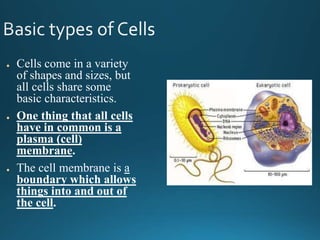
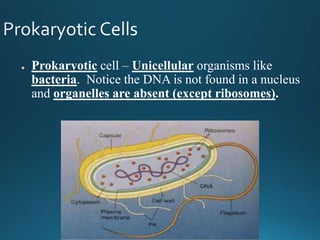
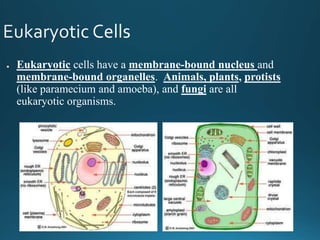
The document summarizes the history and key discoveries that led to the development of the cell theory. It describes how early microscope inventors like Hans and Zacharias Janssen and Robert Hooke first observed cells in cork and tissues. Later scientists like Anton van Leeuwenhoek, Matthias Schleiden, Theodore Schwann, and Rudolph Virchow used improved microscopes to observe that plants and animals are made of cells, leading to the cell theory which states that cells are the fundamental unit of life.