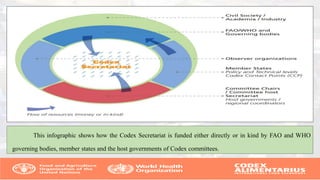
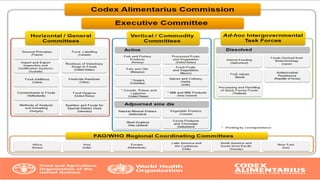
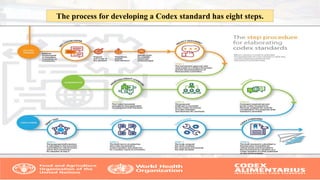
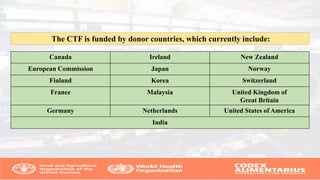
The Codex Alimentarius Commission (CAC), established in 1963 by FAO and WHO, develops international food standards to protect consumer health and ensure fair trade practices. It has 189 members, including India, and provides guidelines on food safety, hygiene, and labeling, among other issues. The CAC also collaborates with scientific bodies to ensure standards reflect current scientific knowledge and assist in harmonizing international food trade.