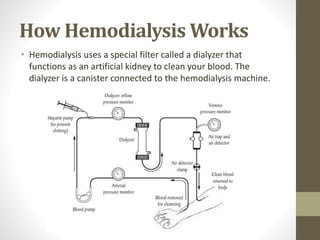
Hemodialysis is a treatment option for kidney failure that involves using a machine to filter waste from the blood outside of the body. During hemodialysis, blood travels through tubes from the body into a dialyzer that acts as an artificial kidney, removing wastes, salt, and extra water before returning cleaned blood to the body. Treatments typically occur three times a week and last 3-5 hours. Potential complications include problems with vascular access sites and changes in fluid and mineral balance that can cause side effects like low blood pressure. Adhering to dietary restrictions on fluids, potassium, phosphorus, and sodium is important for hemodialysis patients.