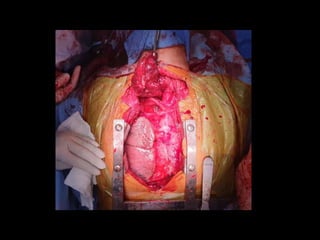
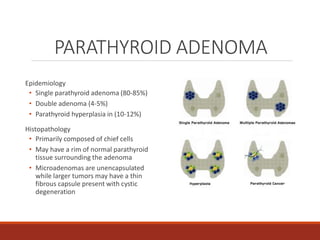
The document describes a case presentation at the TCVS Conference on October 10, 2019 by clinical clerks Alexander Xerxes Malicse and Jessica Martinez. It details the history of a 54-year-old Filipino man who presented with a large anterior neck mass, joint pains, flank pain, and difficulty walking over several years. Various tests revealed primary hyperparathyroidism secondary to a parathyroid adenoma, multinodular nontoxic goiter, and chronic kidney disease from hypercalcemia. The patient was admitted for cystoscopy, DJ stent replacement, total thyroidectomy, parathyroidectomy, and sternotomy to remove the enlarged right parathyroid gland.