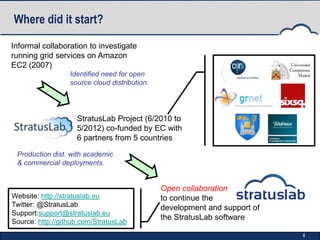
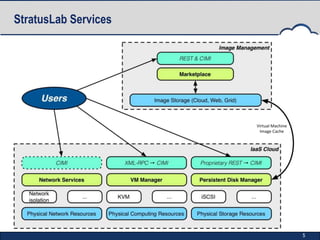
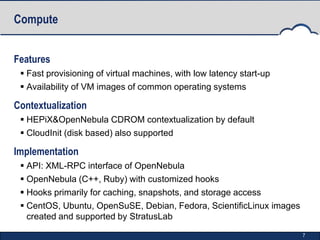
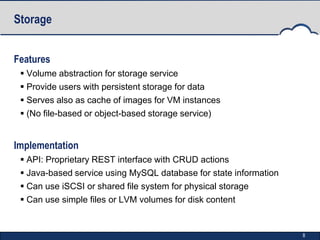
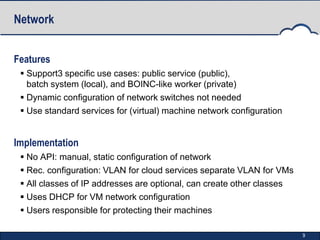
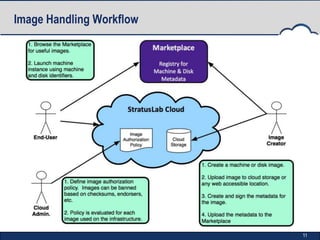
StratusLab is an open-source Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) cloud distribution that aims to simplify cloud operations for users, application developers, and data centers. It began in 2010 and has developed multiple releases, enhancing features such as virtual machine provisioning, storage services, and networking capabilities. The project is supported by an evolving roadmap, encouraging collaboration and feedback from the community.