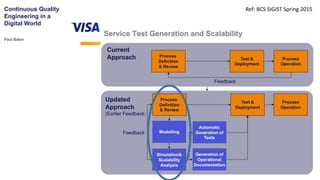
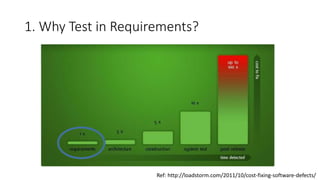
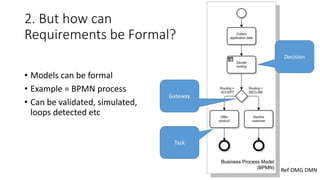
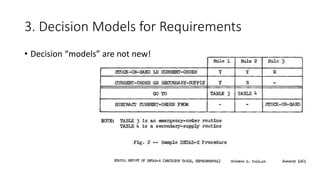
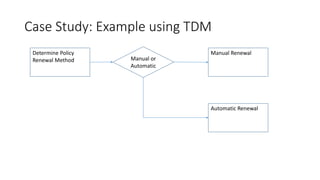
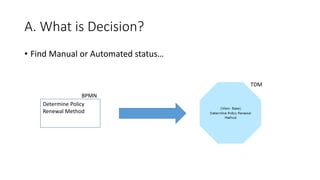
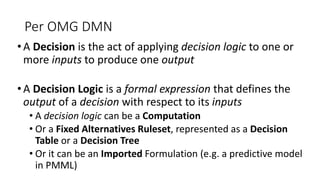
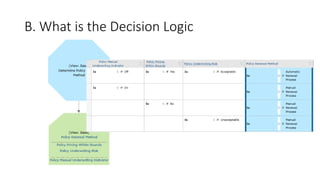
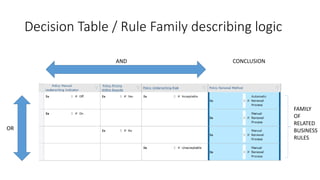
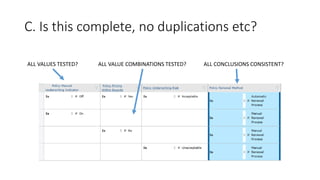
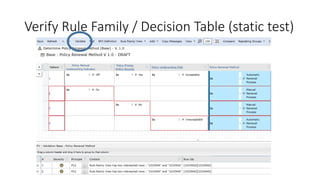
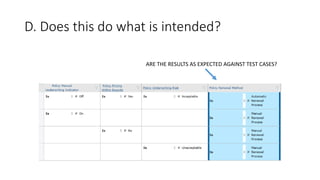
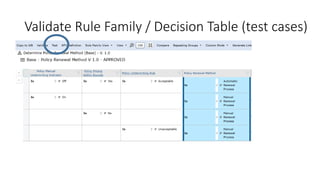
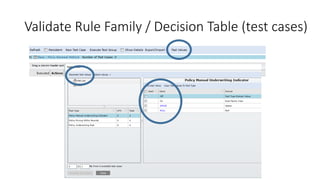
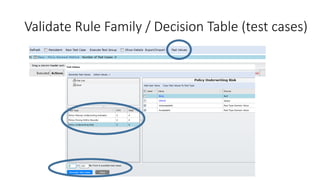
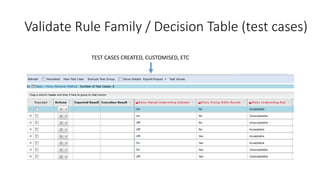
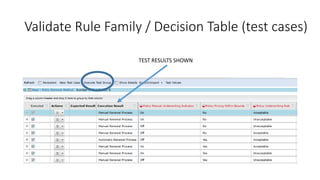
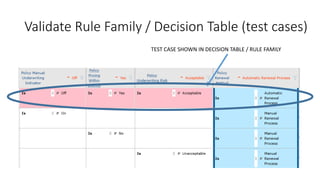
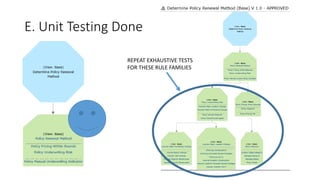
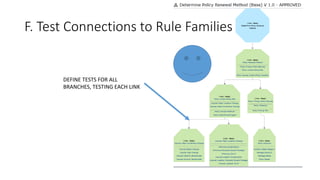
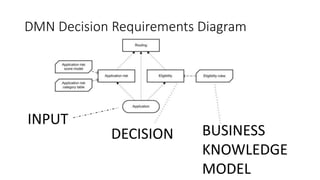
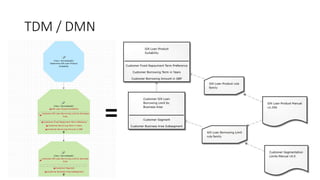
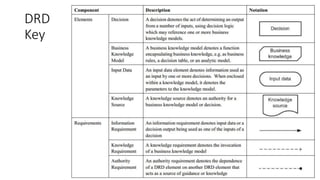
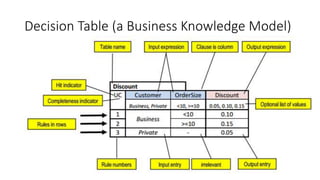
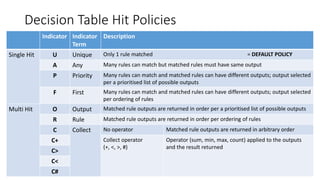
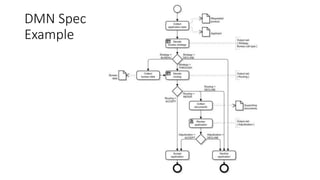
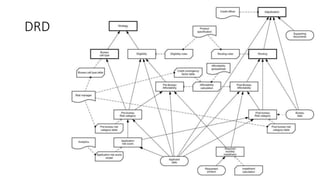
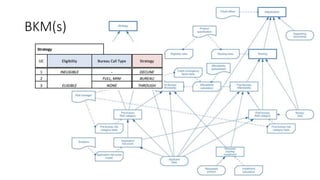
The document discusses best practices in testing business logic during the requirements phase, highlighting methodologies like agile development, test-driven development, and decision modeling. It emphasizes the importance of formal models, such as BPMN and decision tables, for verifying and validating business logic to ensure completeness and correctness. Additionally, it presents various decision modeling methodologies and tools, illustrating their application through case studies.