Embed presentation
Download to read offline

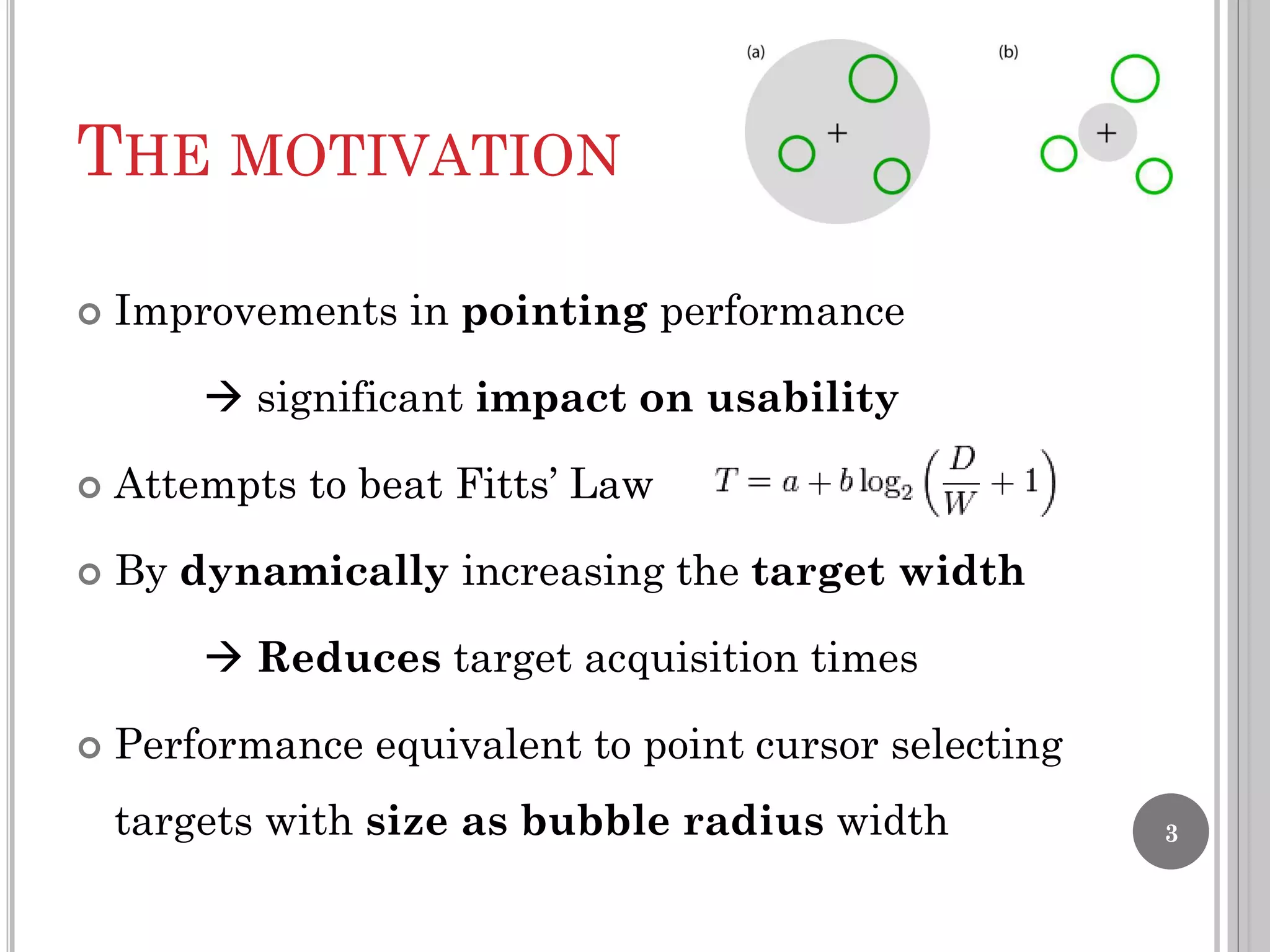
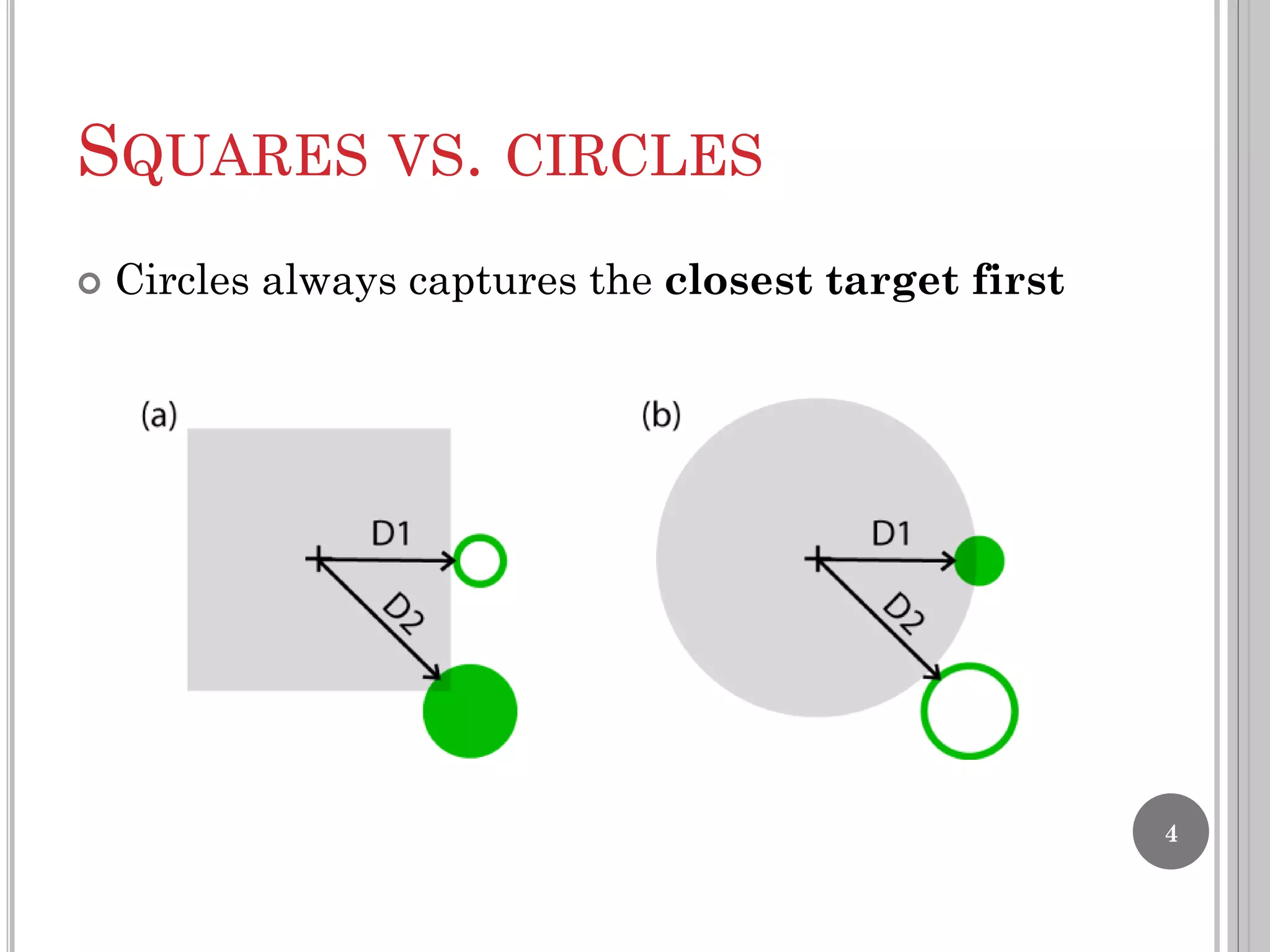
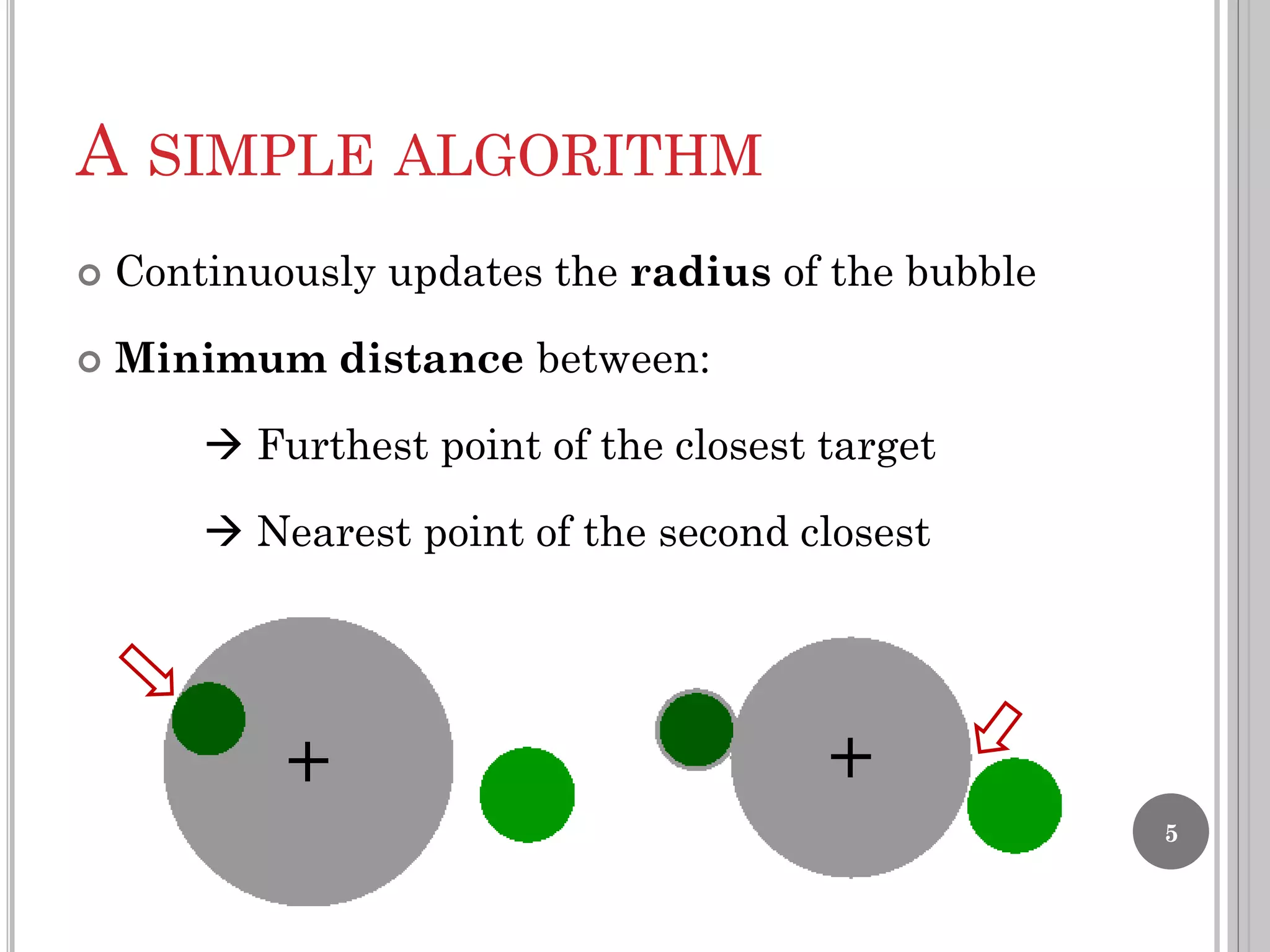
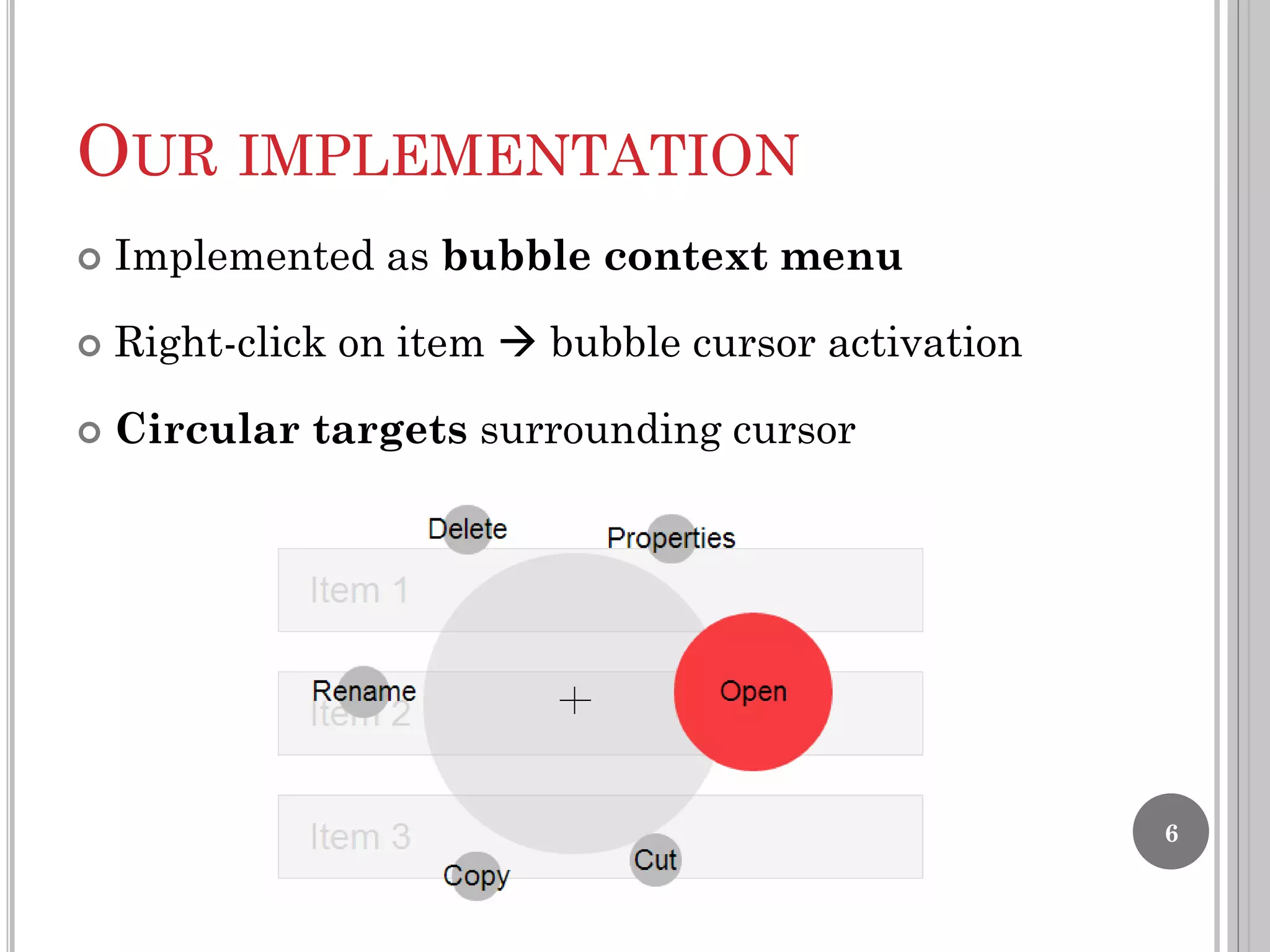
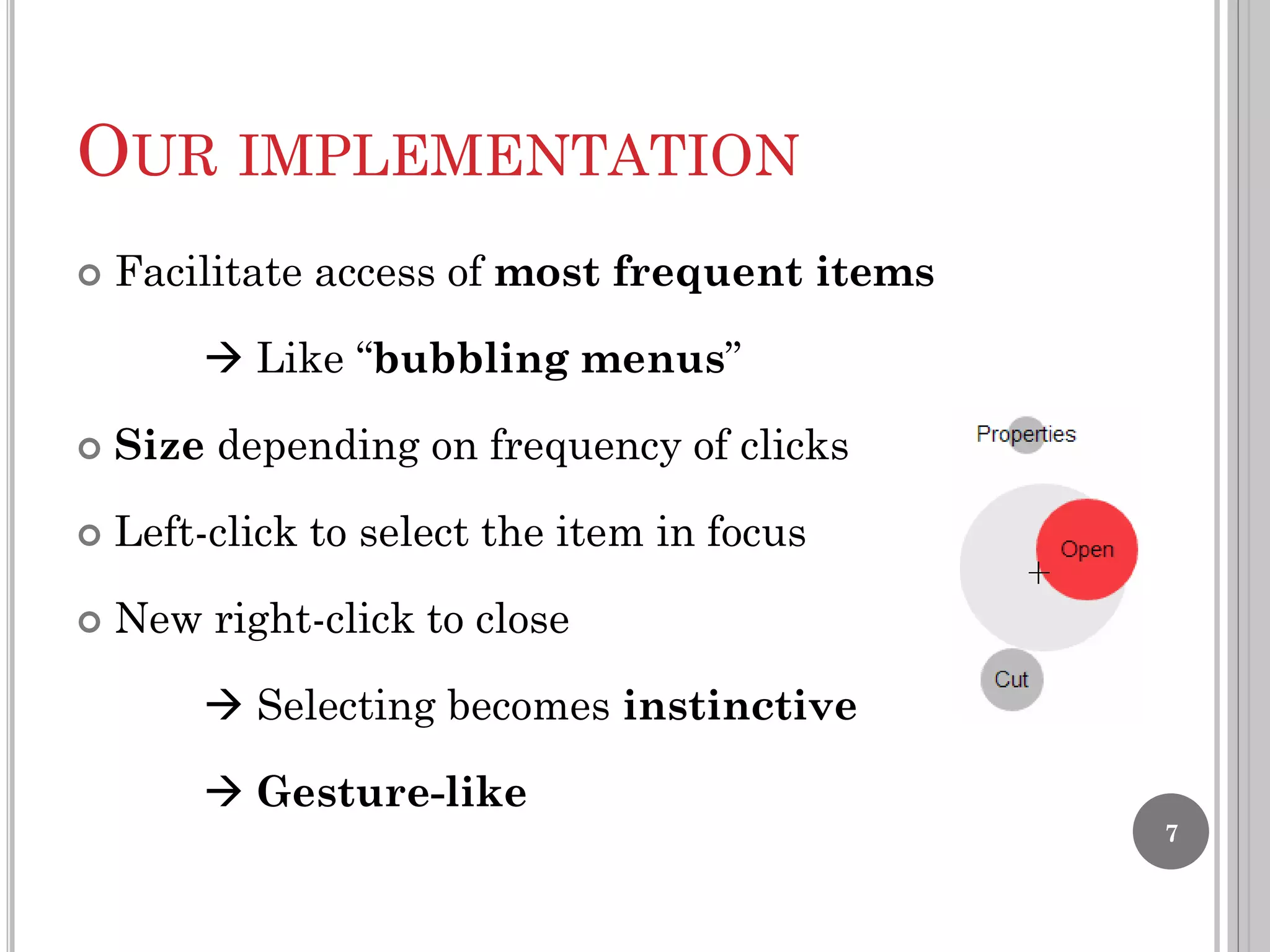


The document summarizes the bubble cursor, a target acquisition technique that dynamically resizes the cursor activation area based on the proximity of surrounding targets. This improves pointing performance by effectively increasing the width of targets and reducing acquisition times compared to a standard point cursor. The bubble cursor algorithm continuously updates the radius to match the minimum distance between the closest and second closest targets, ensuring only the closest target can be selected. The authors implemented the bubble cursor as a context menu with circular targets around the cursor, with selection occurring by left-click when a target is in focus.







