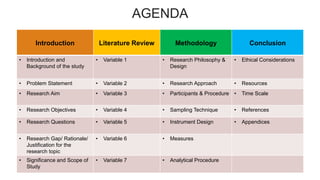
This document outlines the structure and content of a thesis proposal on organizational change. It includes an introduction providing background on the research topic and outlining the research problem, aim, objectives and questions. It then covers the literature review, presenting the theoretical framework and hypotheses. The methodology section describes the research strategy, sample, measures and analytical procedures. Finally, it includes a timeline, references and conclusion. The proposal examines how change appropriateness and uncertainty impact employee attitudes, with perceived management support as a mediator and change communication as a moderator.