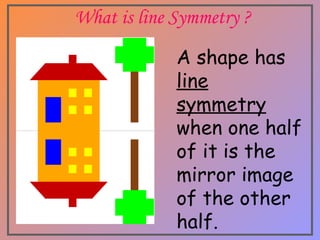
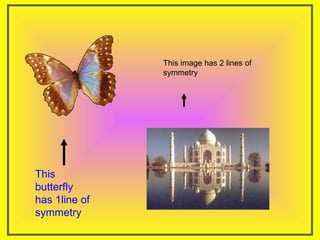
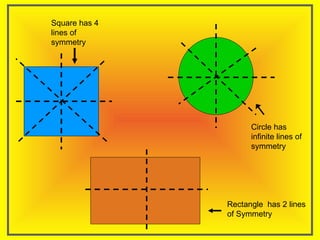
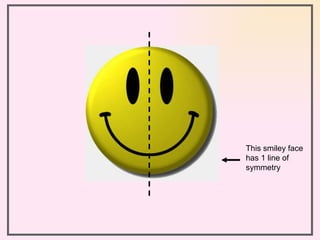
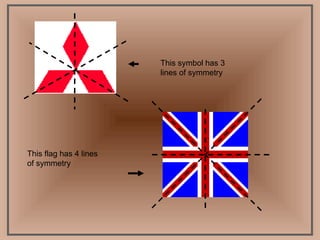
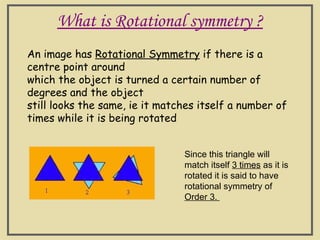
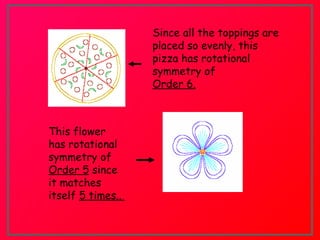
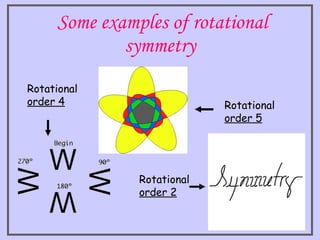
The document discusses two types of symmetry: line symmetry and rotational symmetry. Line symmetry occurs when an object can be split into two mirror image halves. Shapes like circles have infinite lines of symmetry while squares have four lines of symmetry. Rotational symmetry is when an object looks the same when rotated part of a full rotation, such as a triangle having rotational symmetry of order 3 if it matches itself when rotated 120 degrees. Examples of objects with different orders of rotational symmetry are provided.