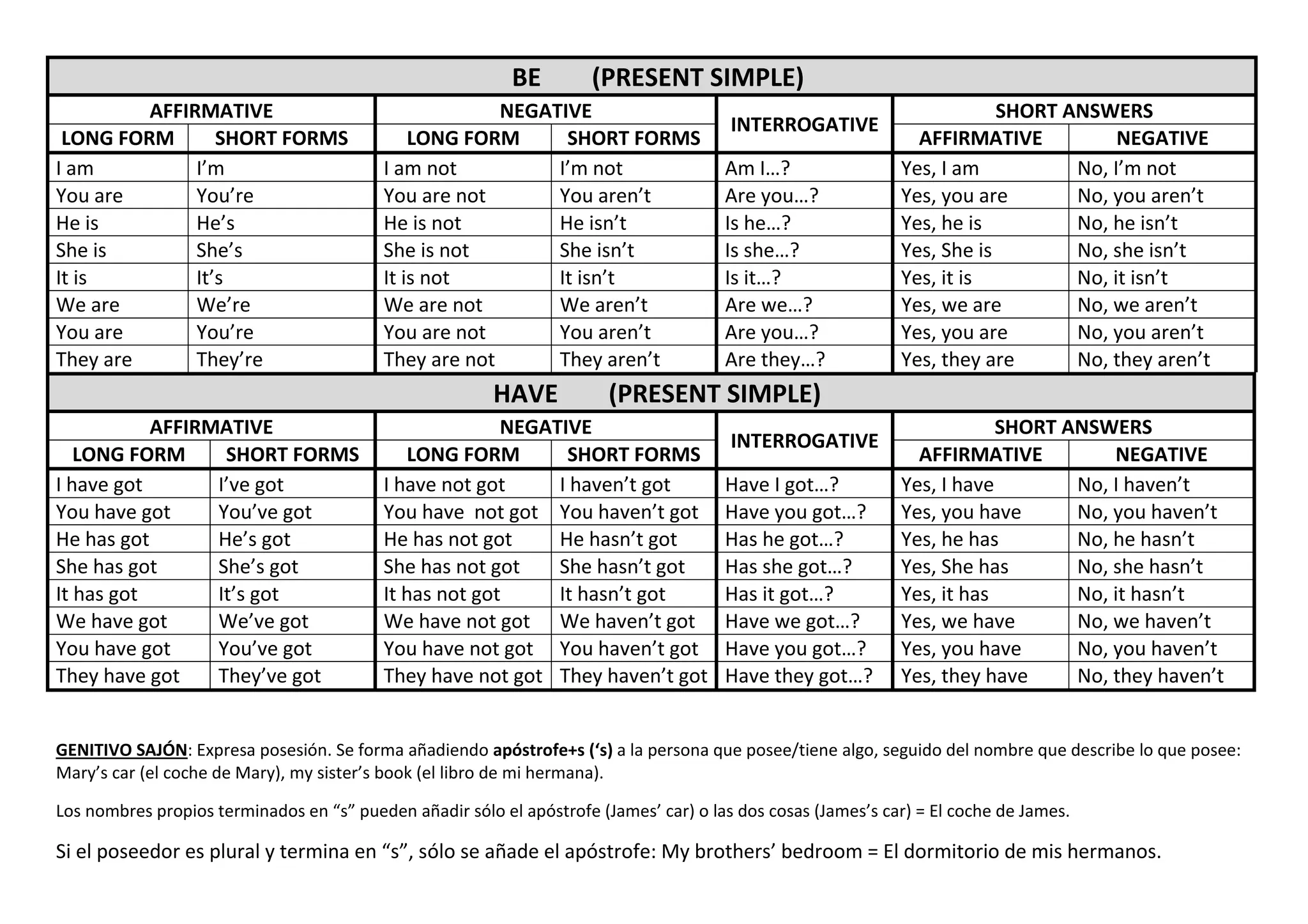
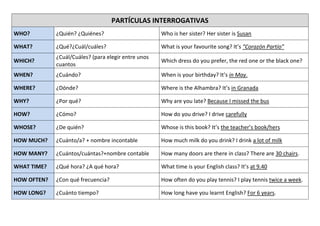
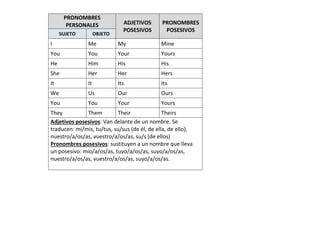
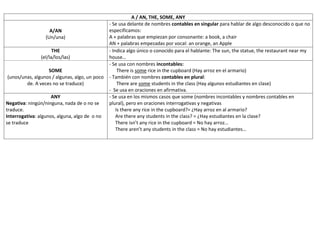
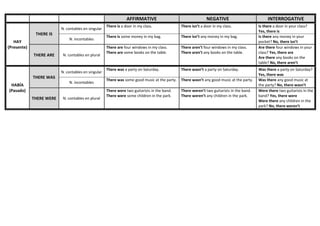
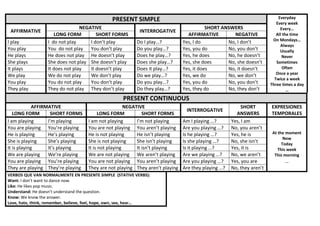
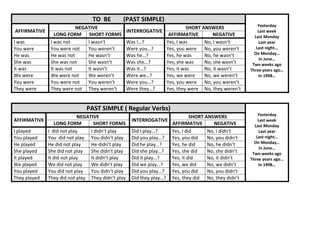
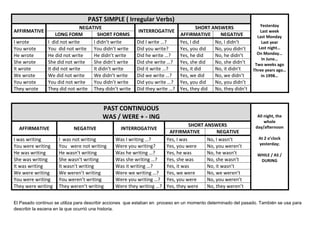
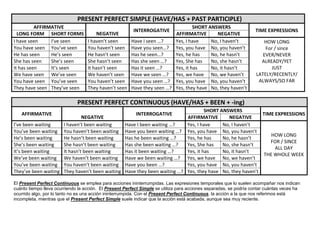
This document provides examples of affirmative, negative, and interrogative forms for common verbs and verb tenses in English, including:
- Present simple (regular and irregular verbs)
- Present continuous
- Past simple (regular and irregular verbs)
- Past continuous
- Present perfect
It also includes examples of common time expressions used with different tenses, possessive pronouns and adjectives, interrogative words, articles, quantifiers, and an explanation of the Saxon genitive. The document serves as a reference for proper grammar structures in English.