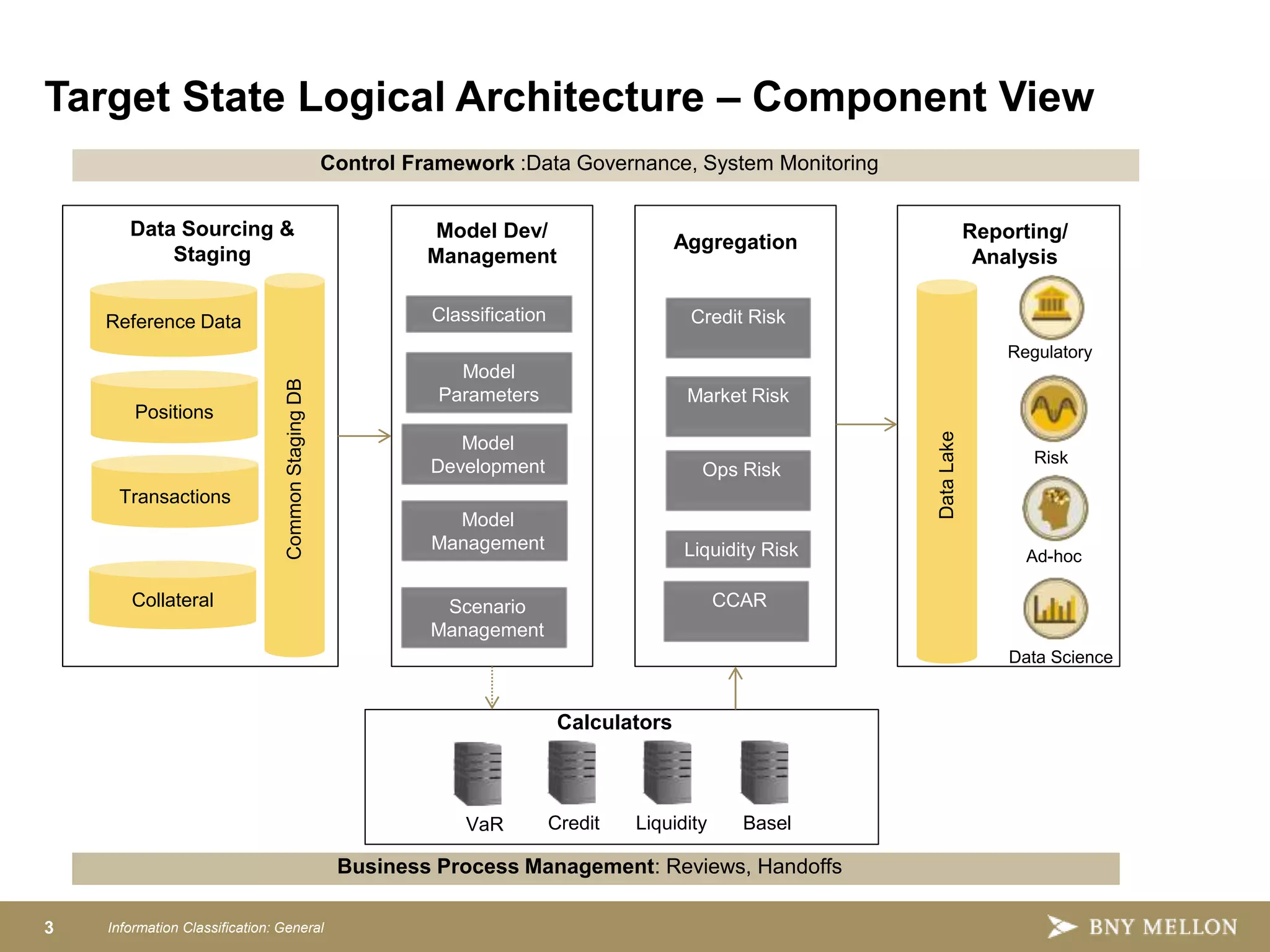
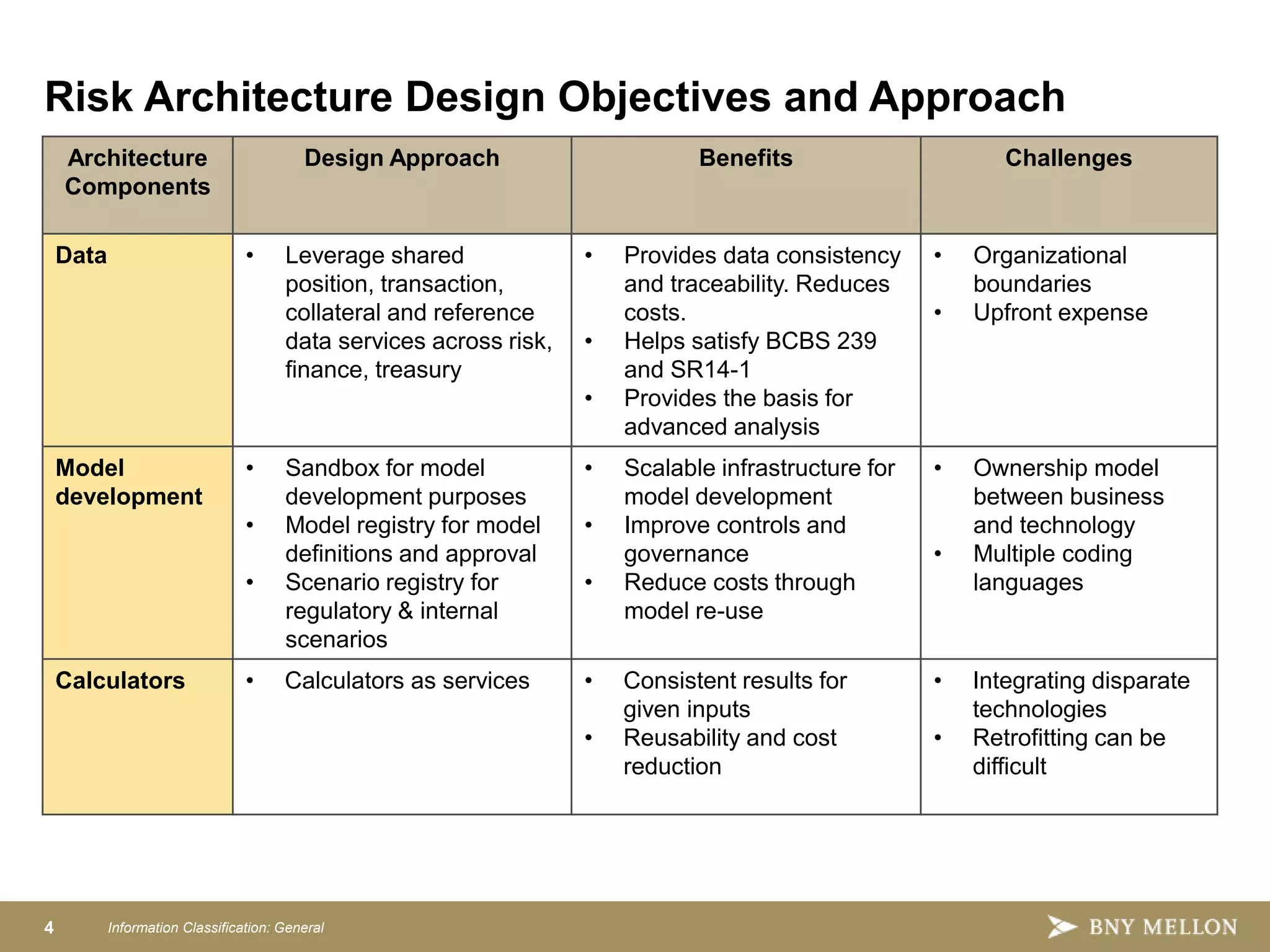
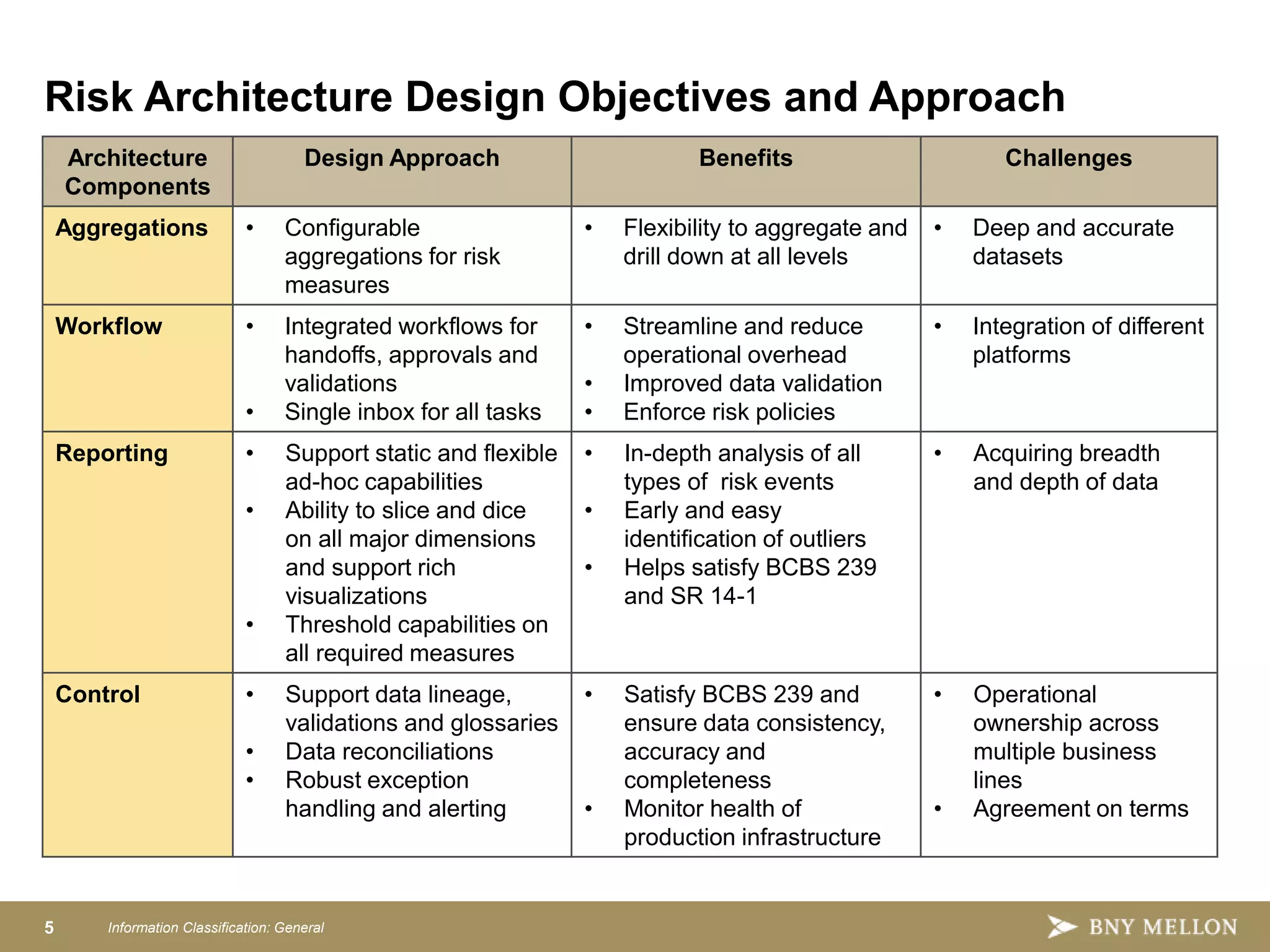
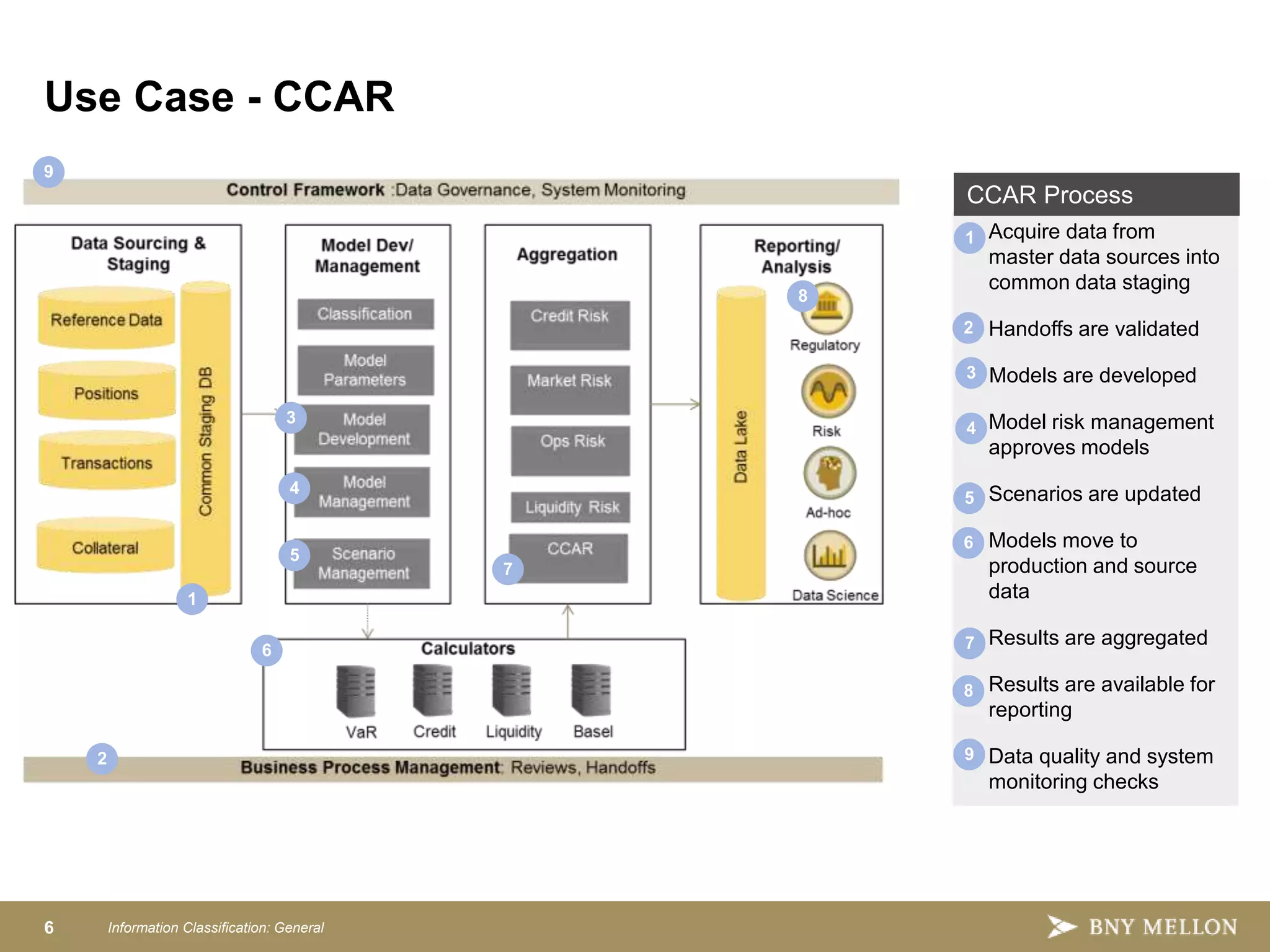
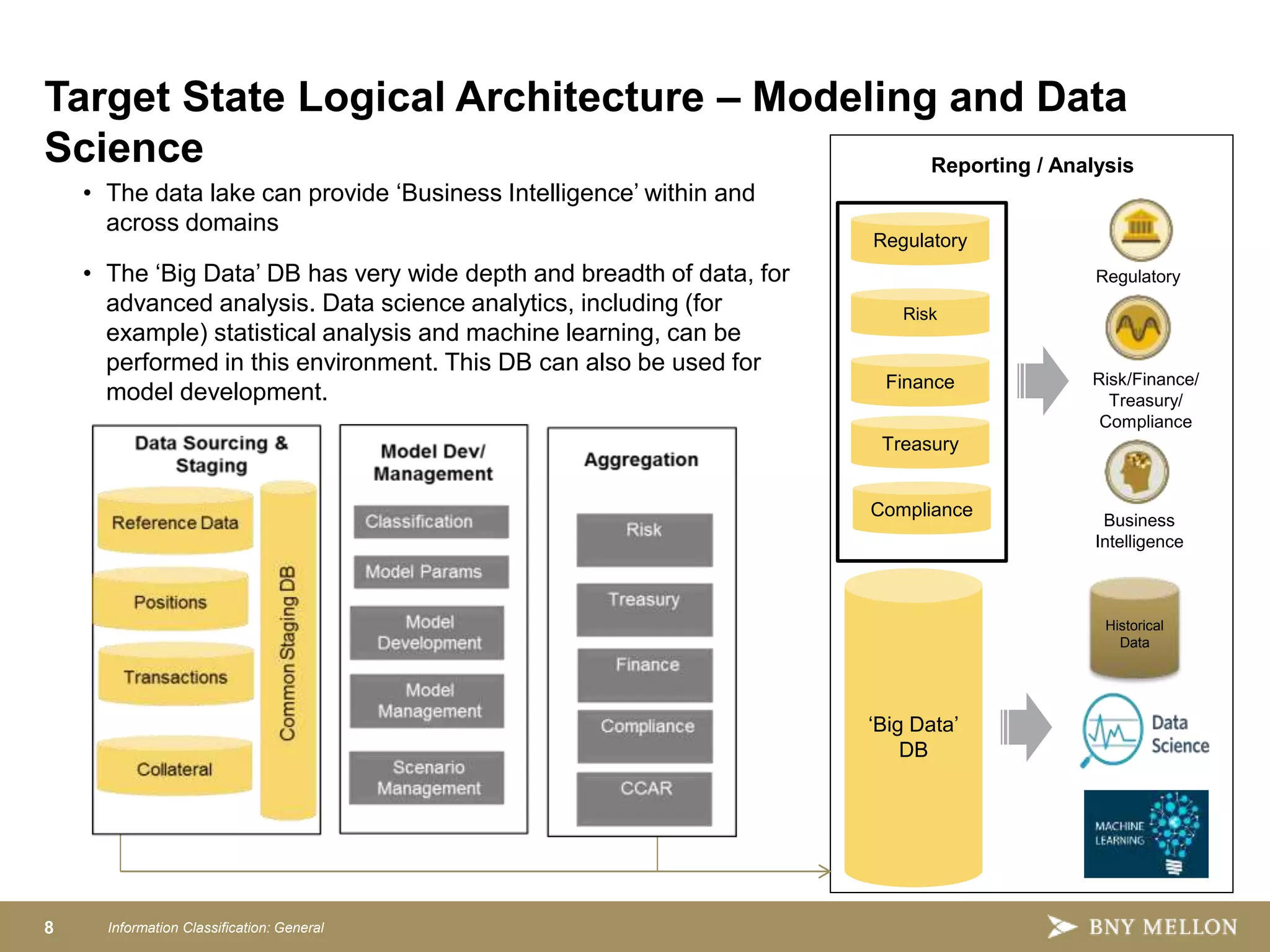
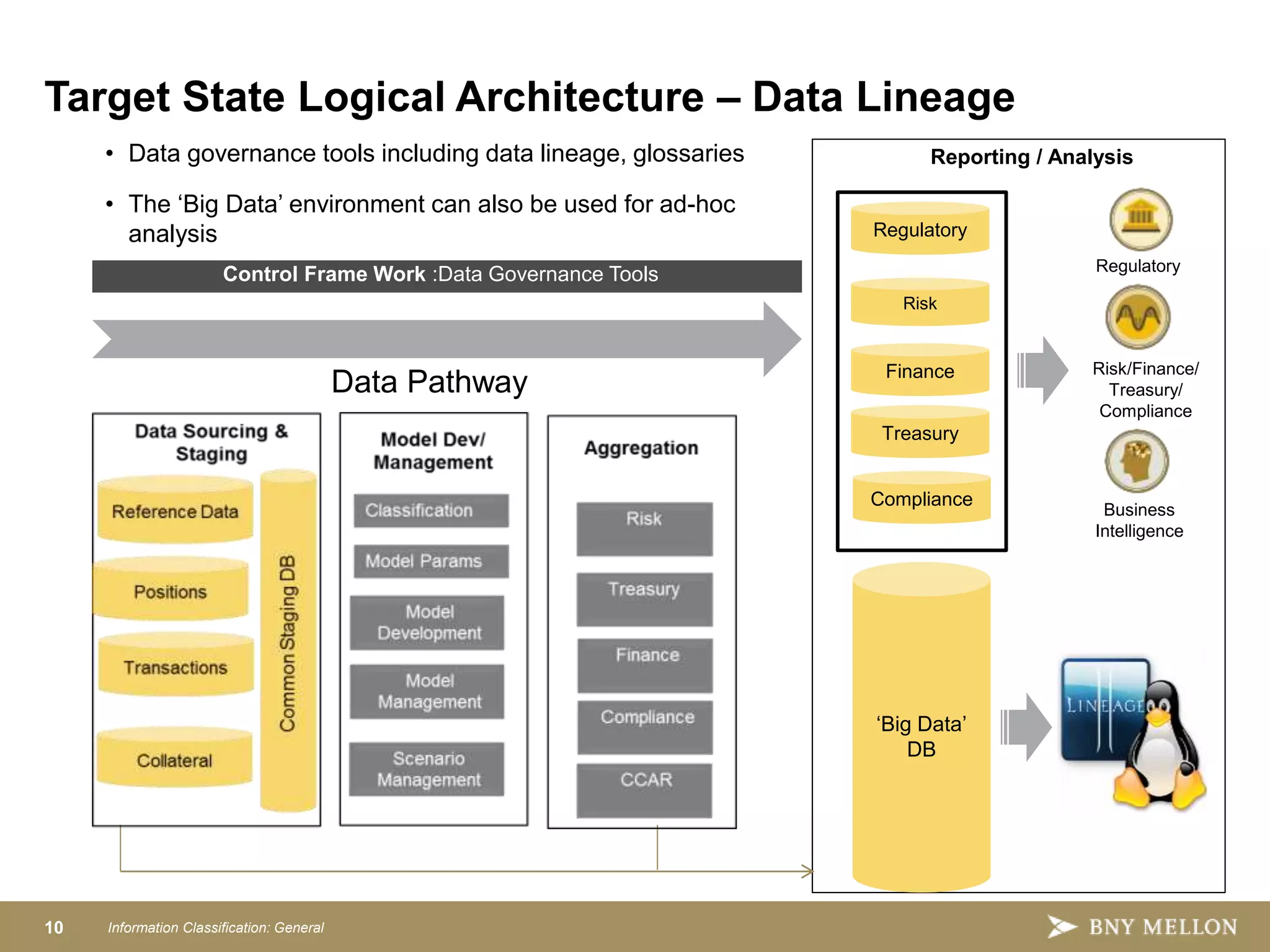
Strategic Enterprise Risk Architecture aims to create an end-to-end architecture for risk management including data, processing, and reporting. This would satisfy both regulatory requirements and internal risk analysis while reducing costs and improving data consistency. The target state architecture features shared data services, model development sandboxes, reusable risk calculators, configurable aggregations, integrated workflows, and advanced reporting. This provides a single source of risk data, controls, and governance to analyze things like credit, market, and liquidity risk across the organization.