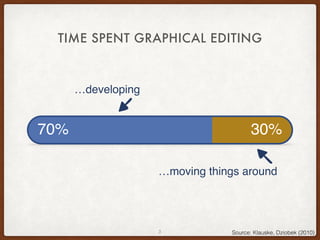
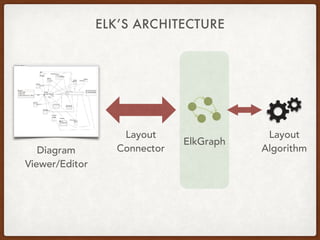
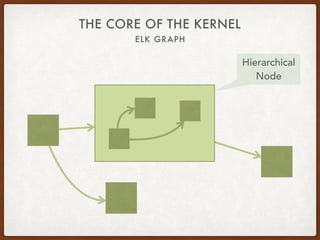
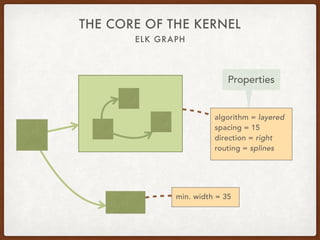
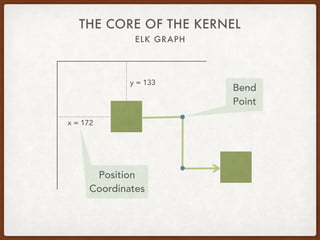
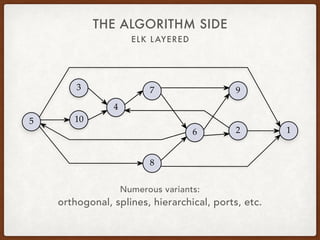
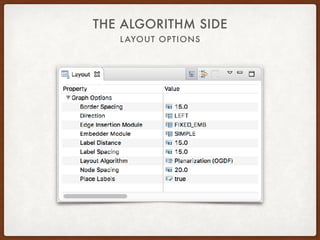
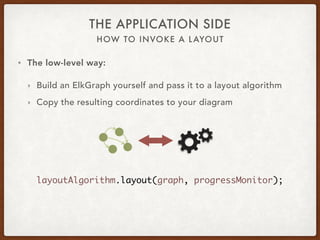
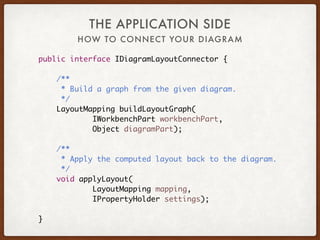
The document discusses the Eclipse Layout Kernel (ELK), which provides algorithms and infrastructure for automatically laying out diagrams. It summarizes that ELK originated from the KIELER project and contains high-quality layout algorithms with numerous options. It also describes how applications can integrate ELK by building graphs from diagrams and applying computed layouts.