More Related Content
PPTX
ENGINEERING_SQL_COMPLETE_NOTES for DBMS.ptx PPTX
SQL_COMPLETE_NOTE Database management system PPTX
SQL_all_commnads_aggregate_functions.pptx PPTX
4 SQL DML.pptx ASHEN WANNIARACHCHI USESS PDF
Database management system unit 1 Bca 2-semester notes PPTX
Structured query language PDF
SQL for data scientist And data analysist Advanced PDF
Lecture on DBMS & MySQL.pdf v. C. . Similar to SQL_Presentation_Apna_College_Notes.pptx
PPTX
sql_w3schoolspptpresentationmanyamongall-pptx PPTX
DEE 431 Introduction to Mysql Slide 3 PDF
PPTX
Introduction_to_SQL_DML_DDL_DCL with Syntax.pptx PPTX
UNIT-3 Structured Query Language(SQL).pptx PPTX
PPTX
SQL_W3Schoolspptpresentationoneamongall.pptx PPTX
PDF
PPTX
175658630409872728_SQL_Presentation.pptx PPTX
PDF
PDF
sql notes Provideby AGN HUB Tech & It Solutions PPTX
An intoduction to sql and its components PPTX
SQL_Presentation.ppt basic version 12.32 PDF
Introduction to structured query language PPTX
introduction to structural query language PPTX
Unit-3.pptx database management unit four note for computer engineering students PPTX
SQL.pptx Data Types Database Operations Types PPTX
Recently uploaded
PDF
Industrial Tools Manufacturers In India : Torso Tools PDF
Creating a Multi-Agent Flow: Orchestrate multiple specialized agents into a p... PDF
engineering management chapter 5 ppt presentation PPTX
Why TPM Succeeds in Some Plants and Struggles in Others | MaintWiz PPTX
The Hidden Cost of Bad Spare Parts Planning (And How AI CMMS Fixes It) PDF
AWS Re:Invent 2025 Recap by FivexL - Guilherme, Vladimir, Andrey PDF
Rajesh Prasad- Brief Profile with educational, professional highlights PPTX
Why Most SAP PM Implementations Fail — And How High-Reliability Plants Fix It PDF
PROBLEM SLOVING AND PYTHON PROGRAMMING UNIT 3.pdf PDF
Unit Weight in Term of Volumetric Water Content.pdf PPTX
Batch-1(End Semester) Student Of Shree Durga Tech. PPT.pptx PPTX
unit v awp IN ANTENNA AND WAVE PROP IN JNTUH PDF
Role of Training and Development in Enhancing Safety Performance in Opencast ... PPTX
Fuel Injection Pump Test Bench – Precision Testing & Calibration for Diesel E... PDF
MoD_2.pptx solid rockets of the rocket.pdf PDF
Computer Network Lab Manual ssit -kavya r.pdf or Computer Network Lab Manual ... PPTX
INTEGRATED COMMUNICATION AND SENSING Presentation.pptx PPTX
Optimum mesh size for various fishing gears by B2B.pptx PPTX
A professional presentation on Cosmos Bank Heist PDF
Applications of AI in Civil Engineering - Dr. Rohan Dasgupta SQL_Presentation_Apna_College_Notes.pptx
- 1.
SQL (Structured QueryLanguage)
• Based on Notes by Apna College
• Name: __________
• Class: __________
• Subject: __________
- 2.
What is aDatabase?
• A database is a collection of interrelated data
• Stores organized information for easy access
- 3.
What is DBMS?
•DBMS is software used to create and manage
databases
• Helps organize and control data
- 4.
What is RDBMS?
•RDBMS stores data in tables
• Rows = Records
• Columns = Attributes
• Examples: MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle
- 5.
What is SQL?
•SQL stands for Structured Query Language
• Used to store, retrieve, update and delete
data
• SQL is a language, not a database
- 6.
- 7.
SQL vs MySQL
•SQL is a query language
• MySQL is an RDBMS software that uses SQL
- 8.
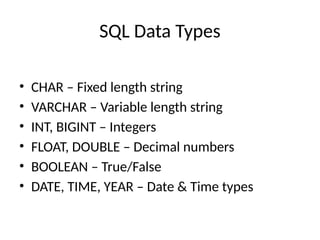
SQL Data Types
•CHAR – Fixed length string
• VARCHAR – Variable length string
• INT, BIGINT – Integers
• FLOAT, DOUBLE – Decimal numbers
• BOOLEAN – True/False
• DATE, TIME, YEAR – Date & Time types
- 9.
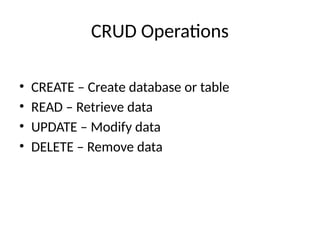
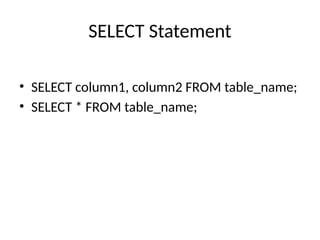
Types of SQLCommands
• DDL – Define structure
• DQL – Query data
• DML – Modify data
• DCL – Control access
• TCL – Manage transactions
- 10.
- 11.
- 12.
- 13.
- 14.
DISTINCT & LIKE
•DISTINCT removes duplicates
• LIKE is used for pattern search
• % and _ are wildcards
- 15.
IN, BETWEEN, ISNULL
• IN matches values from a list
• BETWEEN filters a range
• IS NULL checks missing values
- 16.
- 17.
- 18.
- 19.
- 20.
- 21.
- 22.
- 23.
Types of Joins
•INNER JOIN
• LEFT JOIN
• RIGHT JOIN
• FULL JOIN
• CROSS JOIN
• SELF JOIN
- 24.
- 25.
- 26.
Joins vs Subqueries
•Joins combine tables
• Subqueries are nested queries
• Joins are faster for large data
• Subqueries are easier for simple logic
- 27.
Conclusion
• SQL isessential for managing relational
databases
• Used in apps, banking, schools, businesses
• Learning SQL builds strong data skills