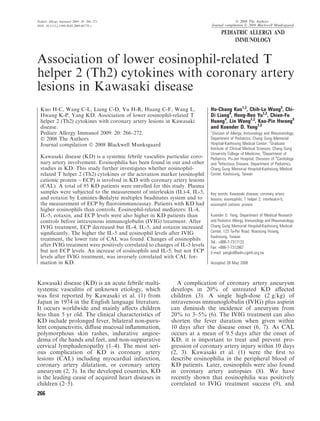
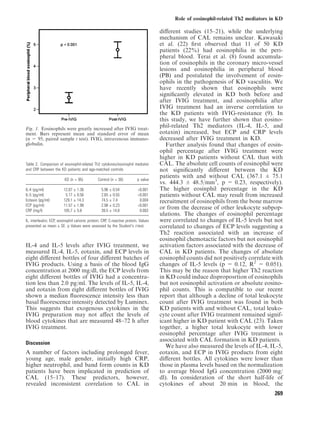
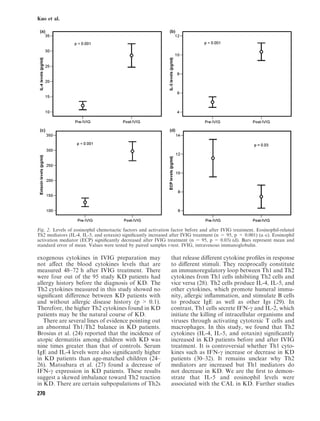
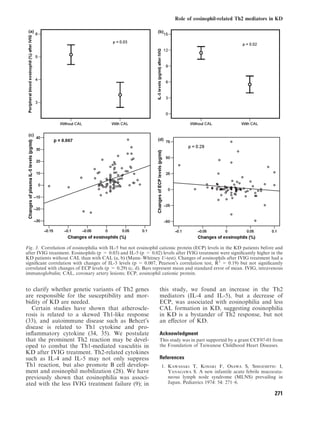
This study investigated whether lower levels of eosinophil-related T helper 2 (Th2) cytokines are associated with coronary artery lesions in patients with Kawasaki disease. The researchers measured levels of interleukin (IL)-4, IL-5, eotaxin, and eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) in 95 Kawasaki disease patients before and after intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) treatment and compared them to 30 healthy controls. They found that higher levels of IL-5 and eosinophils after IVIG treatment were associated with a lower rate of coronary artery lesions. An increase in IL-5 and eosinophils levels after treatment, but not ECP, was inversely correlated with