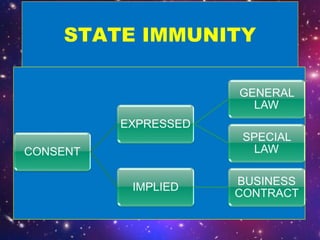
State immunity is a principle of international law that exempts a state from legal prosecution or lawsuits in another state's domestic courts. This stems from the principle of equality between states under international law - that one state cannot exercise authority over another equal state without its consent. As such, under the doctrine of state immunity, a state cannot be sued by another state or private individual without expressly or implicitly waiving its immunity. The Philippines constitution adheres to this principle of state immunity for the government. However, immunity can be waived through legislation, contracts, or filing a complaint that exposes the state to counterclaims.