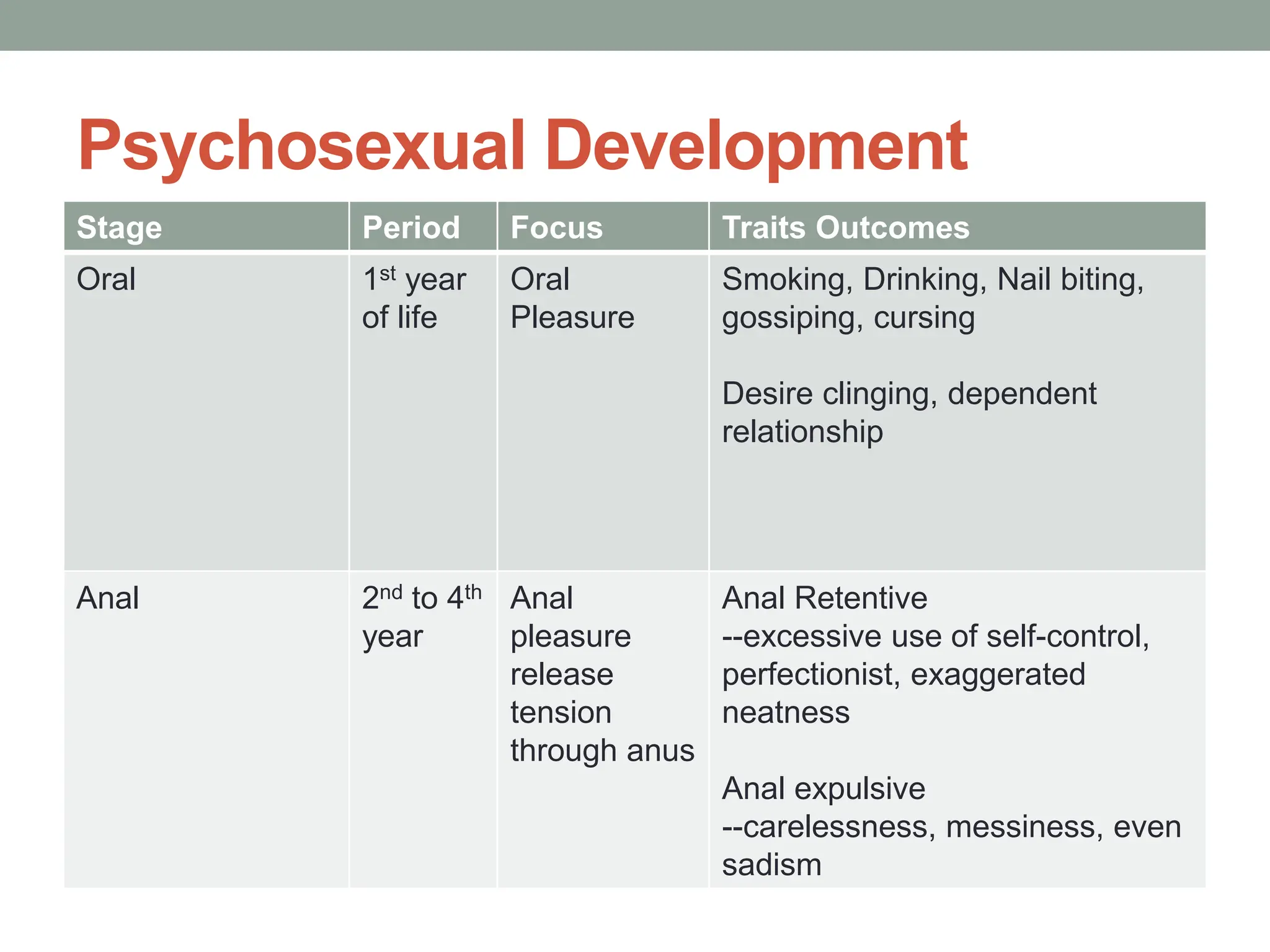
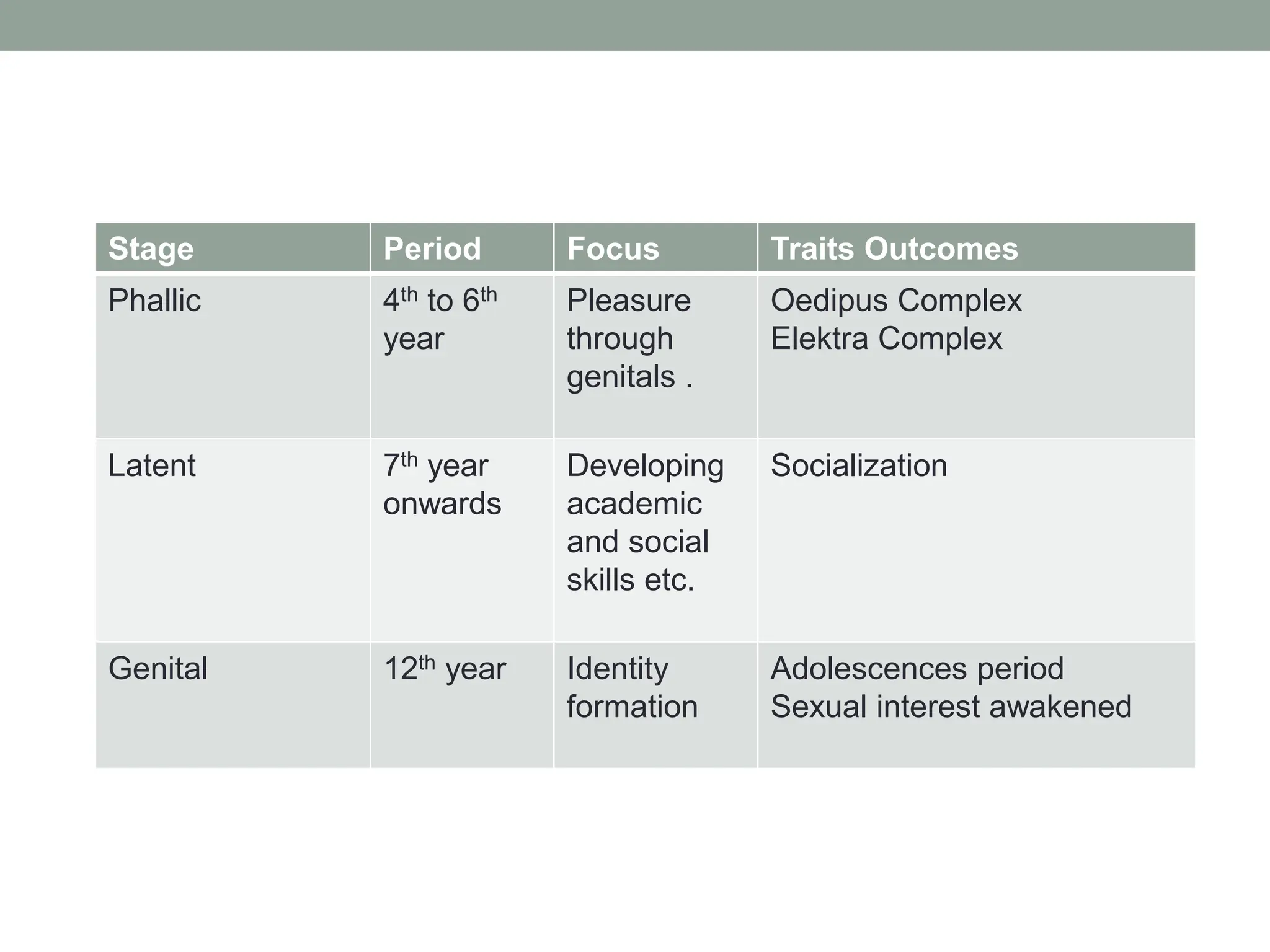
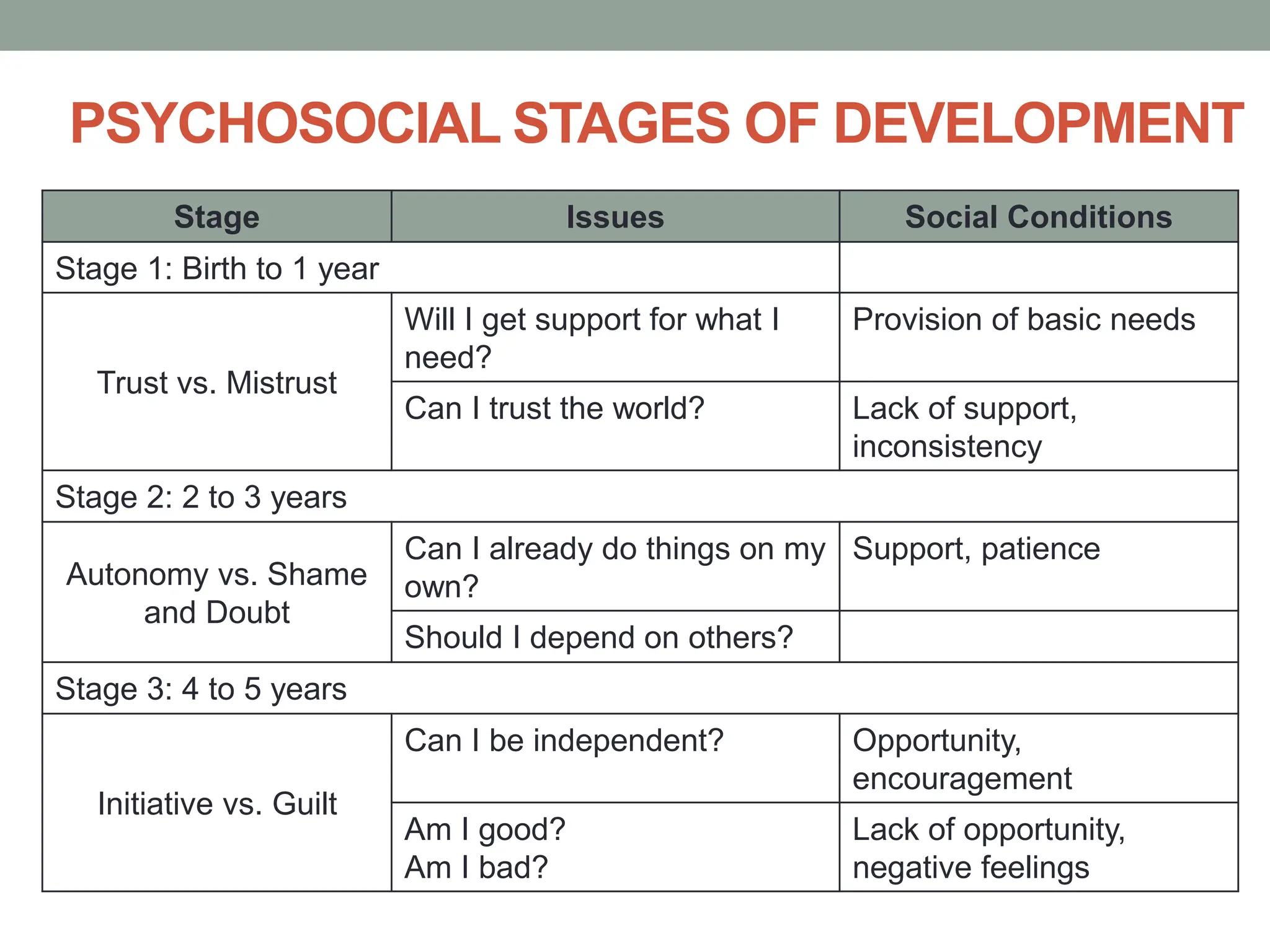
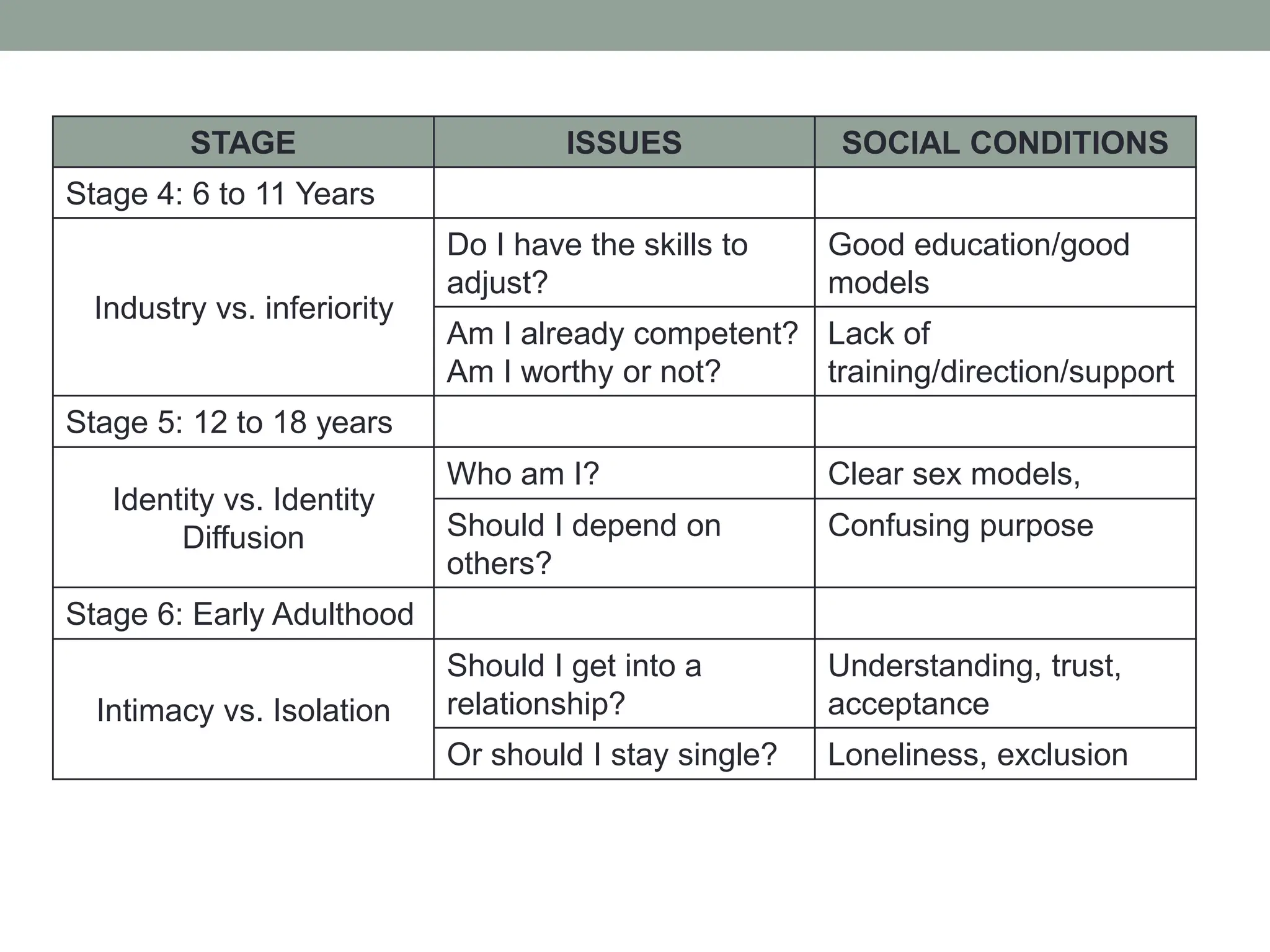
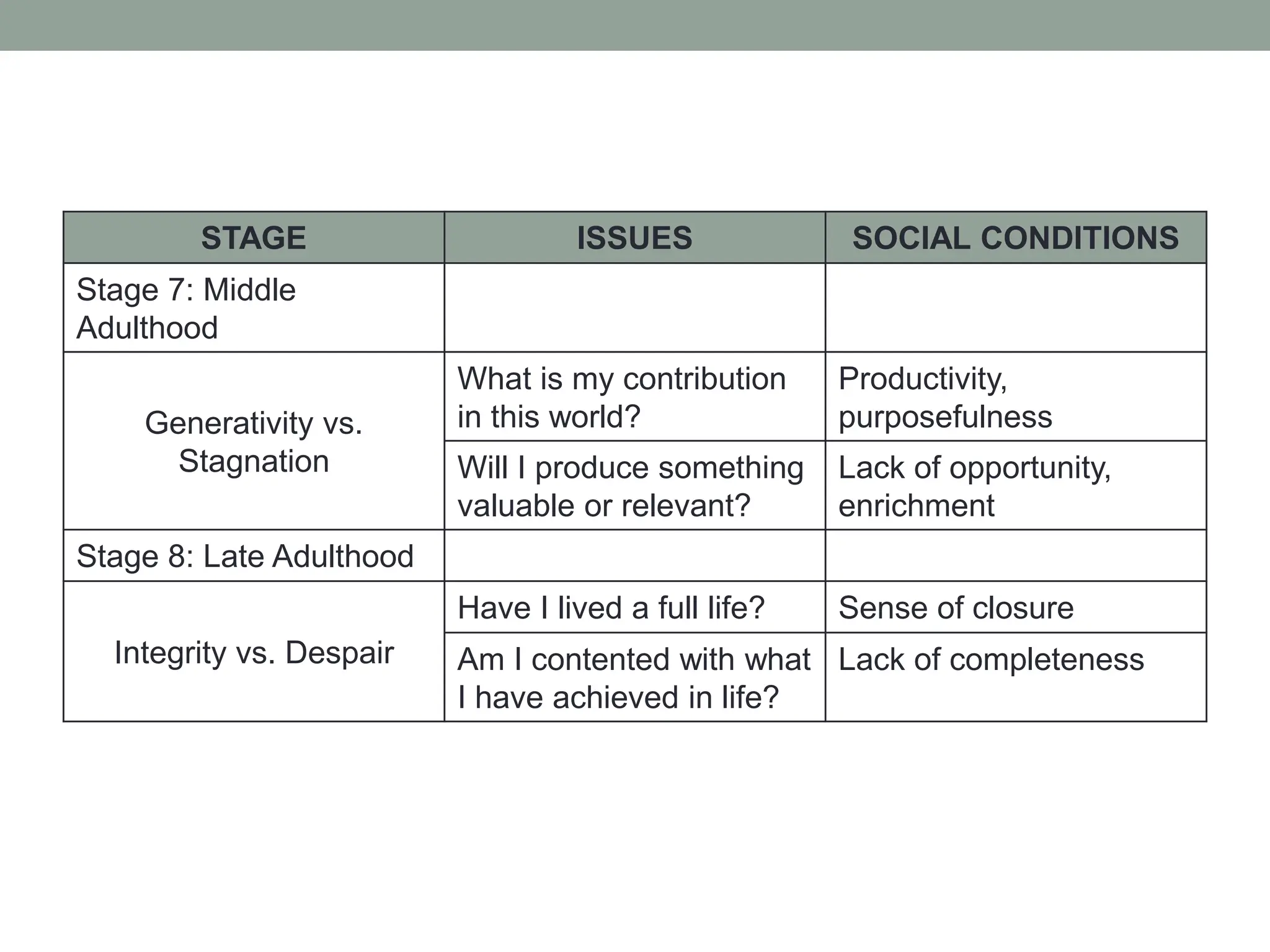
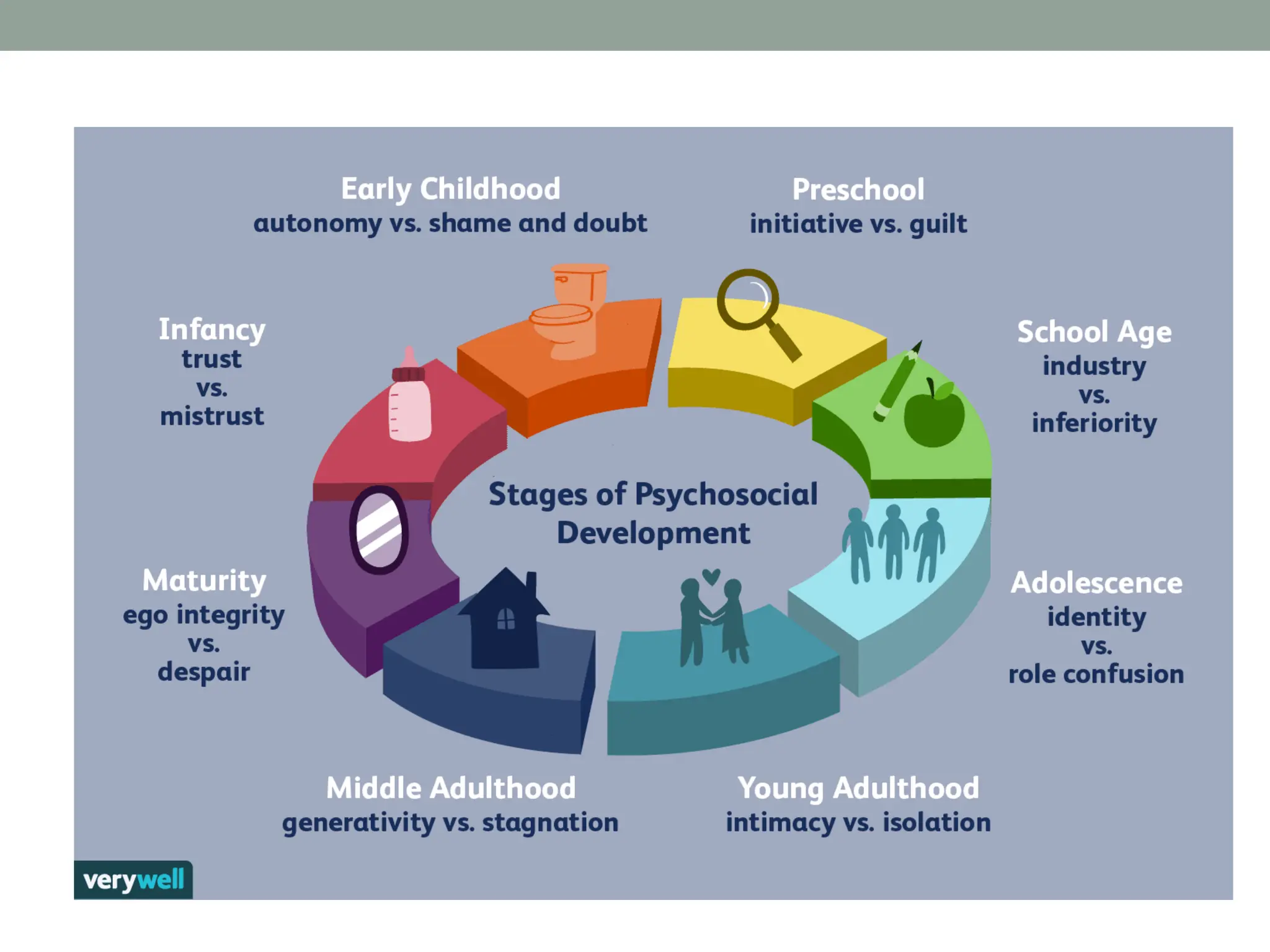
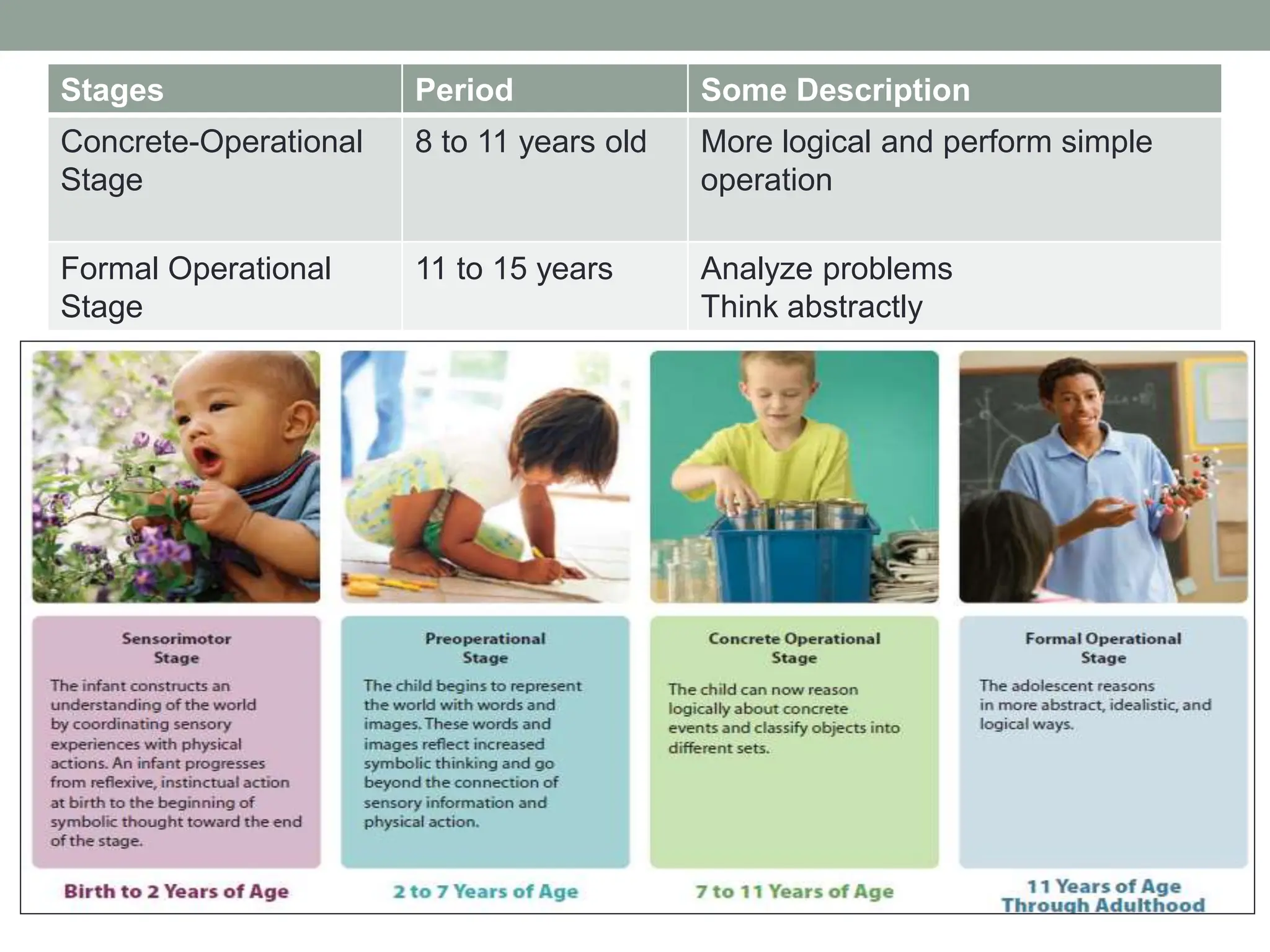
The document outlines key theories of human development, including Sigmund Freud's psychosexual stages, Erik Erikson's psychosocial stages, Jean Piaget's cognitive development stages, and Lawrence Kohlberg's moral reasoning stages. Each theory presents distinct stages with accompanying challenges and traits that influence individual growth and development. Additionally, behavioral assumptions highlight the impact of learning and environment on personal development.