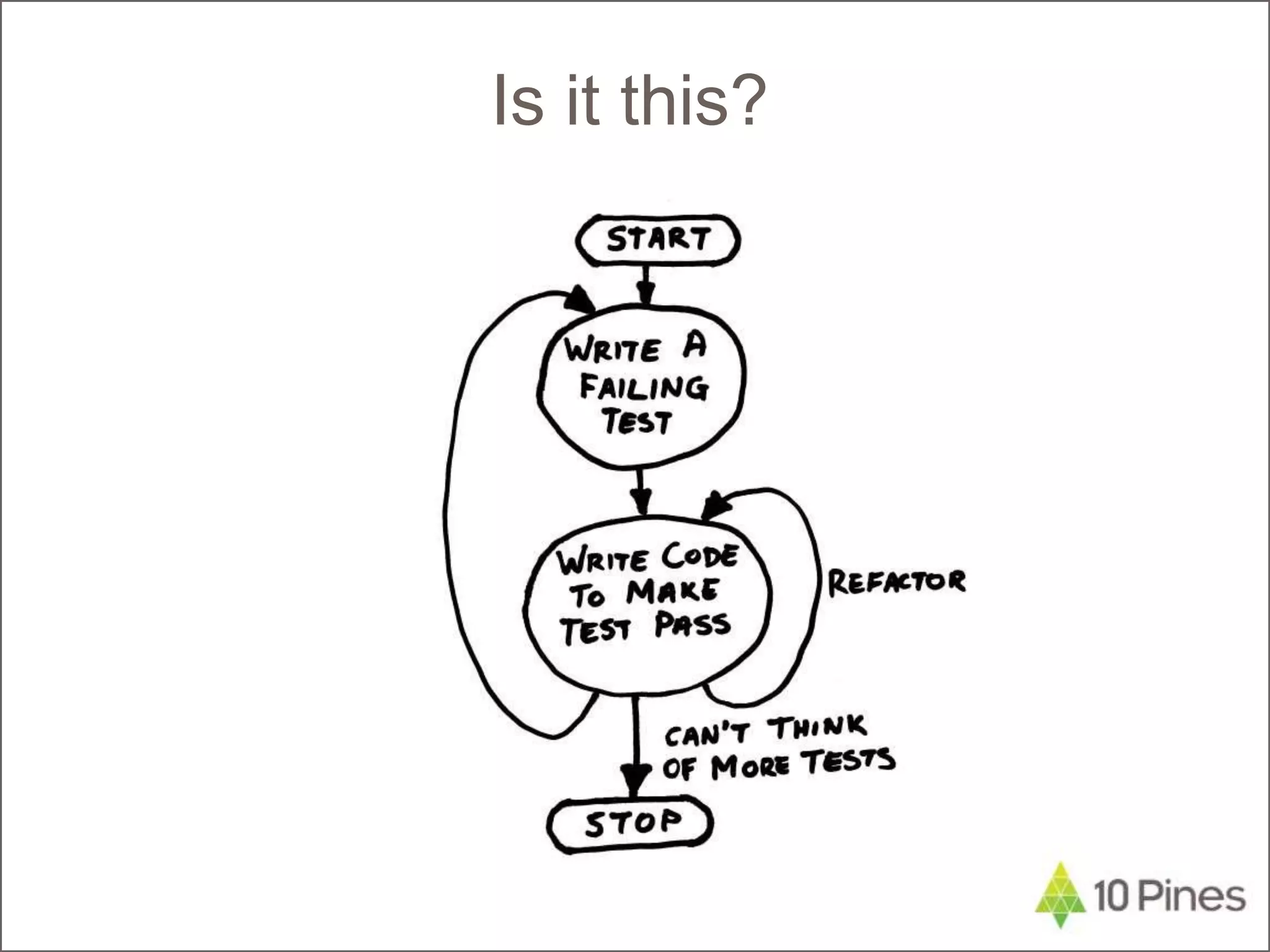
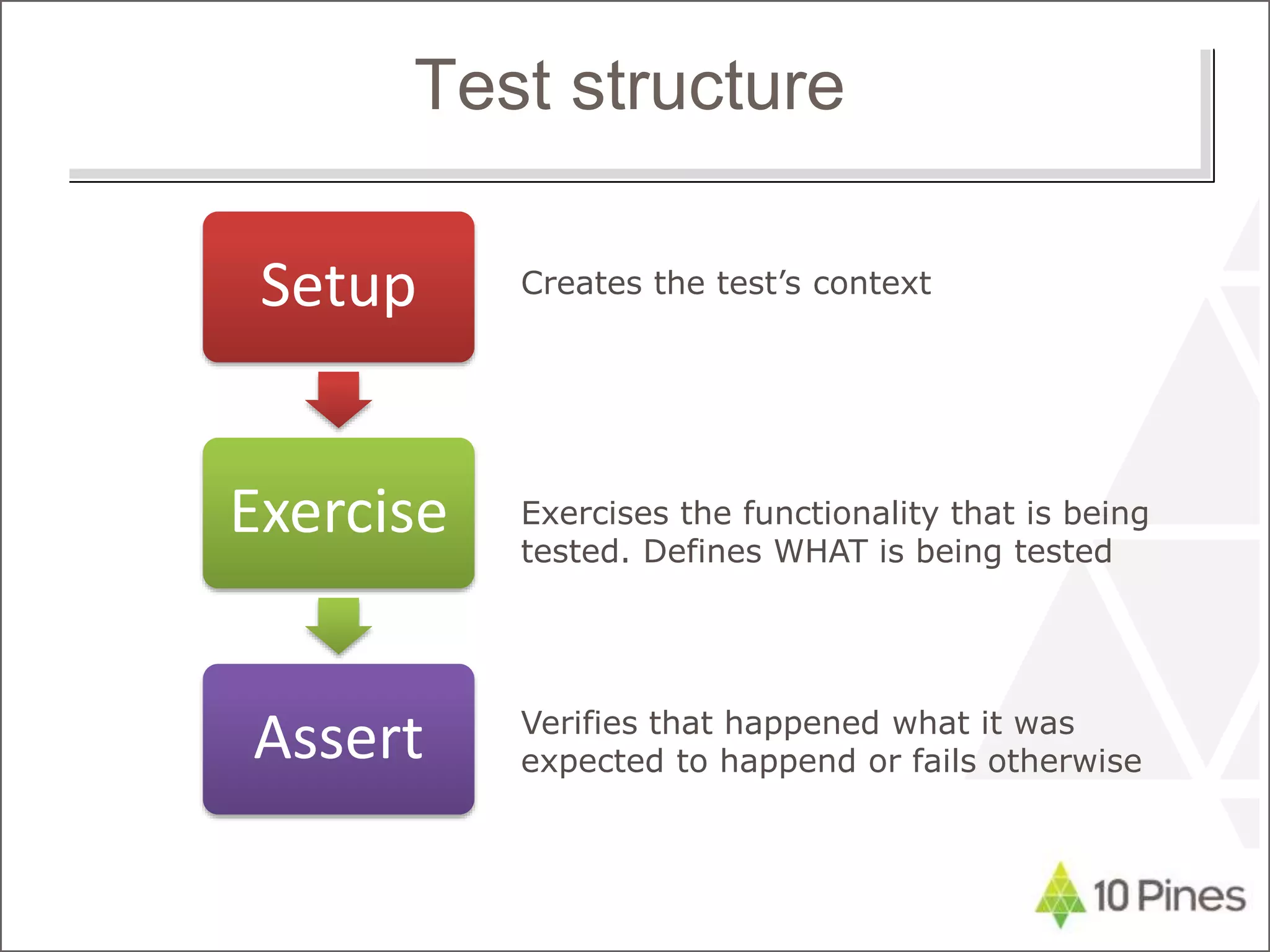
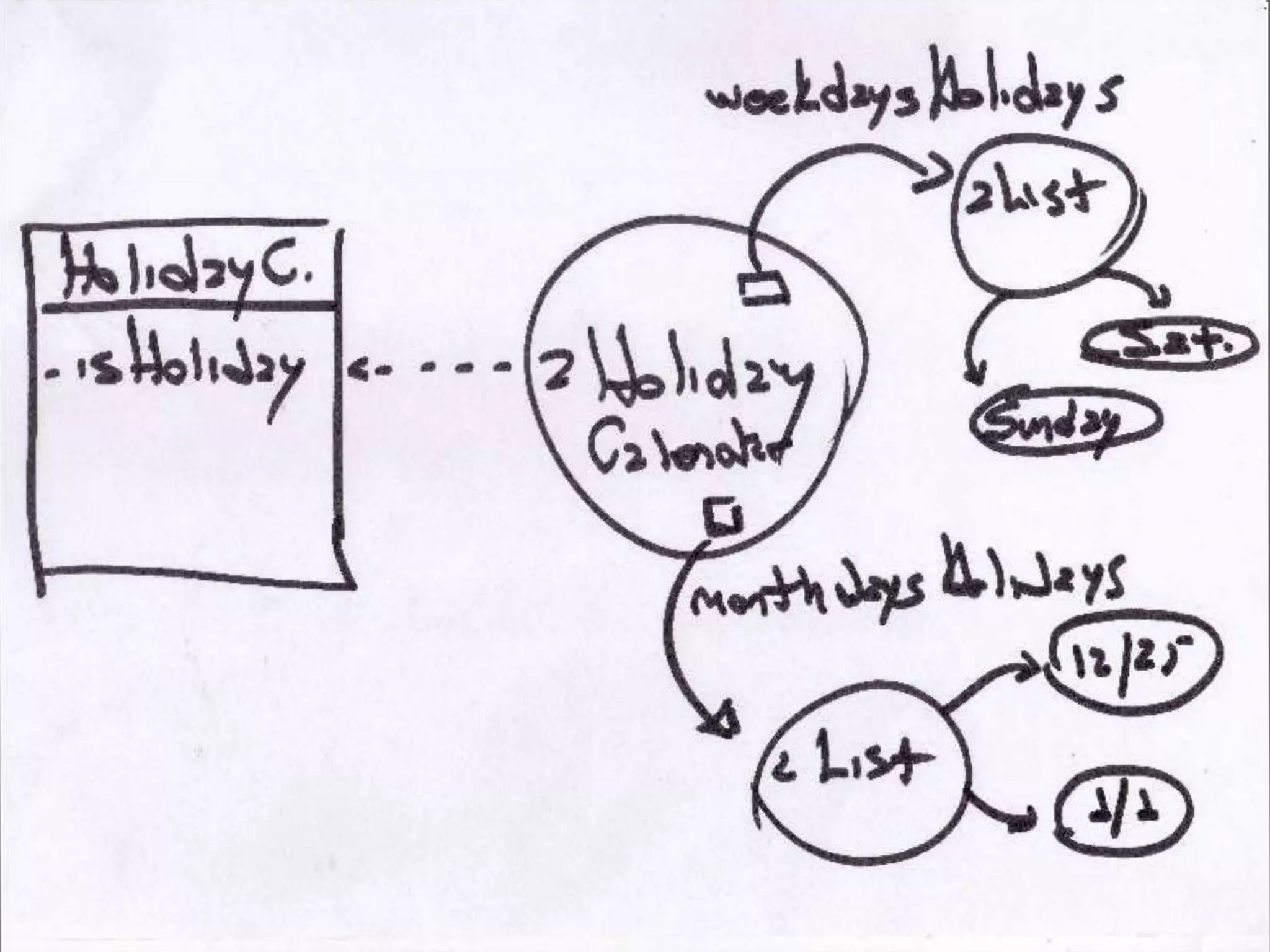
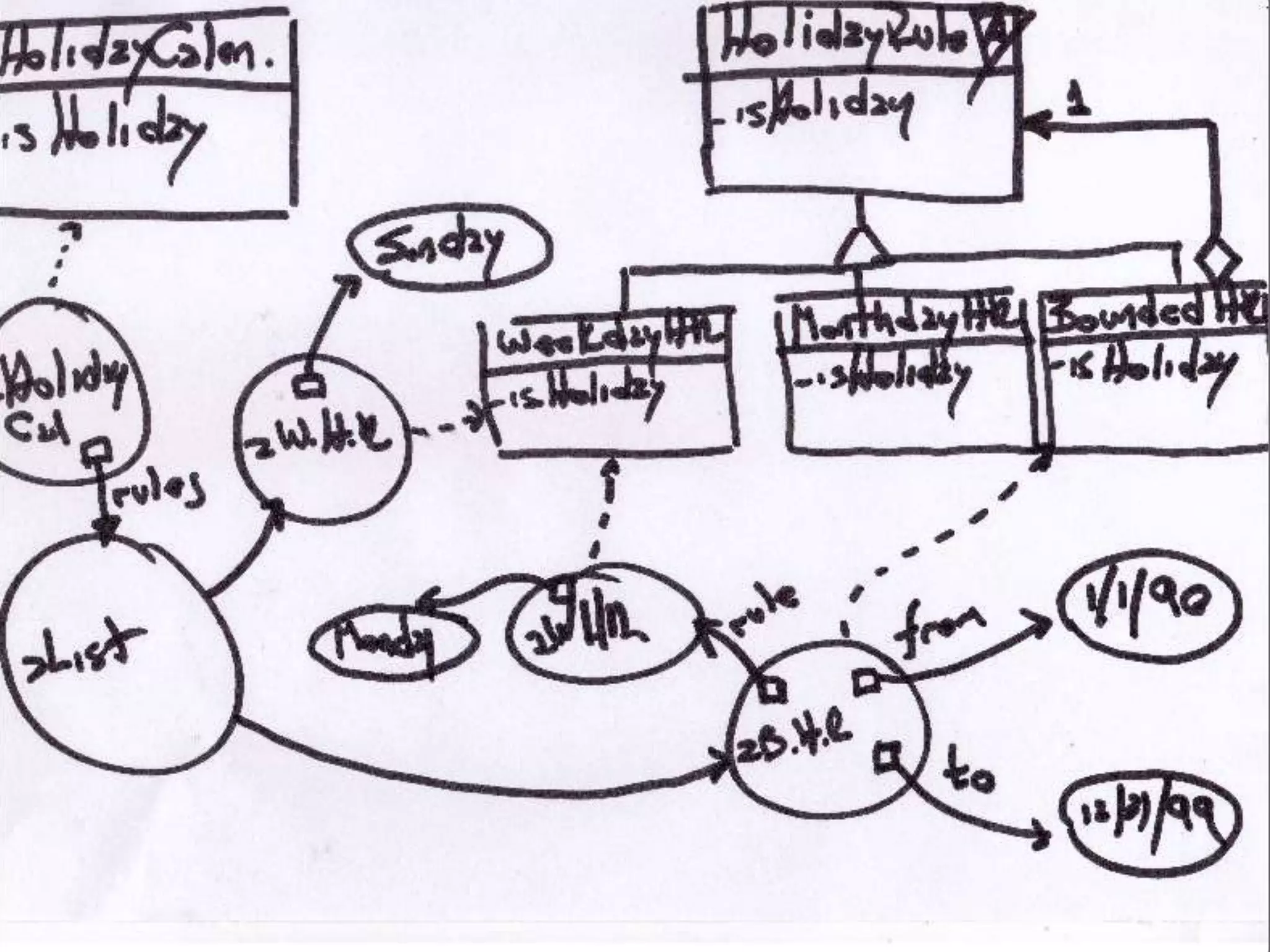
The document discusses test-driven development (TDD) and refactoring. It explains what TDD is, how to implement it in three steps - writing a failing test, making the test pass, and refactoring code - and provides an example of modeling a calendar to track holidays using TDD. The document also discusses benefits of TDD like catching mistakes early, increasing coding confidence, and making it easier to implement new requirements through refactoring.