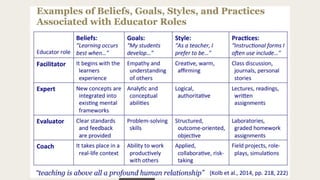
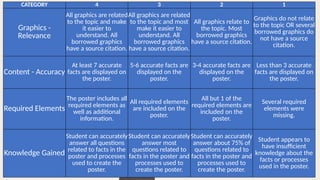
The document discusses various scenarios that challenge individuals' responses in both personal and professional settings. It emphasizes the evolving role of teachers from being knowledge gatekeepers to becoming facilitators of learning who inspire and motivate students. Additionally, it outlines the importance of a teaching philosophy that reflects principles, teaching practices, and assessments to enhance student learning and development.