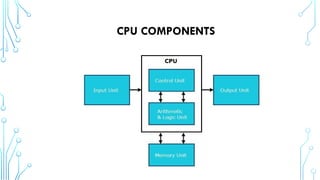
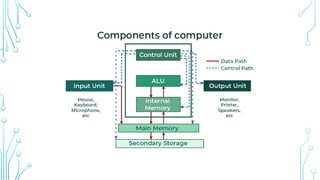
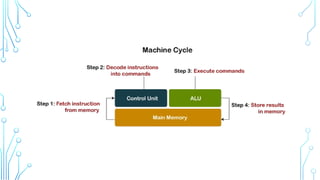
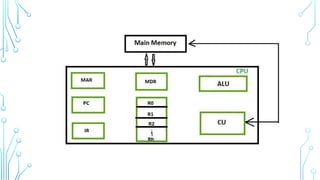
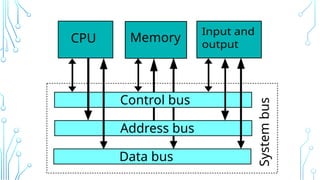
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of the computer, responsible for executing instructions, processing data, and coordinating hardware operations. It performs calculations, logic operations, and controls data flow between memory and peripherals. The CPU consists of key components such as the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU), Control Unit (CU), and registers, working together to ensure efficient processing. It operates through the fetch-decode-execute cycle, interpreting and executing instructions from software programs. The CPU's speed, efficiency, and architecture directly impact a computer’s overall performance, making it a vital component in computing systems.