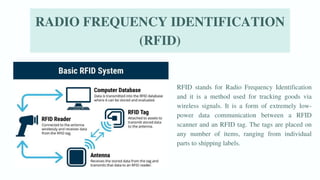
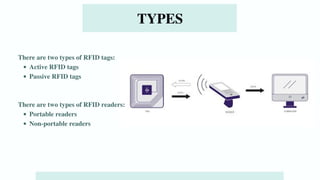
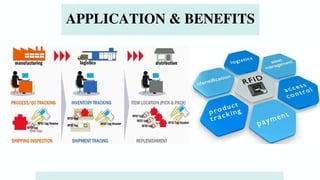
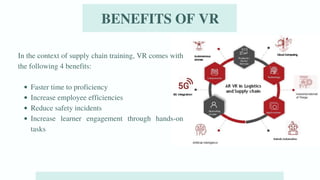
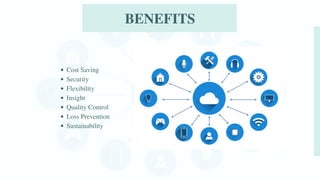
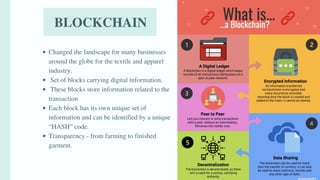
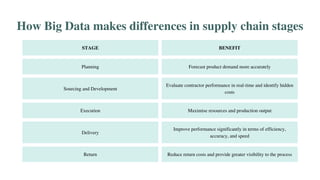
The document discusses various emerging technologies transforming supply chain management, including RFID, AR/VR, blockchain, AI, cloud computing, IoT, and 3D printing. These technologies enhance efficiency, transparency, and customer engagement in supply chains, offering significant benefits such as cost savings, improved productivity, and better data management. The conclusion emphasizes the growing importance of these technological innovations for companies to remain competitive and transparent, particularly appealing to younger consumers.