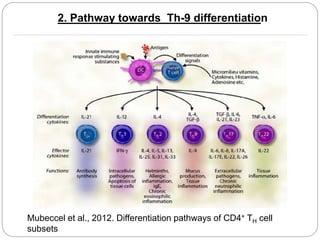
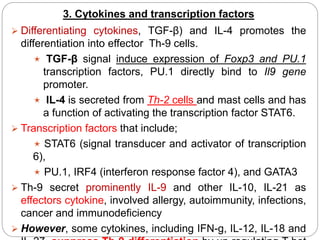
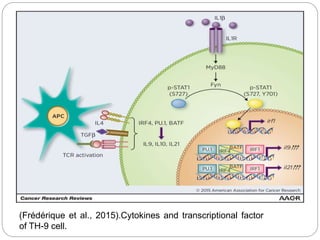
This document summarizes a presentation on T-helper 9 (Th9) cells, a relatively new member of the Th cell family. The presentation outlines that Th9 cells differentiate from naive CD4+ T cells in response to TGF-β and IL-4 cytokines. Th9 cells secrete IL-9 and play roles in allergies, parasite expulsion, autoimmune diseases, cancer, and other conditions. While Th9 cells can promote inflammation and tissue damage, they also help expel parasites and inhibit tumor growth. Further research is needed to understand Th9 cell mechanisms and potential immunotherapy applications.