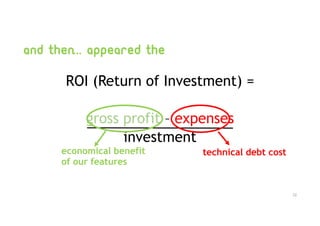
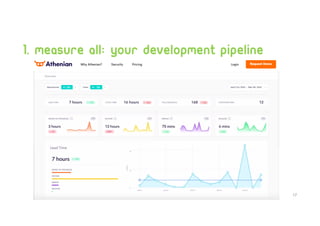
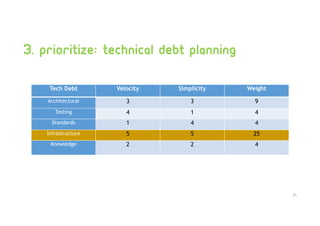
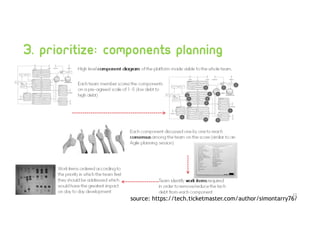
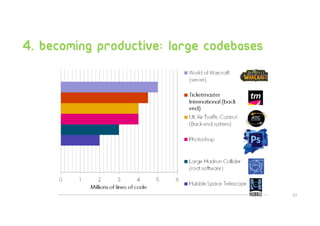
Technical debt management strategies involve measuring all aspects of development including code quality, productivity, and the development pipeline. It is important to control increasing technical debt in new code by fixing leaks through code reviews and pull request checks. Existing technical debt should be prioritized and fixed based on categories like architectural debt and testing debt. Large codebases can be managed productively using continuous integration and delivery pipelines, automatic rollbacks, pull request reminders, and refactors/clean ups assisted by tools.