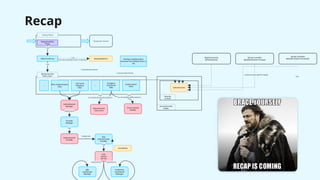
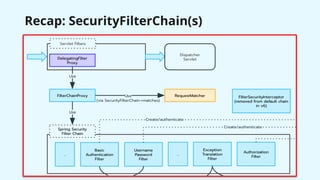
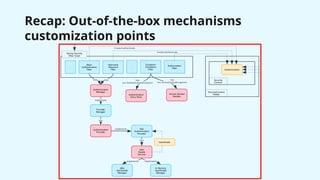
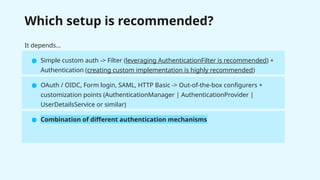
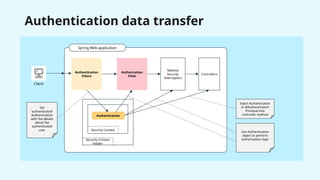
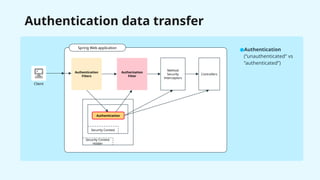
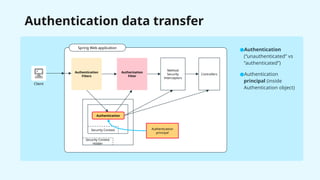
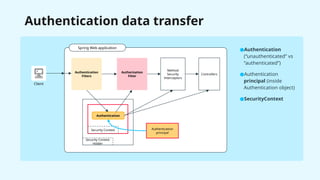
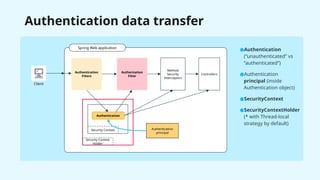
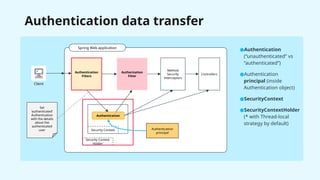
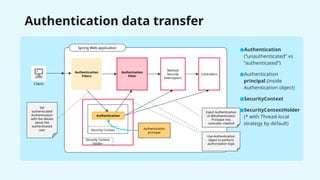
The document provides a detailed overview of Spring Security, focusing on its authentication mechanisms and customizations, including JWT and API key setups. It discusses the architecture, modularization of security configurations, and various authentication filters while emphasizing the importance of understanding the basics for effective implementation. Recommendations on when to use different setups and customizable points in Spring Security are also highlighted.








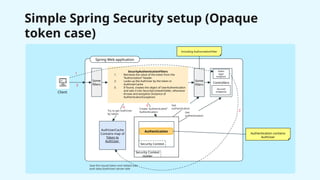
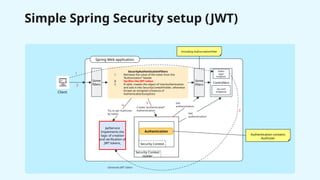
![Simple Spring Security setup
1
2
3
REST API auth with token (JWT or Opaque token)
Opaque token - random string with no meaning
JWT - string with encoded content and signature
can be:
● read by anyone;
● verified by owner of the key (public key or
symmetric key);
● issued by owner of the key (private key or
symmetric key)]
Authentication requirements for the project:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springsecuritydeepdiveintobasics-250131202440-d2fdb7ac/85/Spring-Security-Deep-dive-into-basics-Ihor-Polataiko-pptx-19-320.jpg)













![Form login [.formLogin(...)] FormLoginConfigurer
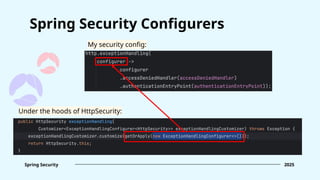
Spring Security 2025
Configurers of out-of-the-box
mechanisms
HTTP Basic [.httpBasic(...)] HttpBasicConfigurer
Registration of UserDetailsService
implementation [.userDetailsService(...)] DaoAuthenticationConfigurer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springsecuritydeepdiveintobasics-250131202440-d2fdb7ac/85/Spring-Security-Deep-dive-into-basics-Ihor-Polataiko-pptx-40-320.jpg)

![AuthenticationFilter
1
2
AuthenticationConverter implementation: fetch authentication credentials from request
[HttpServetRequest -> “unauthenticated” Authentication]
AuthenticationManager implementation: perform actual authentication logic
[“unauthenticated” Authentication -> “authenticated” Authentication]
Reduce the amount of boilerplate code
At minimum, you’d have to specify:
3 Success and Failure handlers (not required, but usually unavoidable)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springsecuritydeepdiveintobasics-250131202440-d2fdb7ac/85/Spring-Security-Deep-dive-into-basics-Ihor-Polataiko-pptx-42-320.jpg)




![Supporting multiple authentication
mechanisms
01 Define Authentication implementations
Spring Security 2025
Implementation steps:
02 Define AuthenticationProvider implementations
03 Define Filter(s) [leverage AuthenticationFilter to reduce boilerplate code]
04 Create custom configurer for each authentication mechanism
Leverage “sharedObjects” from HttpSecurity (builder of SecurityFilterChain) to fetch
AuthenticationManager implementation](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springsecuritydeepdiveintobasics-250131202440-d2fdb7ac/85/Spring-Security-Deep-dive-into-basics-Ihor-Polataiko-pptx-47-320.jpg)


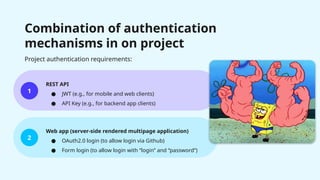
![Combination of authentication mechanisms
in on project
1
2
REST API security
[Server side rendered] web application security
Two SecurityFilterChain(s):](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springsecuritydeepdiveintobasics-250131202440-d2fdb7ac/85/Spring-Security-Deep-dive-into-basics-Ihor-Polataiko-pptx-51-320.jpg)

![Combination of authentication mechanisms in on project
As the result of the setup:
4 implementations of Authentication
● 2 custom: JwtAuthentication and ApiKeyAuthentication
● 2 from out-of-the-box mechanisms: OAuth2AuthenticationToken and UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken
5+ configurers applied:
● 2 custom: JwtAuthenticationConfigurer and ApiKeyAuthenticationConfigurer
● 3 from out-of-the-box mechanisms: FormLoginConfigurer [.formLogin(...)], DaoAuthenticationConfigurer [.userDetailsService(...)], OAuth2LoginConfigurer
[.oauth2Login(...)]
5+ filters
● 2 custom: JwtAuthenticationFilter [JwtAuthenticationConfigurer] and ApiKeyAuthenticationFilter [ApiKeyAuthenticationConfigurer]
● 3 from out-of-the-box mechanisms: OAuth2AuthorizationRequestRedirectFilter [OAuth2LoginConfigurer], OAuth2LoginAuthenticationFilter
[OAuth2LoginConfigurer], UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter [FormLoginConfigurer]
6 AuthenticationProvider(s) registered
● 2 custom: JwtAuthenticationProvider [JwtAuthenticationConfigurer] and ApiKeyAuthenticationProvider [ApiKeyAuthenticationConfigurer]
● 3 from out-of-the-box mechanisms: OidcAuthorizationCodeAuthenticationProvider [OAuth2LoginConfigurer], OAuth2LoginAuthenticationProvider
[OAuth2LoginConfigurer], DaoAuthenticationProvider [DaoAuthenticationConfigurer]
● 1 default: AnonymousAuthenticationProvider [AnonymousConfigurer]
AuthUser was made compatible with both UserDetails and OAuth2User contracts (interfaces)
2 SecurityFilterChain beans were registered (each having its own AuthenticationManager!!)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springsecuritydeepdiveintobasics-250131202440-d2fdb7ac/85/Spring-Security-Deep-dive-into-basics-Ihor-Polataiko-pptx-53-320.jpg)