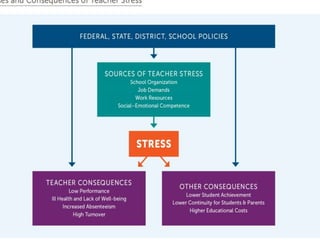
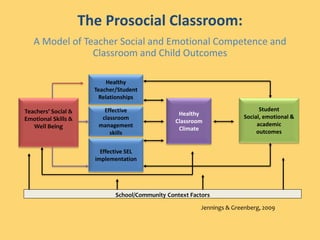
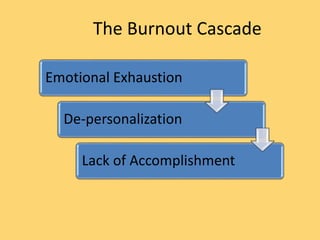
The document discusses trends in declining teacher satisfaction, increasing burnout and attrition. Four main sources of teacher stress are identified: school organization/culture, job demands, lack of work resources, and teachers' personal resources. High teacher stress leads to negative outcomes for students such as higher stress levels, poorer behavior, social-emotional adjustment and academic performance. Promising approaches to reduce teacher stress discussed include quality mentoring, mindfulness programs, workplace wellness programs, and social-emotional learning programs. The goal of the event is to hear expert perspectives on potential solutions and consider innovations that can be tested to address the "crisis" of teacher stress.




![AFT Survey (2015)
• Non-representative survey of 30,000 US Teachers
• 70% found their jobs stressful
I am Enthusiastic About Teaching
Start of my career
Strongly Agree ]Somewhat Agree
Currently
Strongly Agree Somewhat Agree
Somewhat Disagree Strongly Disagree](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stress2-230606112401-f3cebcbd/85/stress2-pptx-5-320.jpg)