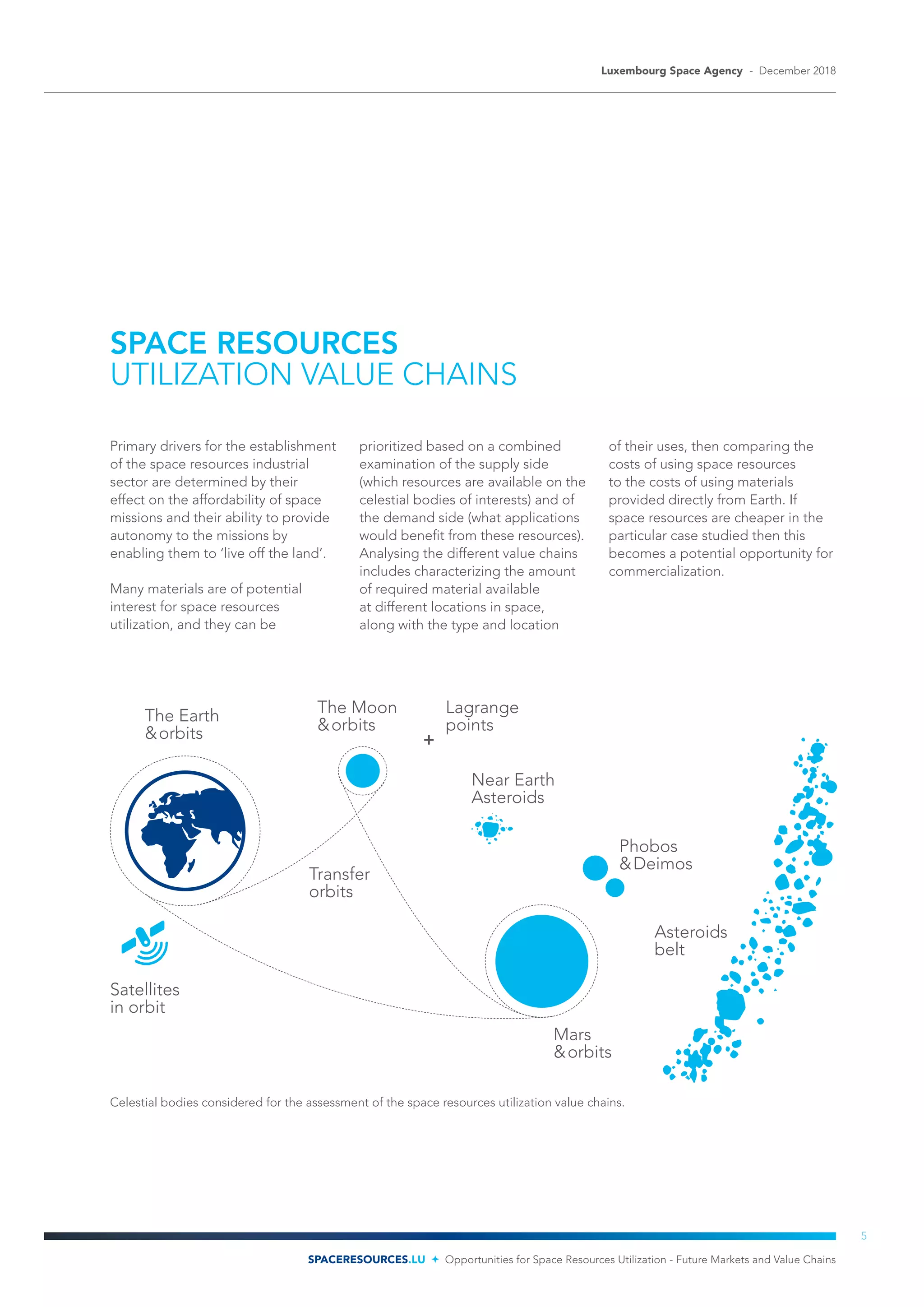
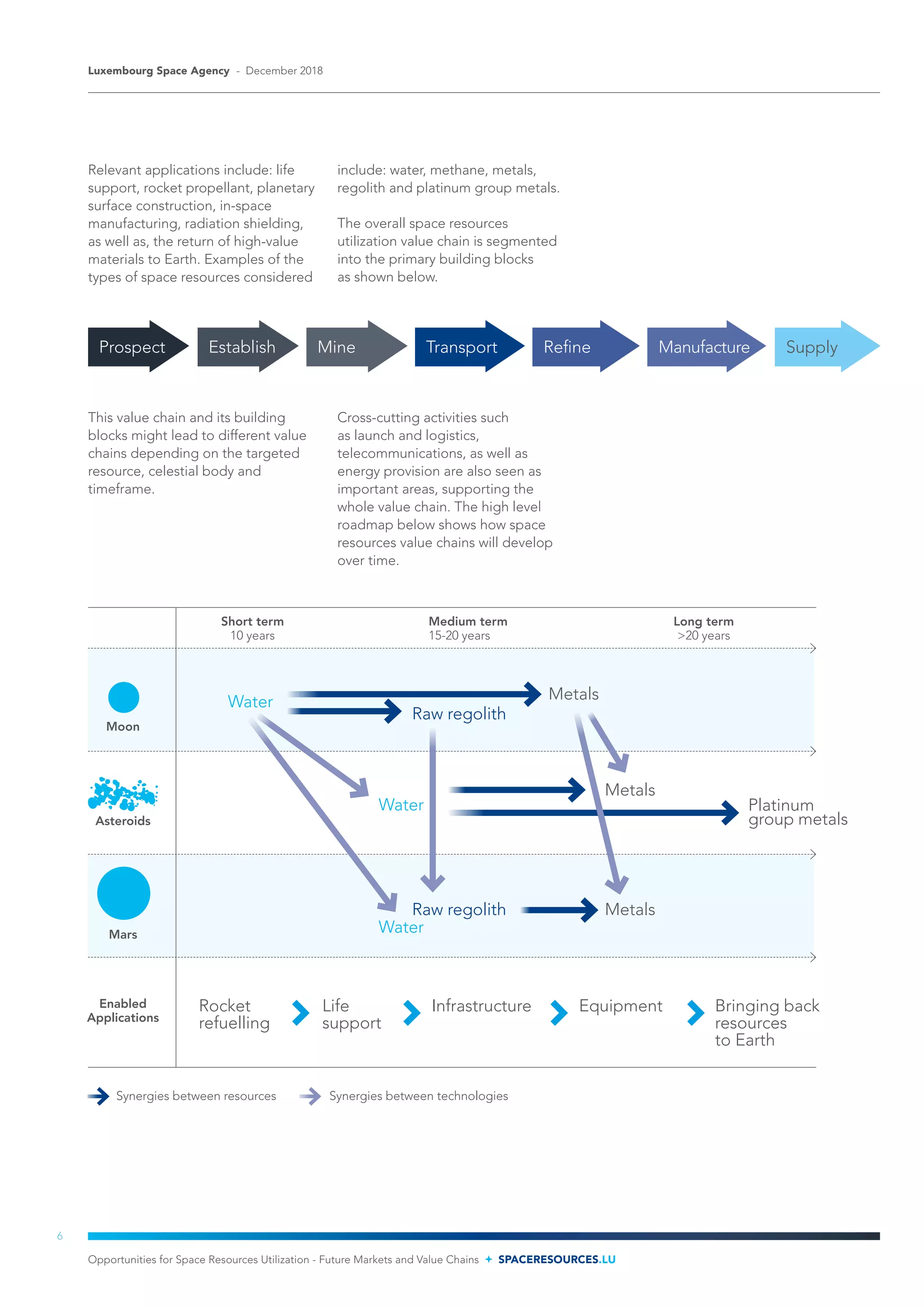
The document discusses opportunities for utilizing space resources to develop commercial industries. It identifies key points in Luxembourg's strategy, including that large quantities of resources are available in the solar system, and that space resources can reduce mission costs and improve economic viability. The document then analyzes potential markets and value chains for space resources, identifying rocket propellant and life support as near and mid-term opportunities. Over $73-170 billion in revenue is estimated from 2018-2045, supporting hundreds of thousands of jobs.