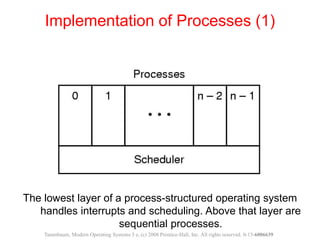
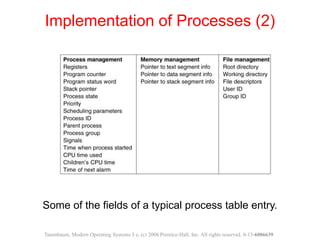
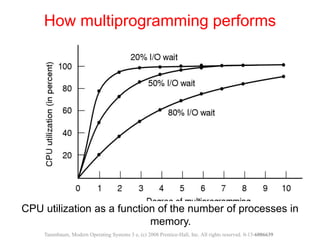
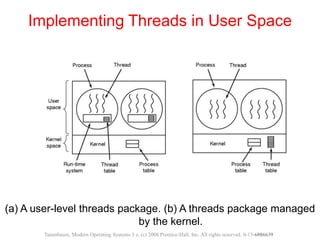
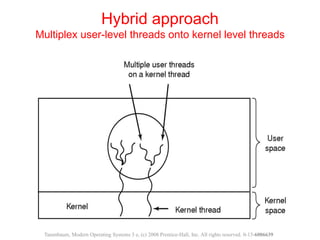
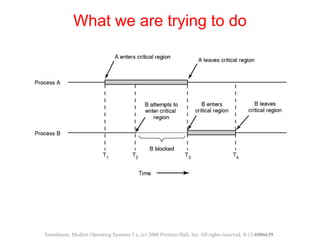
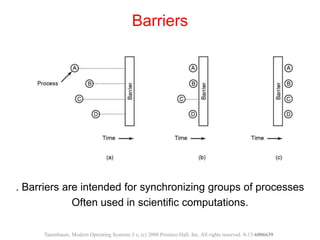
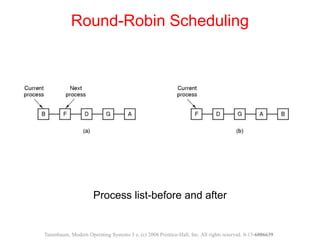
The document discusses processes, threads, and methods for achieving mutual exclusion between processes/threads. It describes processes as independent programs with their own state and resources. Threads are described as lightweight processes that can run concurrently within a process and share resources. Several early techniques for mutual exclusion are presented, including disabling interrupts, lock variables, strict alternation, and Peterson's solution, all of which rely on busy waiting. The document also introduces the Test-and-Set Lock (TSL) instruction for achieving atomic mutual exclusion.