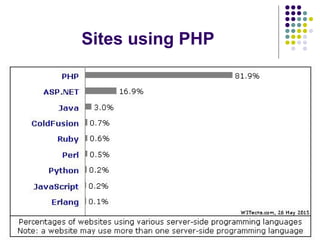
This document discusses PHP, a popular server-side scripting language used for web development. It provides an overview of PHP and compares it to other web development technologies. The key advantages of PHP include being open source, easy to learn and use, having a large community and support, and being suitable for rapid prototyping. While not as robust as other languages, PHP is well suited for building scalable, dynamic web applications and content management systems. Major websites like Facebook, Google, Wikipedia and WordPress are built using PHP.







![Command Line PHP
What is this good for:
Parsing files to put into a database
Ideal for scripts regularly executed using cron (on
*nix or Linux) or Task Scheduler (on Windows).
Anything you use a shell script or perl script to do
Variables of use:
$argc, $argv[]
$stdin, $stdout, $stderr](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/techtalk-php-150527083258-lva1-app6891/85/Tech-talk-PHP-11-320.jpg)