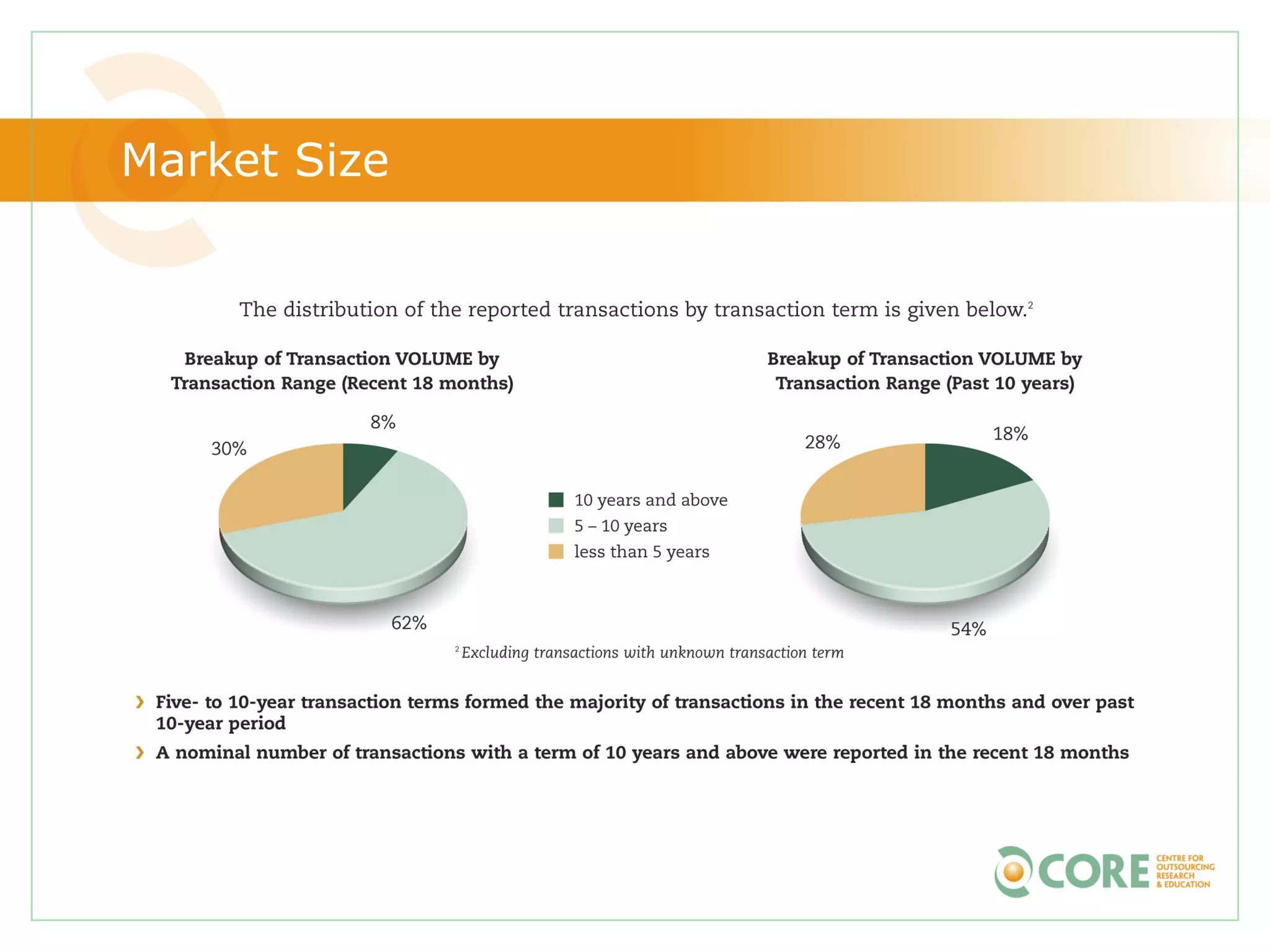
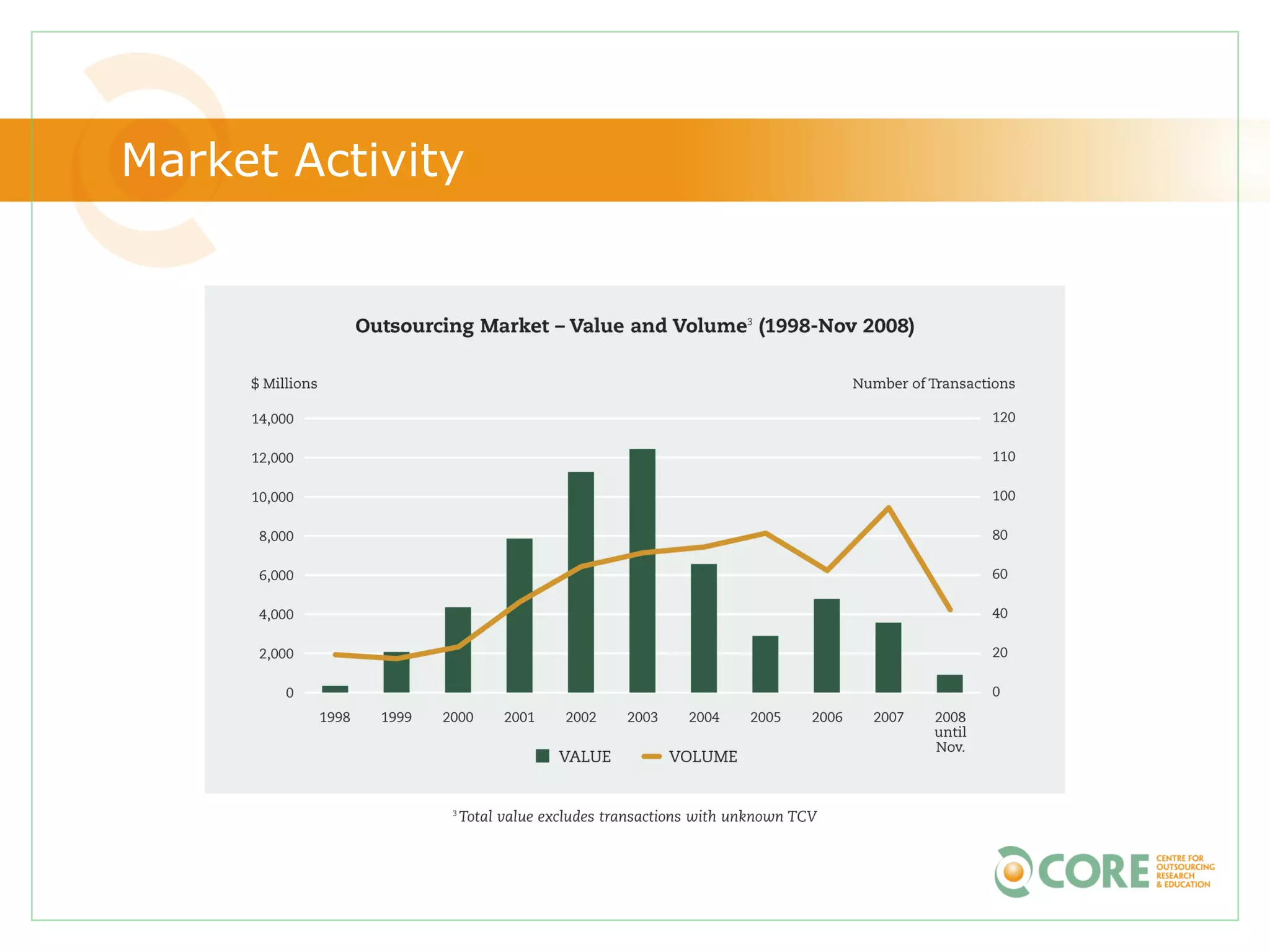
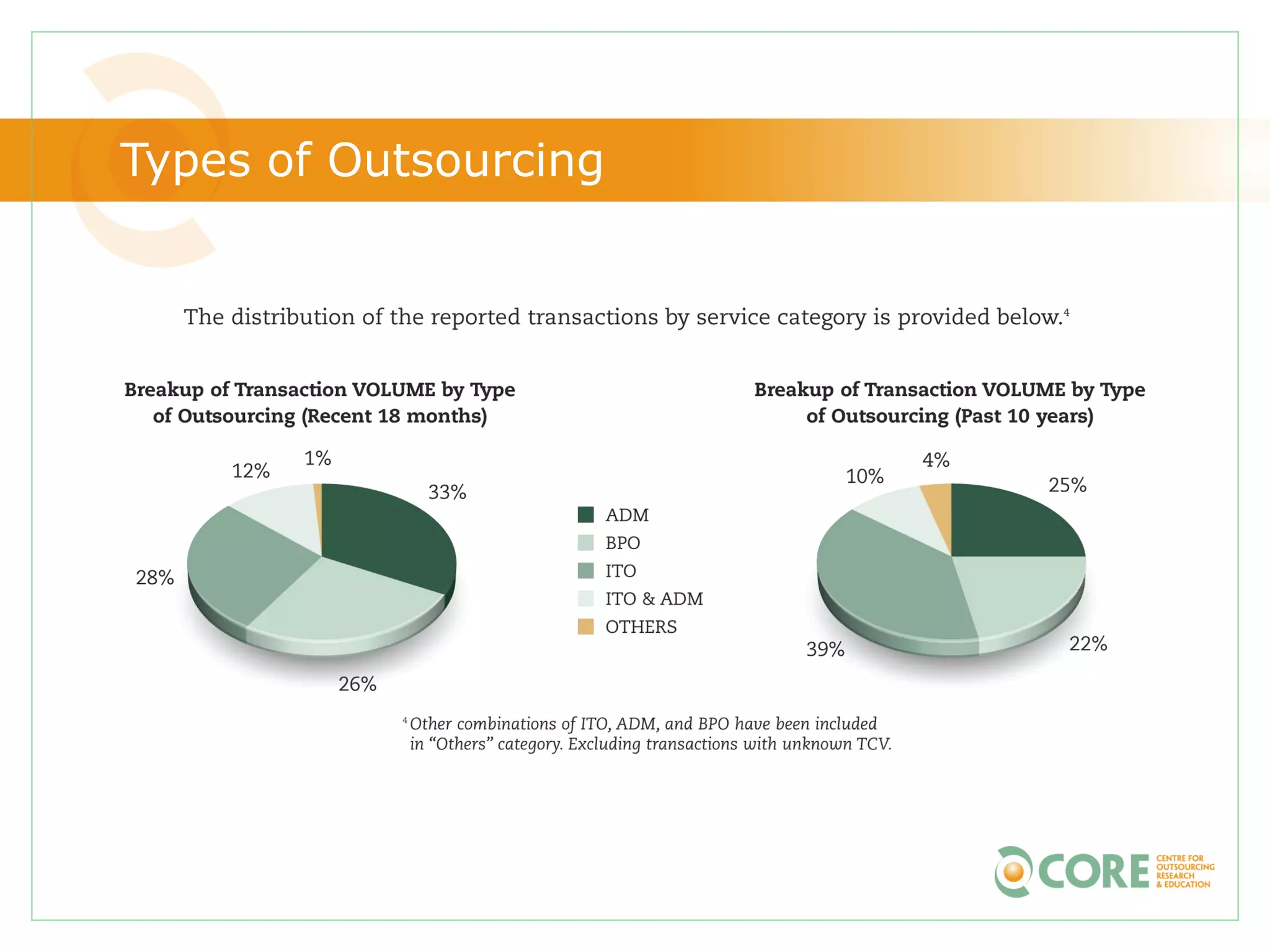
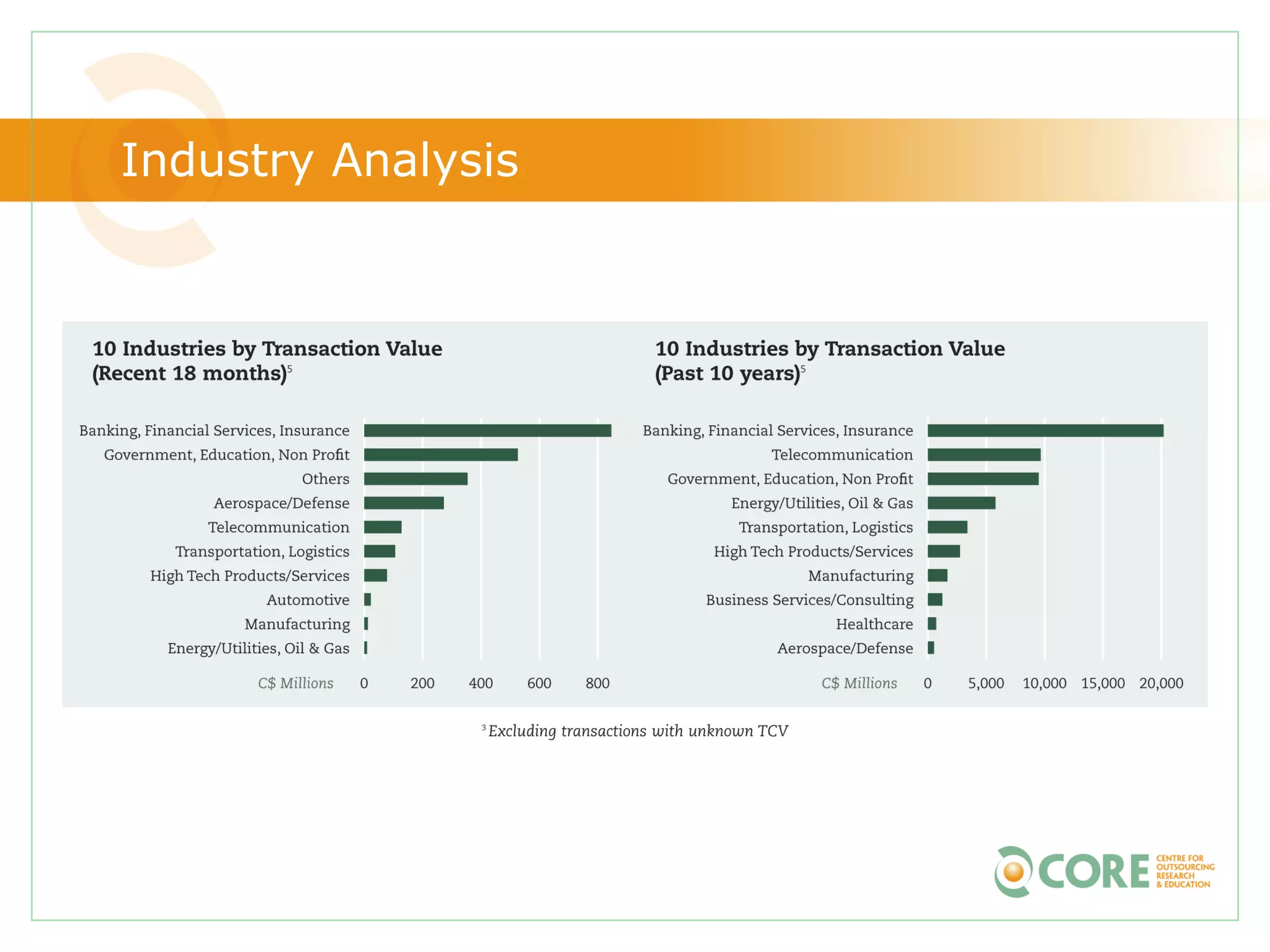
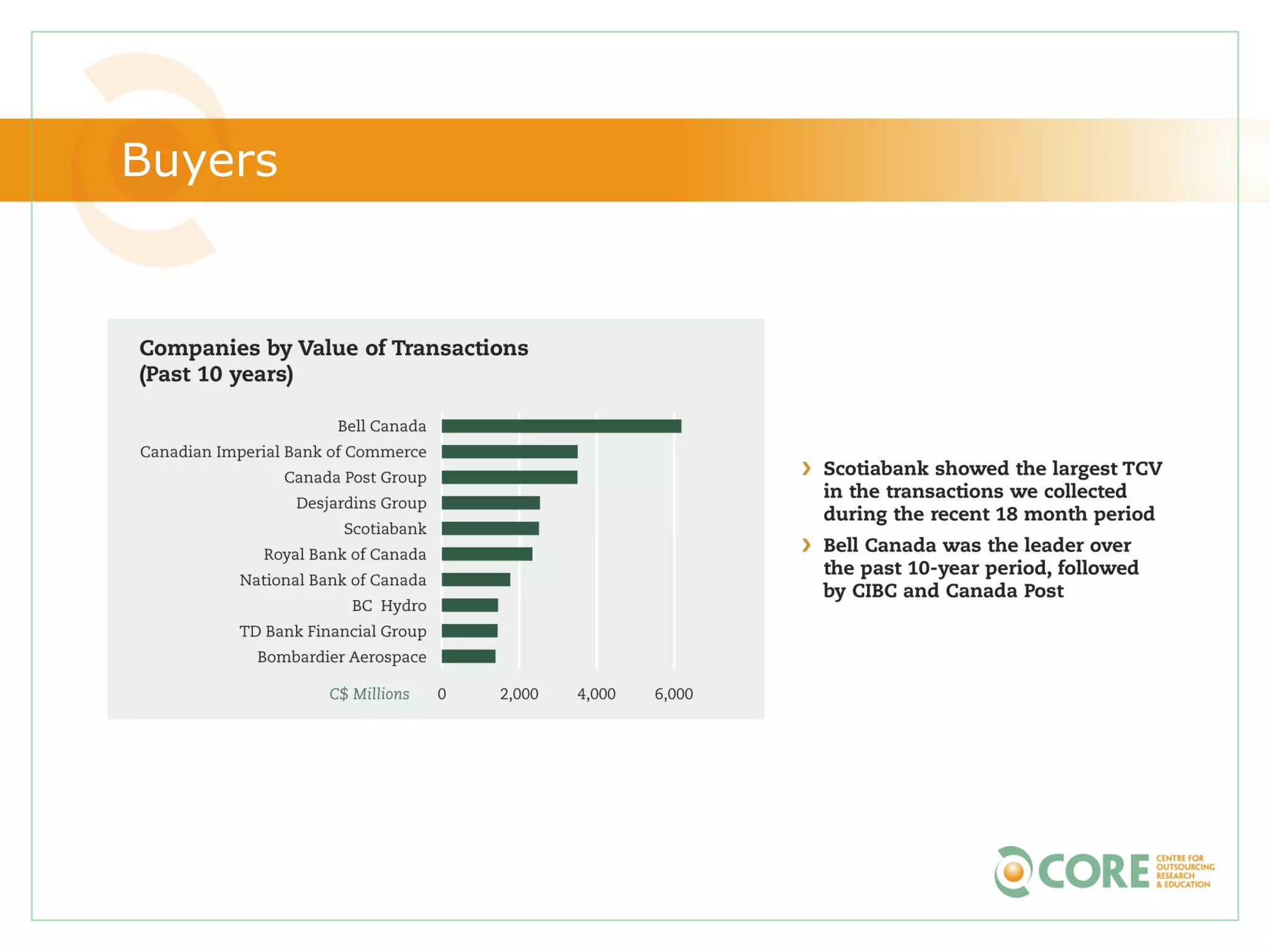
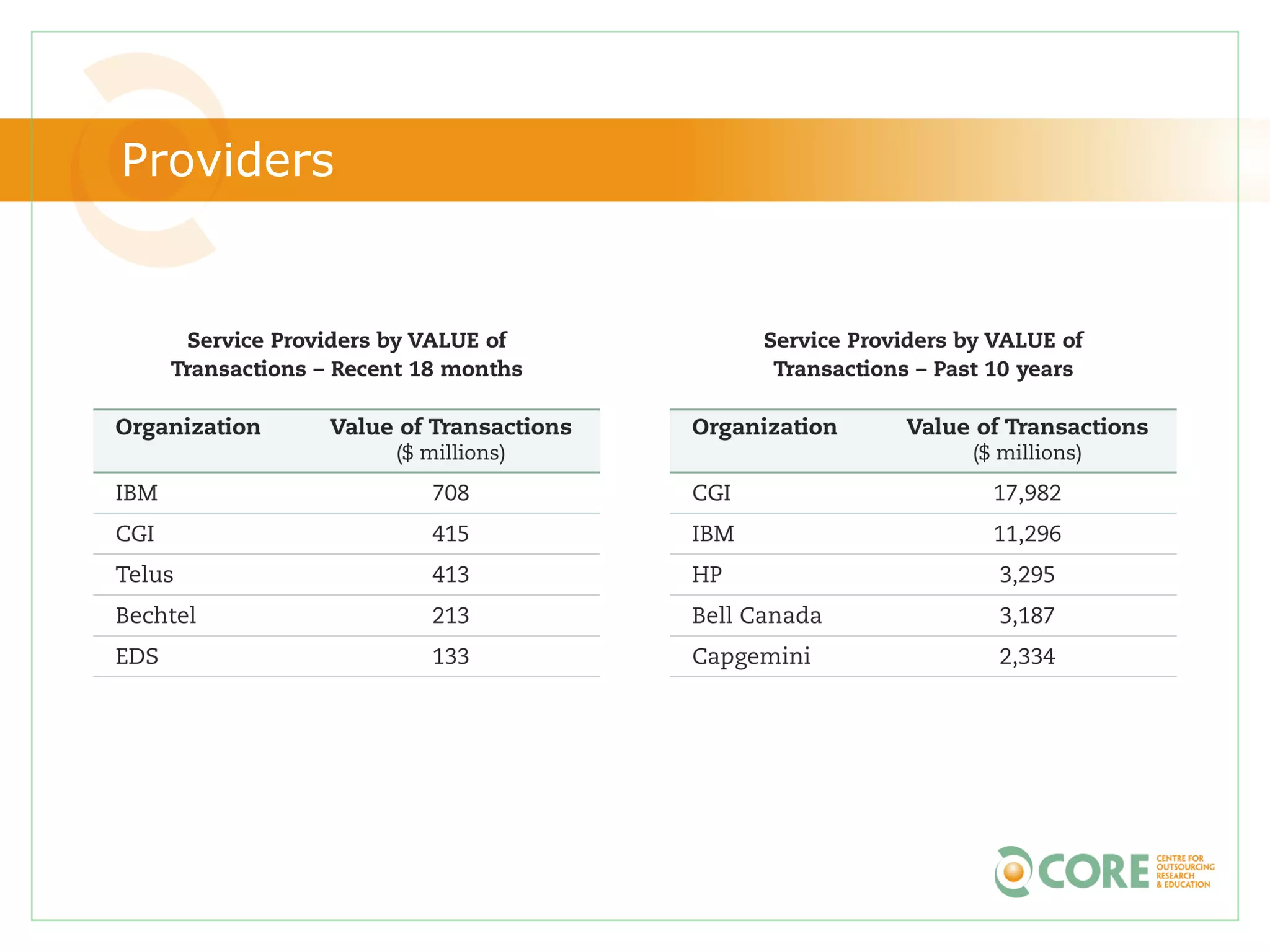
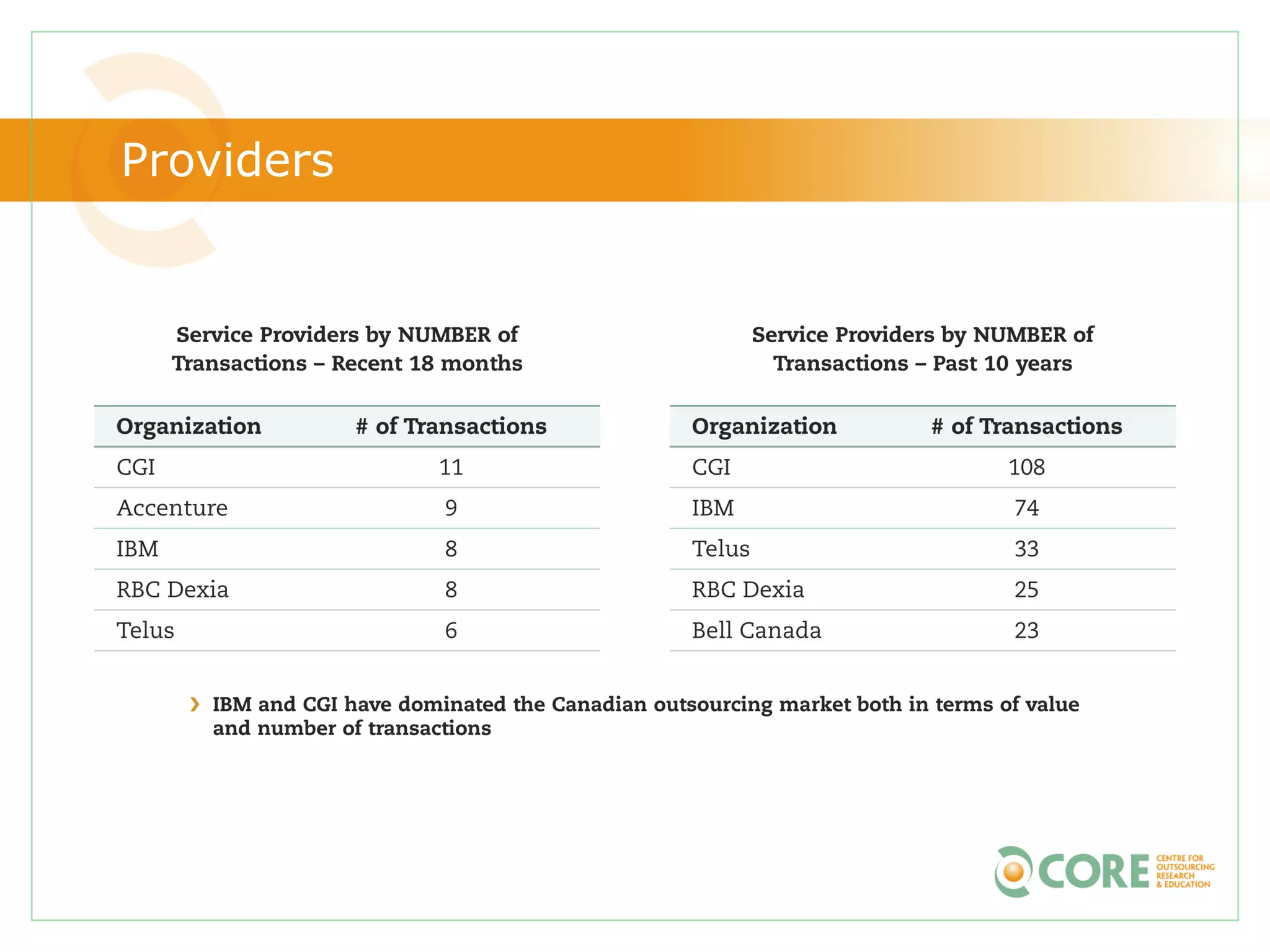
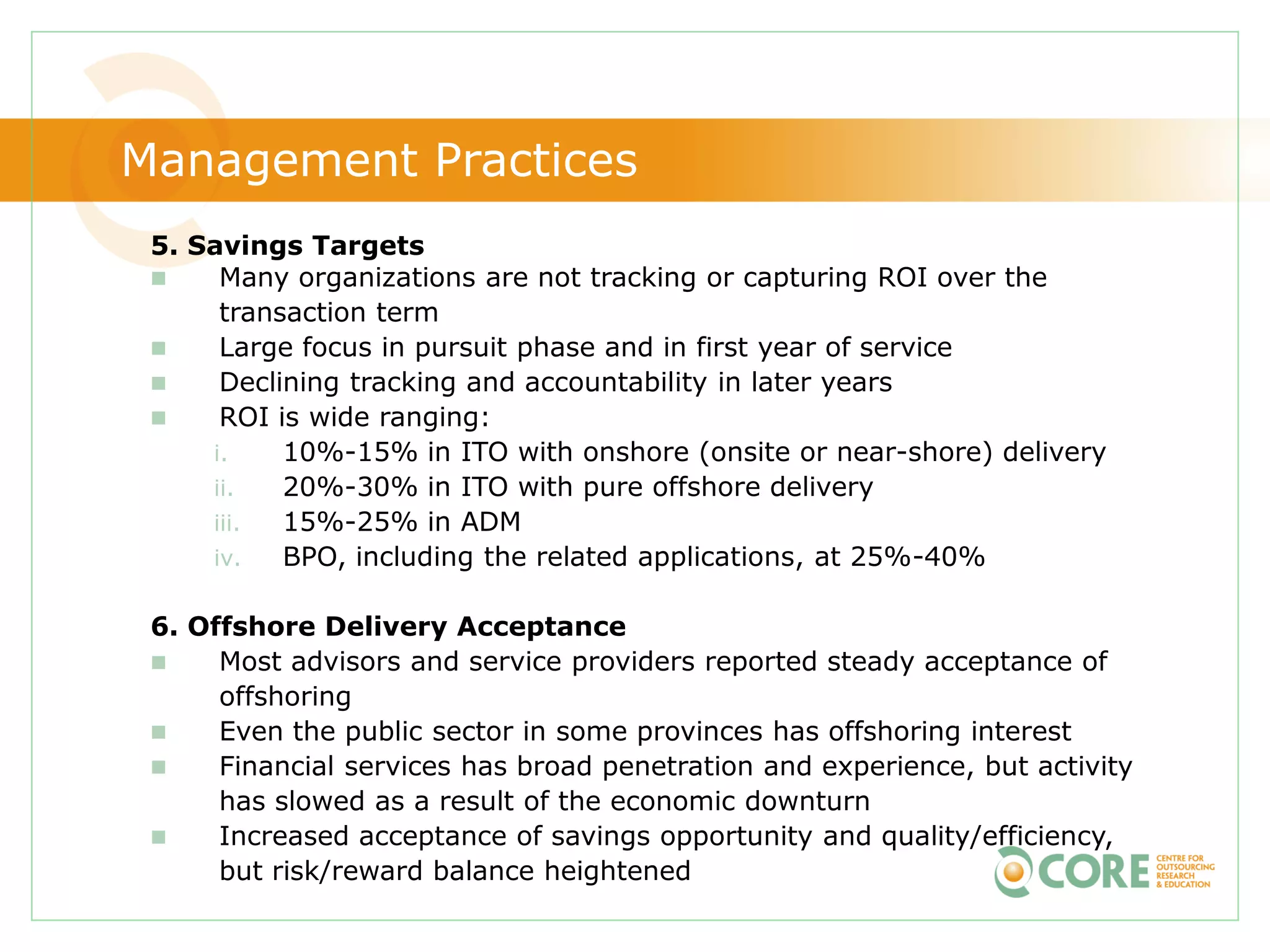
This document provides an agenda and overview for "The State of Canadian Outsourcing: Update 2009" report. The summary includes:
1) The report analyzes trends in the Canadian outsourcing market and management practices between June 2007-November 2008 based on 100 new outsourcing transactions.
2) It focuses on larger transactions over $1 million across all industries for the period of 1998-2008.
3) Both quantitative and qualitative data were collected through surveys of buyers, providers and advisors, as well as public announcements and interviews.