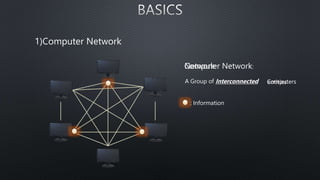
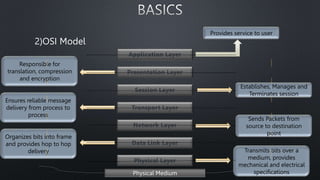
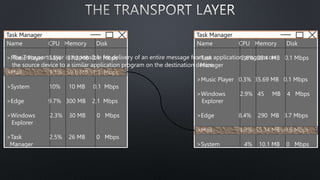
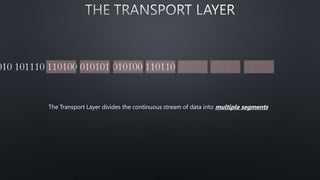
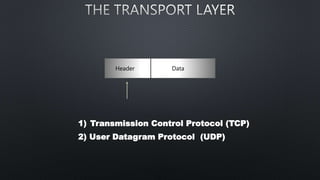
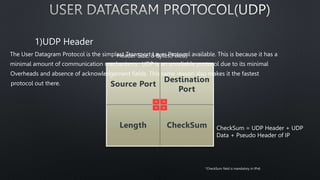
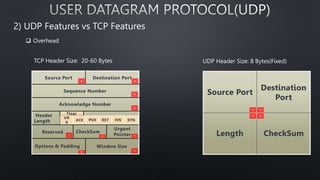
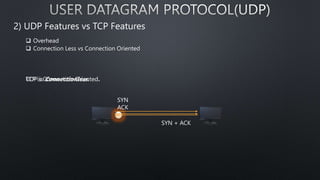
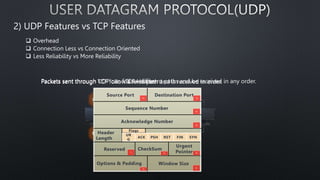
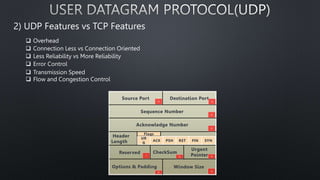
The document discusses computer networks and the OSI model, highlighting the layers responsible for data transmission and their functions. It contrasts the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) and Transmission Control Protocol (TCP), detailing their features, such as connection orientation, reliability, and header sizes. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of UDP in applications requiring speed, like online gaming and video streaming.