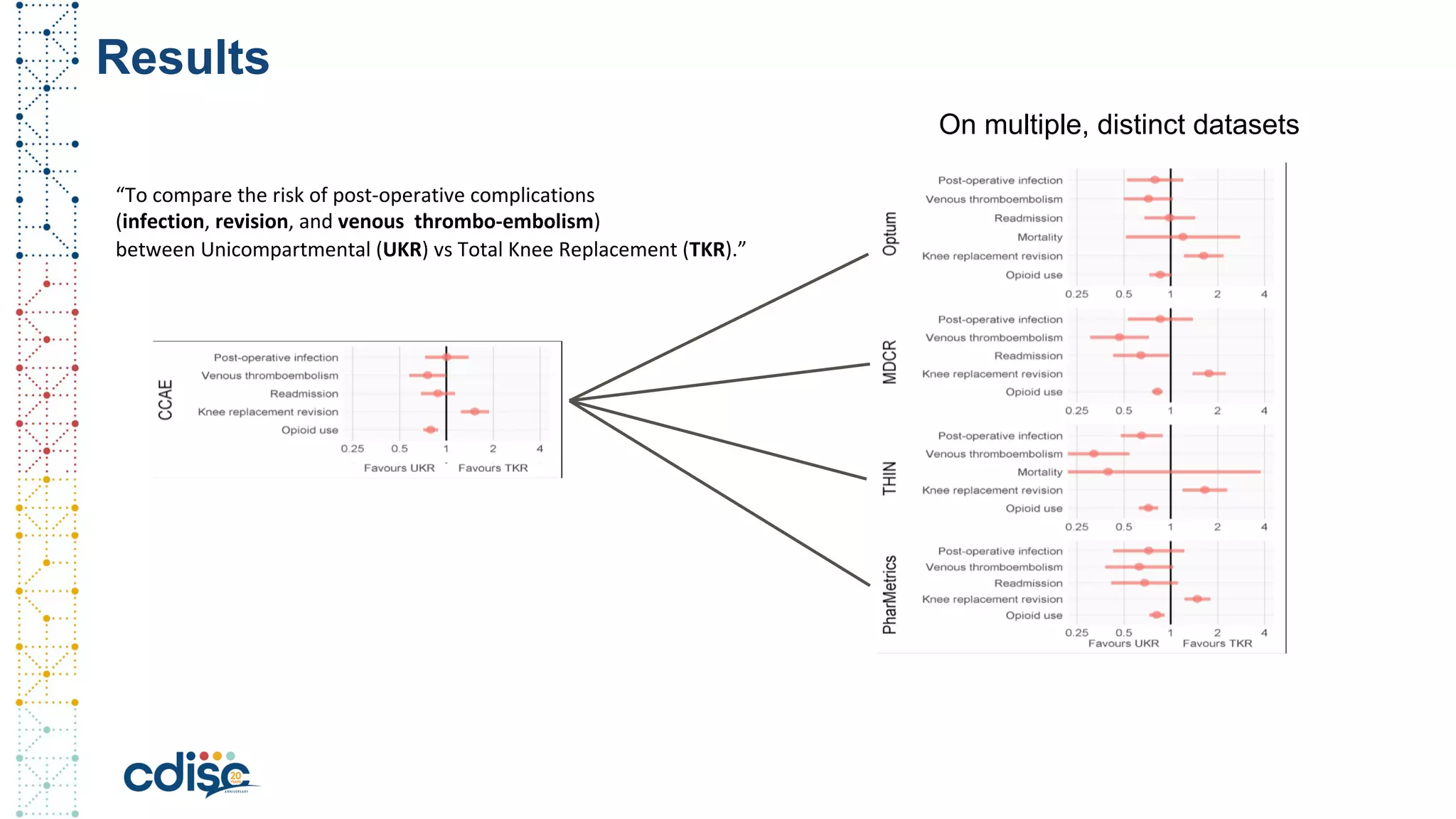
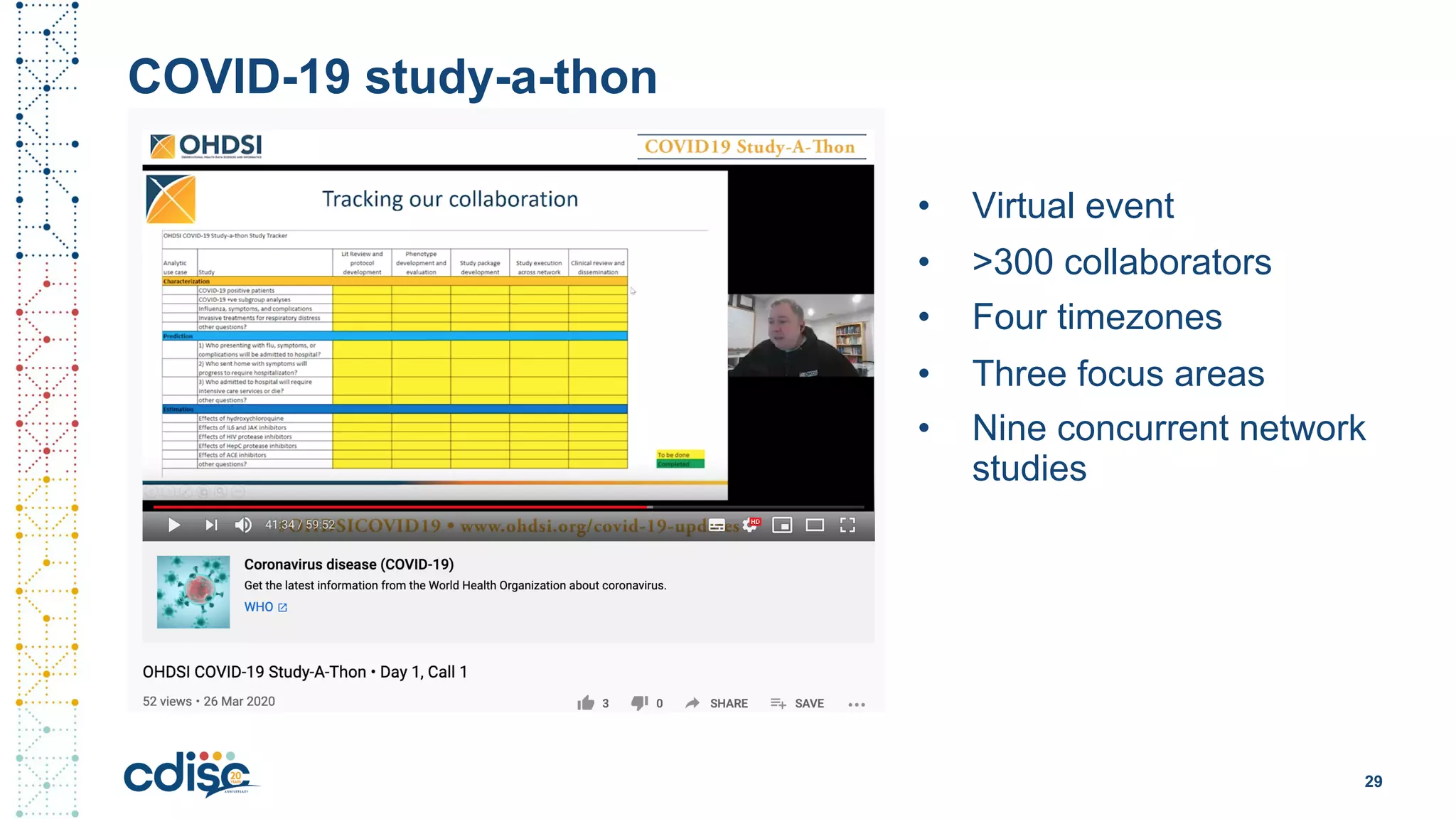
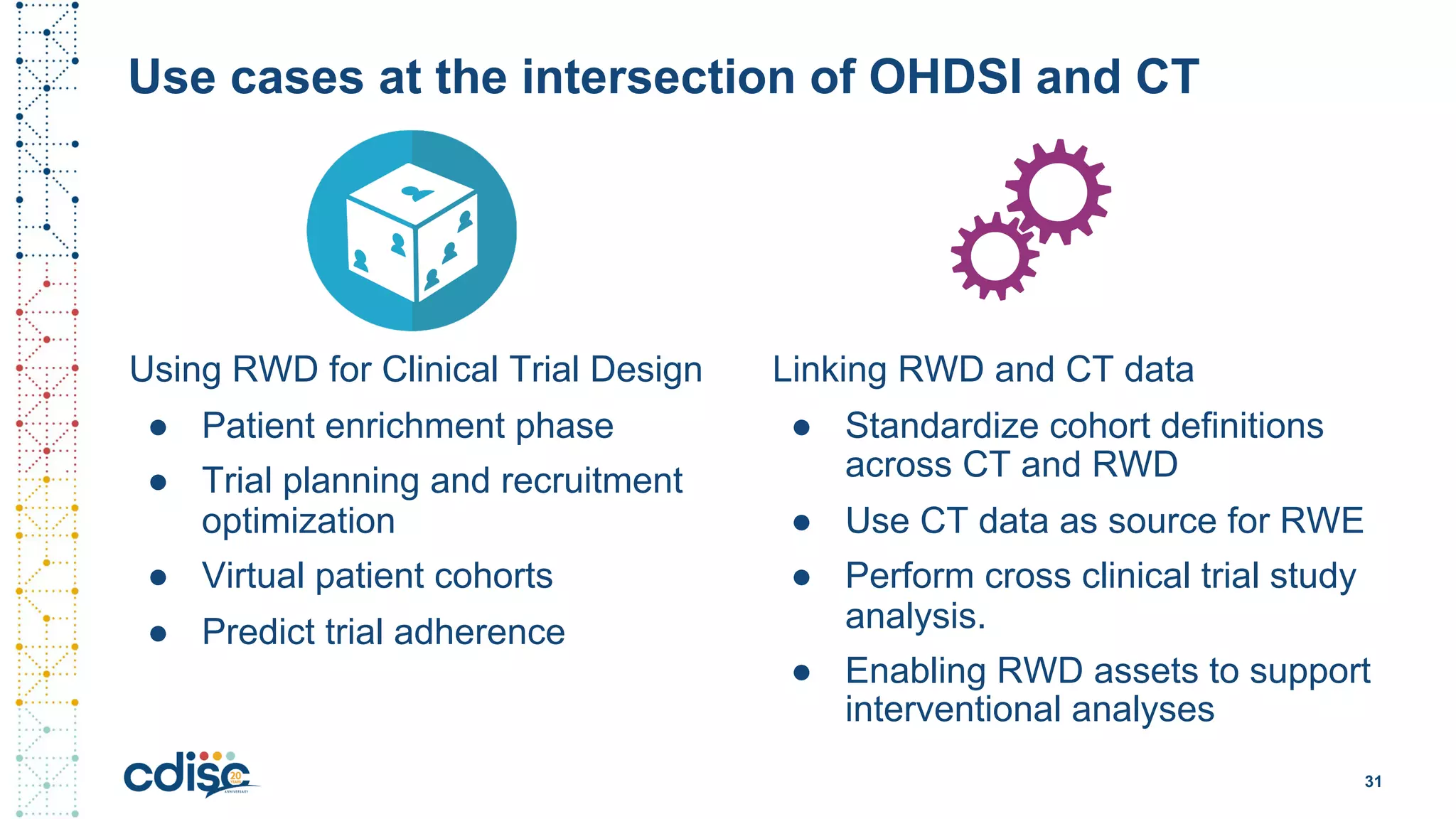
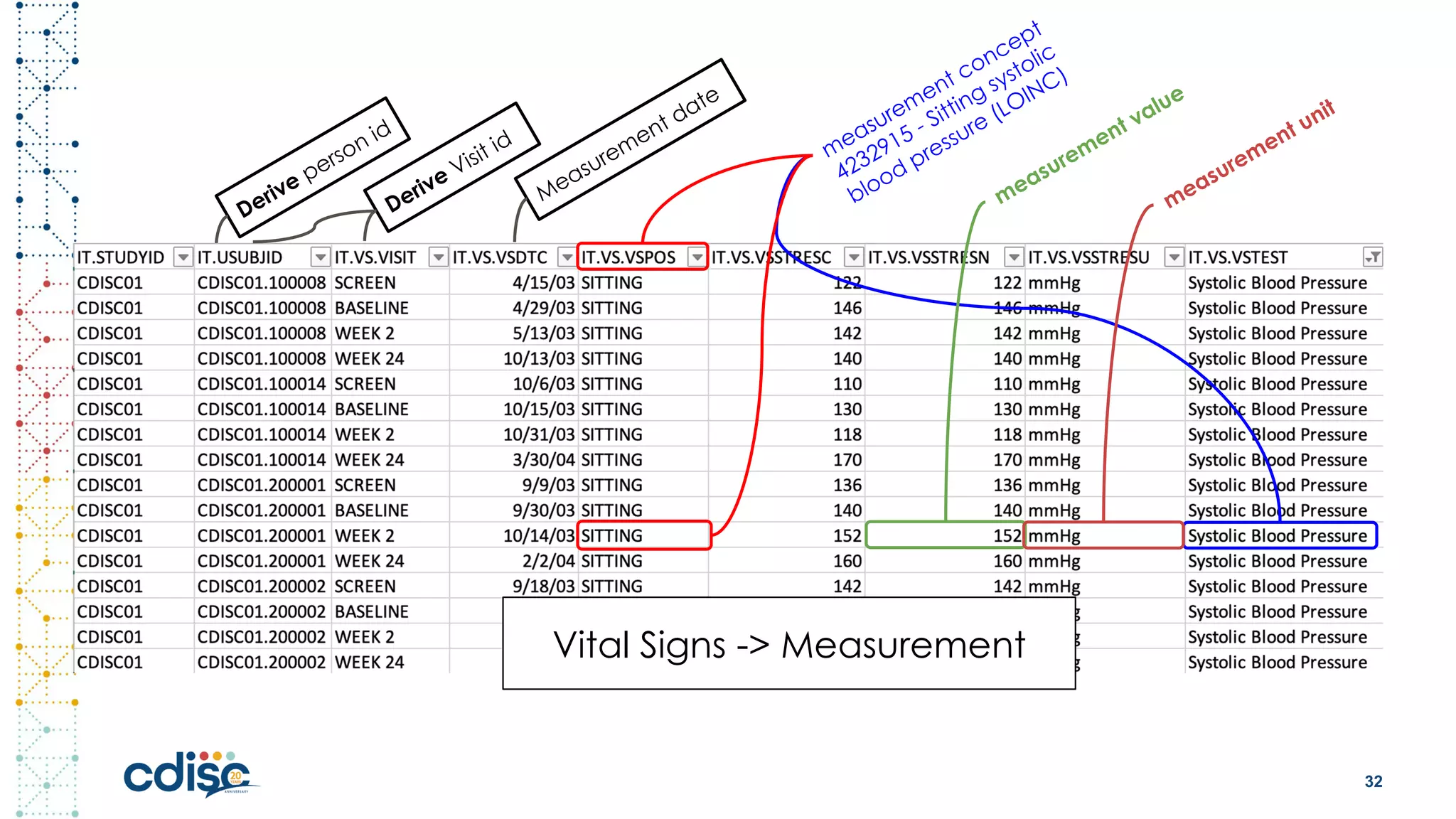
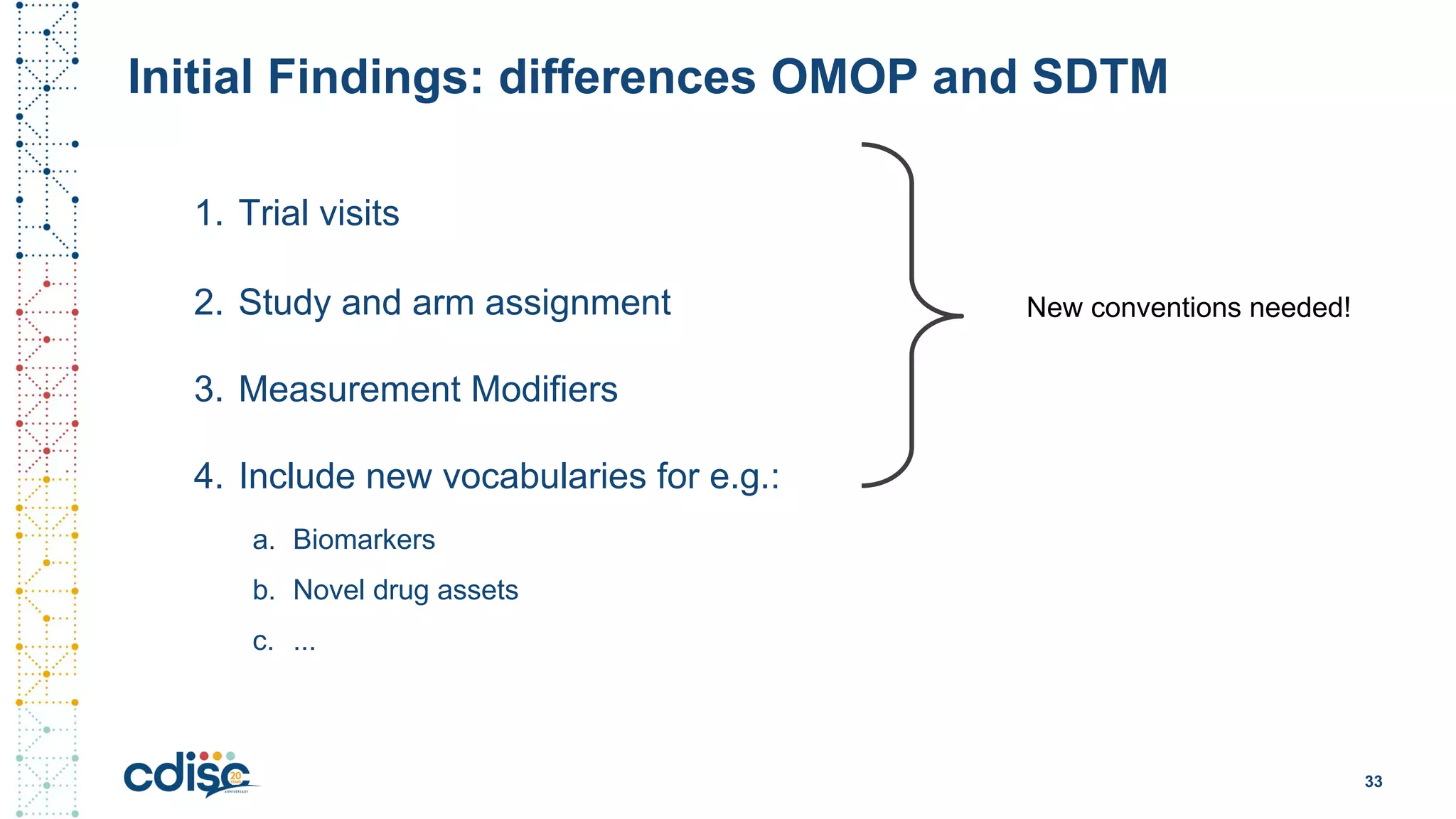
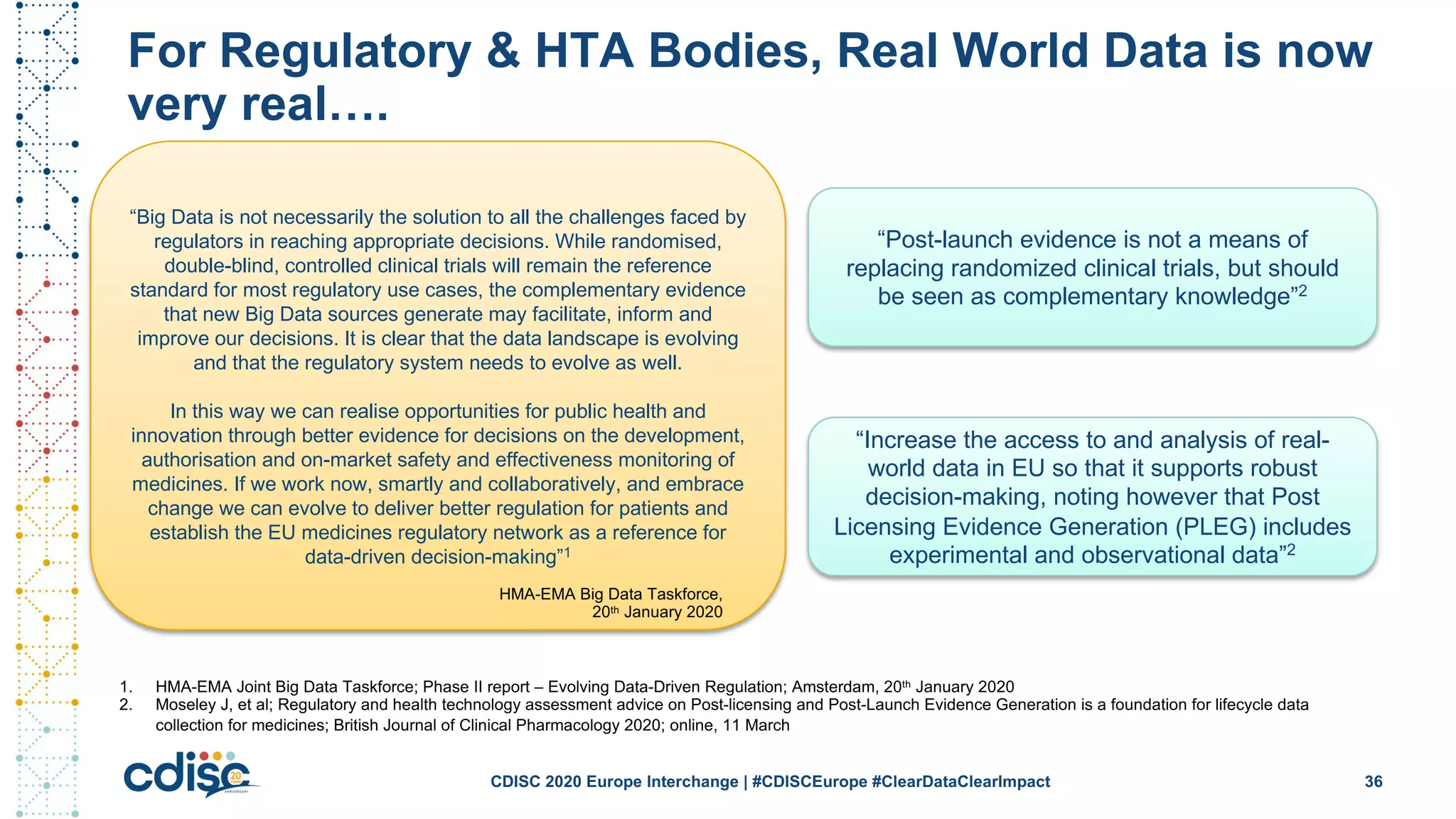
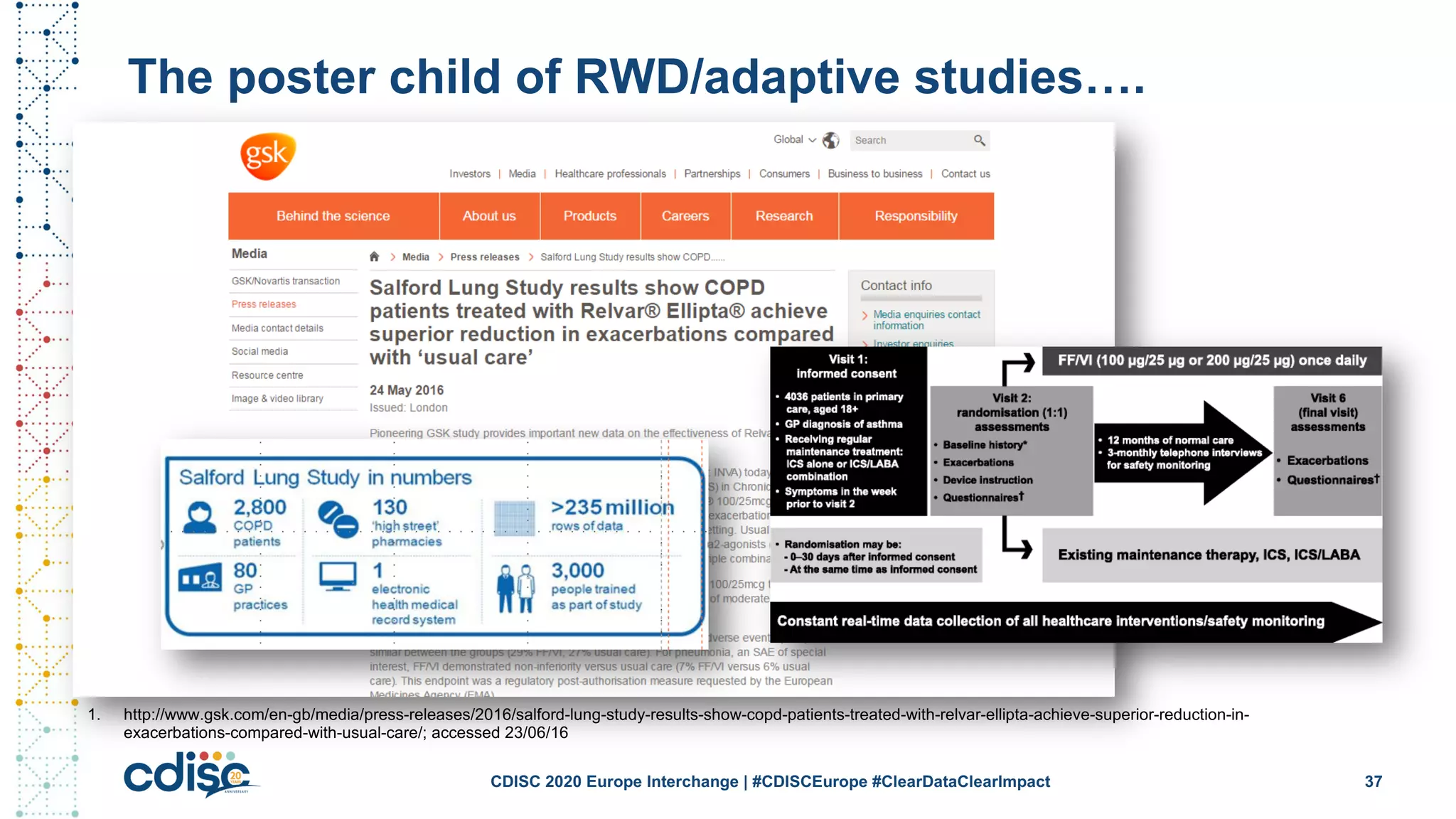
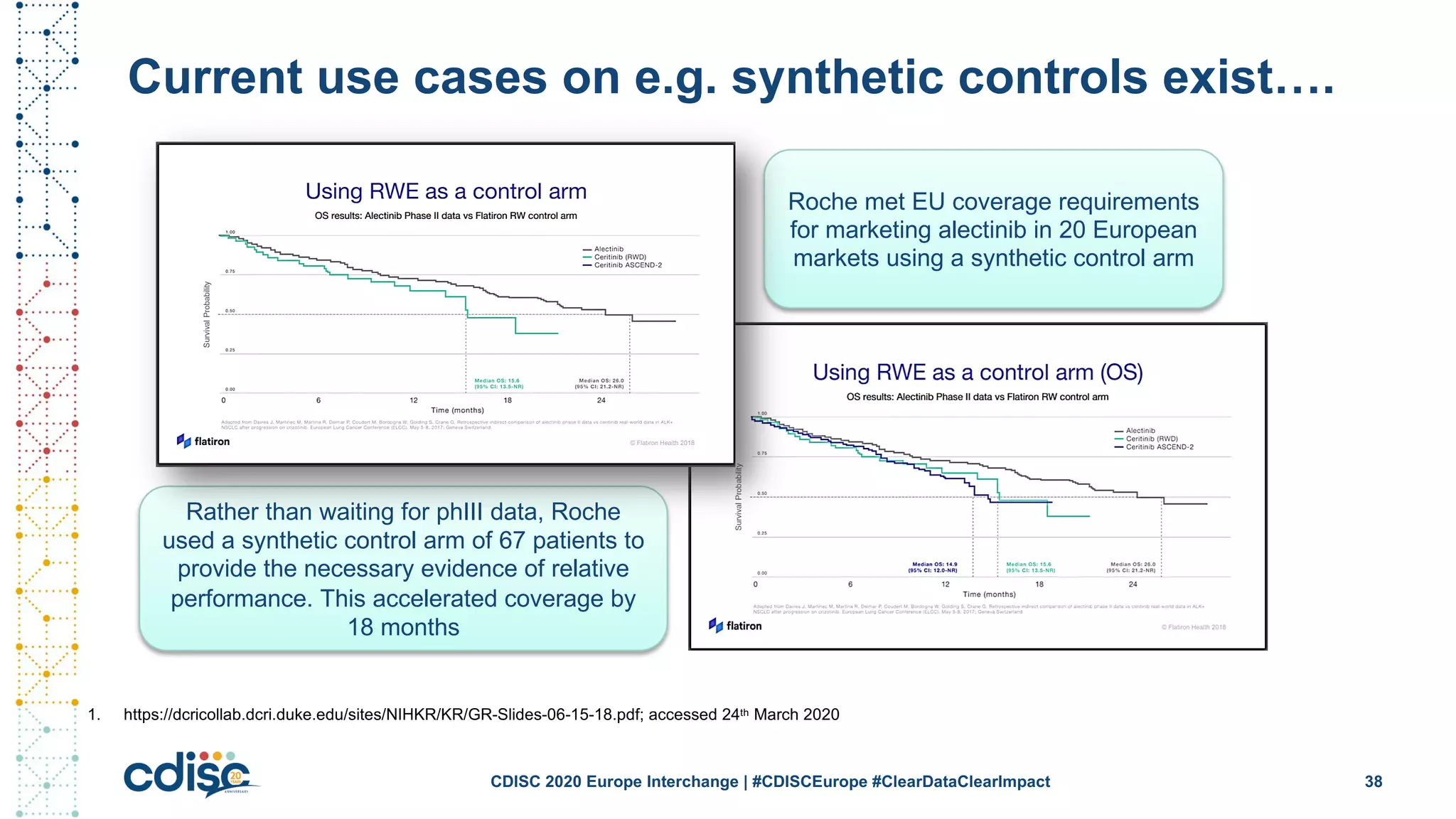
This document summarizes presentations from the CDISC 2020 Europe Interchange conference on April 1-2, 2020. It introduces Maxim Moinat who works on converting healthcare data to the OMOP Common Data Model. It also introduces Nigel Hughes who is the project lead for the IMI2 European Health Data & Evidence Network (EHDEN) and was previously involved in other real-world data projects. The document provides an agenda for the conference sessions which will discuss EHDEN, OHDSI, a EHDEN study-a-thon, using real-world data in clinical trials and for regulatory purposes.