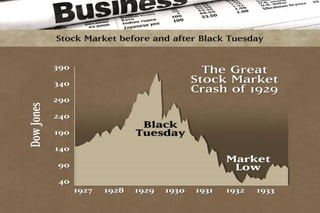
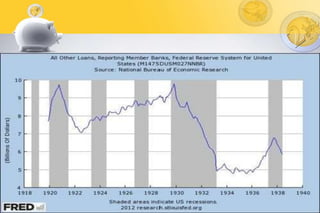
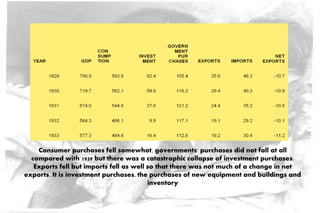
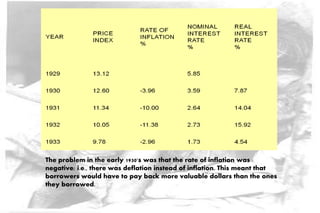
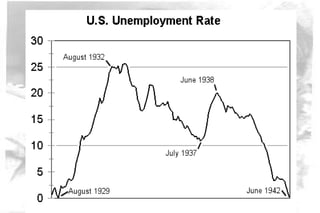
The Great Depression of the 1930s was the longest and most severe economic downturn in modern history. It originated in the United States in 1929 and spread to other countries. Key factors included the stock market crash of 1929, drought conditions that hurt agriculture, declining consumer spending, and restrictive monetary policies. The Depression had widespread impacts such as high unemployment, poverty, homelessness, and shanty towns across America known as "Hoovervilles." New economic theories and policies emerged in response, including Keynesian economics and Roosevelt's New Deal programs to provide relief, recovery, and reform.