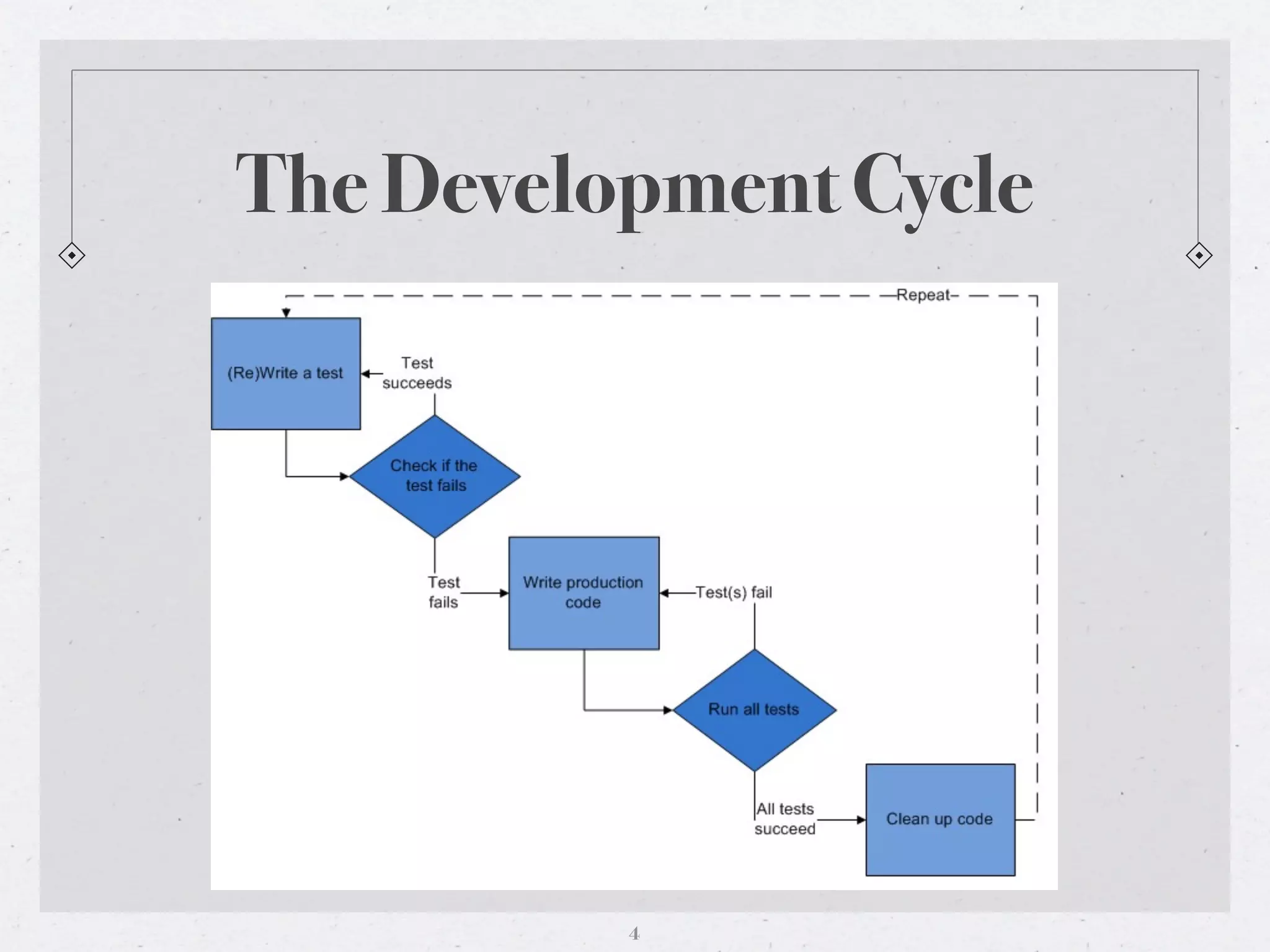
Test-driven development (TDD) is a software development technique that follows three rules: 1) write a failing test first, 2) write code to pass that test, and 3) refactor code as needed. TDD has benefits like more trustworthy code and executable documentation, but also limitations like needing management support and potential for badly written tests. Unit tests test the smallest parts of an application, integration tests combine modules, and system tests evaluate full system compliance with requirements. TDD requires defined requirements before writing tests or code enhancements.