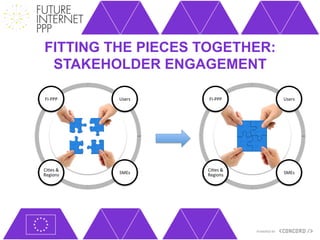
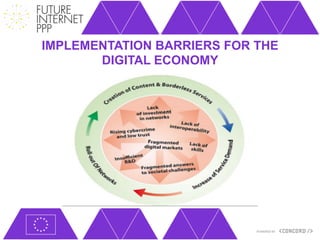
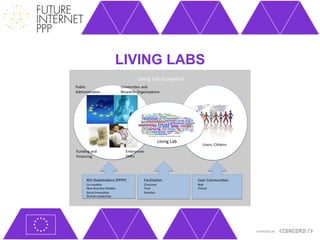
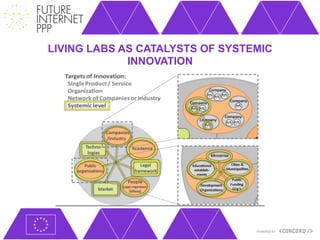
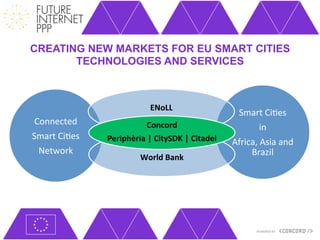
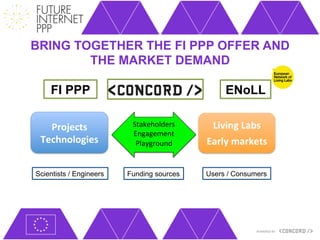
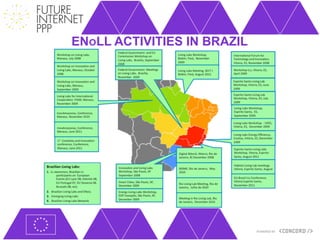
The document discusses the Future Internet Public Private Partnership (FI-PPP) and the Concord project, emphasizing the importance of integrating smart city technologies and facilitating multi-stakeholder engagement through living labs. It outlines the roadmap towards a digital economy, highlighting barriers to implementation and proposing strategies for enhancing collaboration among various stakeholders. The Concord project aims to accelerate the development of experimental infrastructures and foster innovative business models to support sustainable solutions in the digital economy.