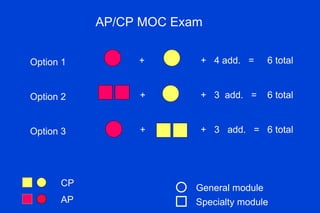
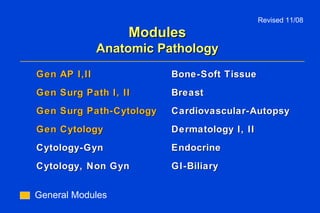
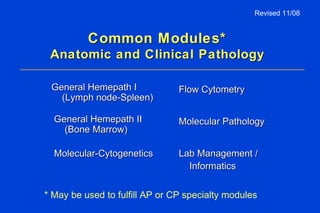
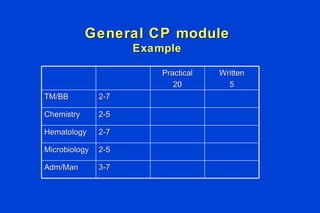
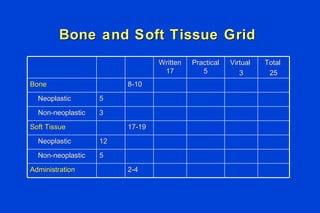
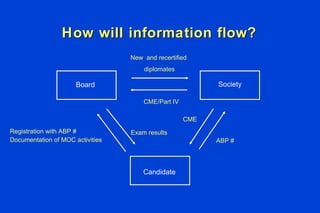
The document outlines the requirements for Maintenance of Certification (MOC) through the American Board of Pathology (ABP). MOC is required to maintain board certification in pathology and consists of 4 parts: professional standing, lifelong learning and self-assessment, cognitive expertise through examination, and evaluation of performance in practice. It describes the specific requirements for each part, including continuing medical education credits, self-assessment modules, content and structure of the certifying examination, and quality improvement activities. The document also addresses common questions about MOC and how requirements may be modified over time to better reflect pathologists' practice patterns.