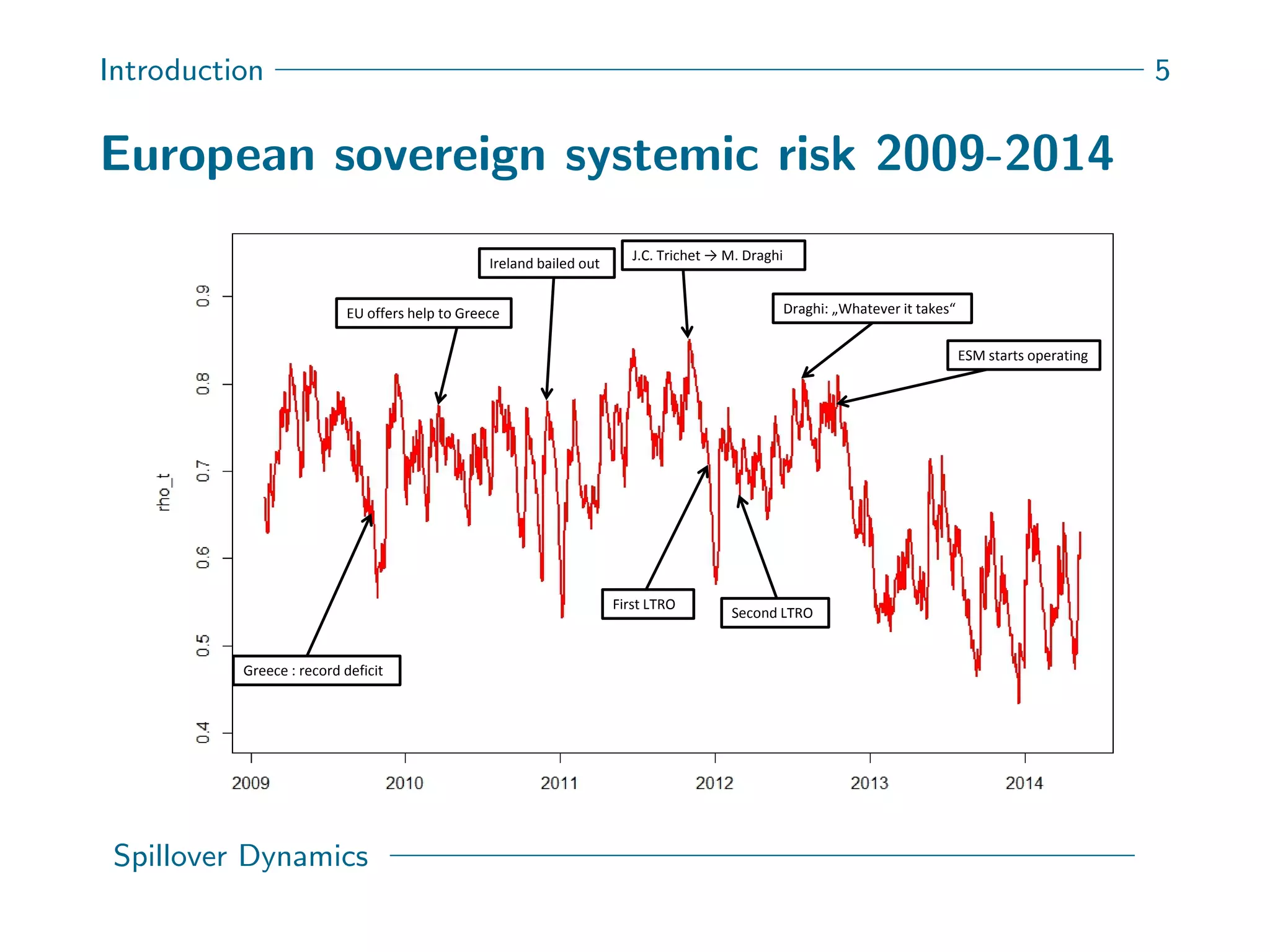
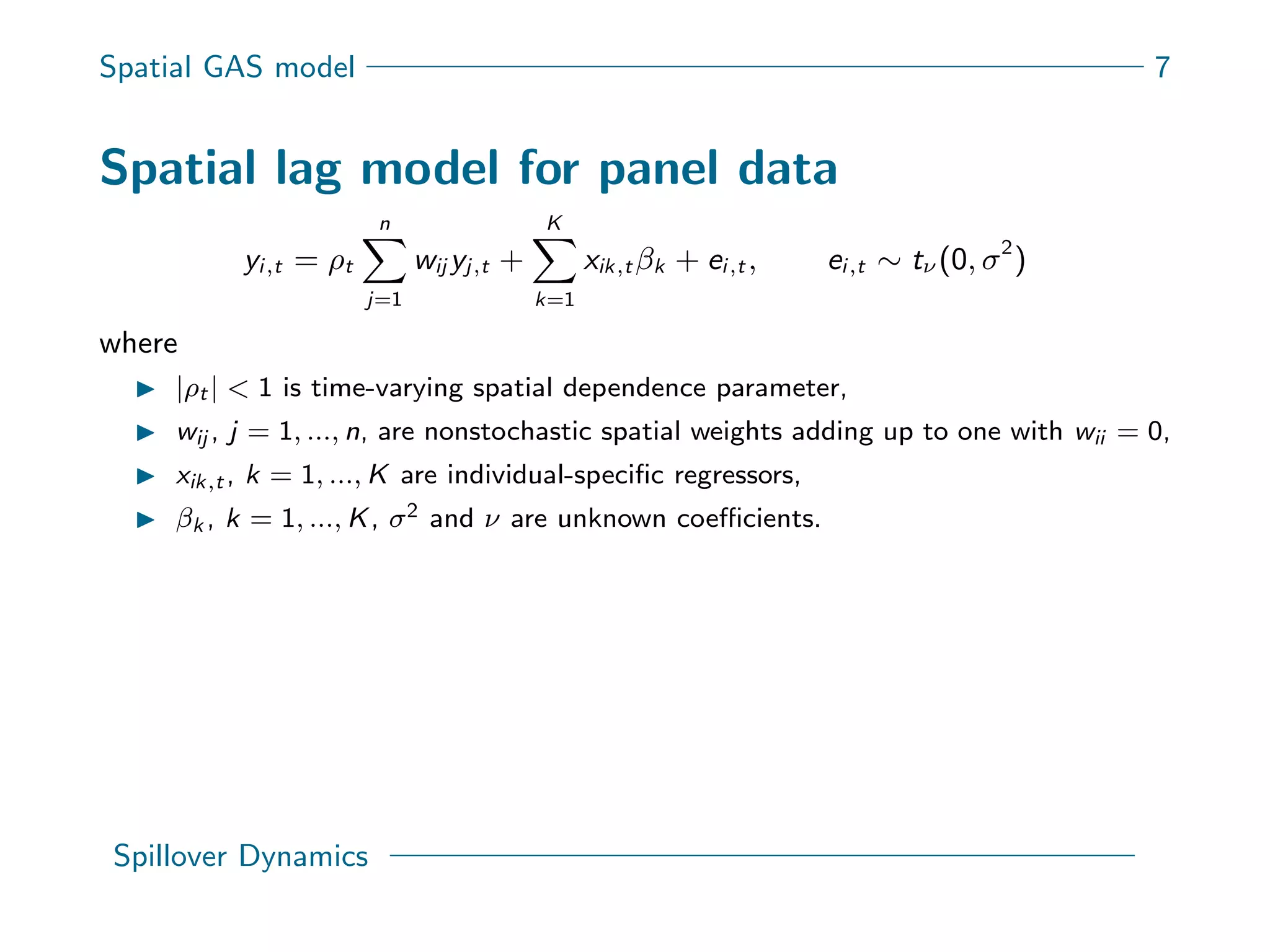
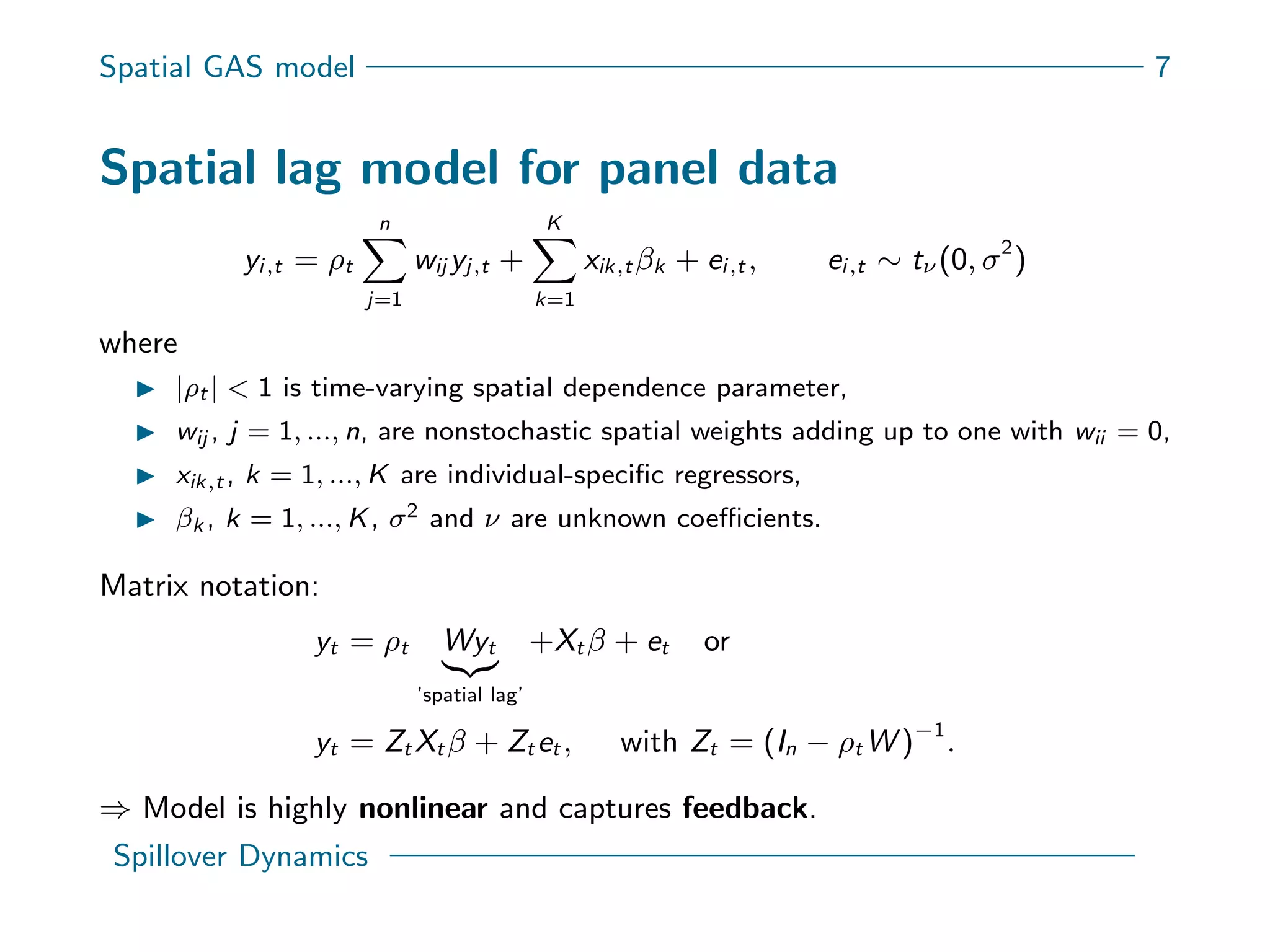
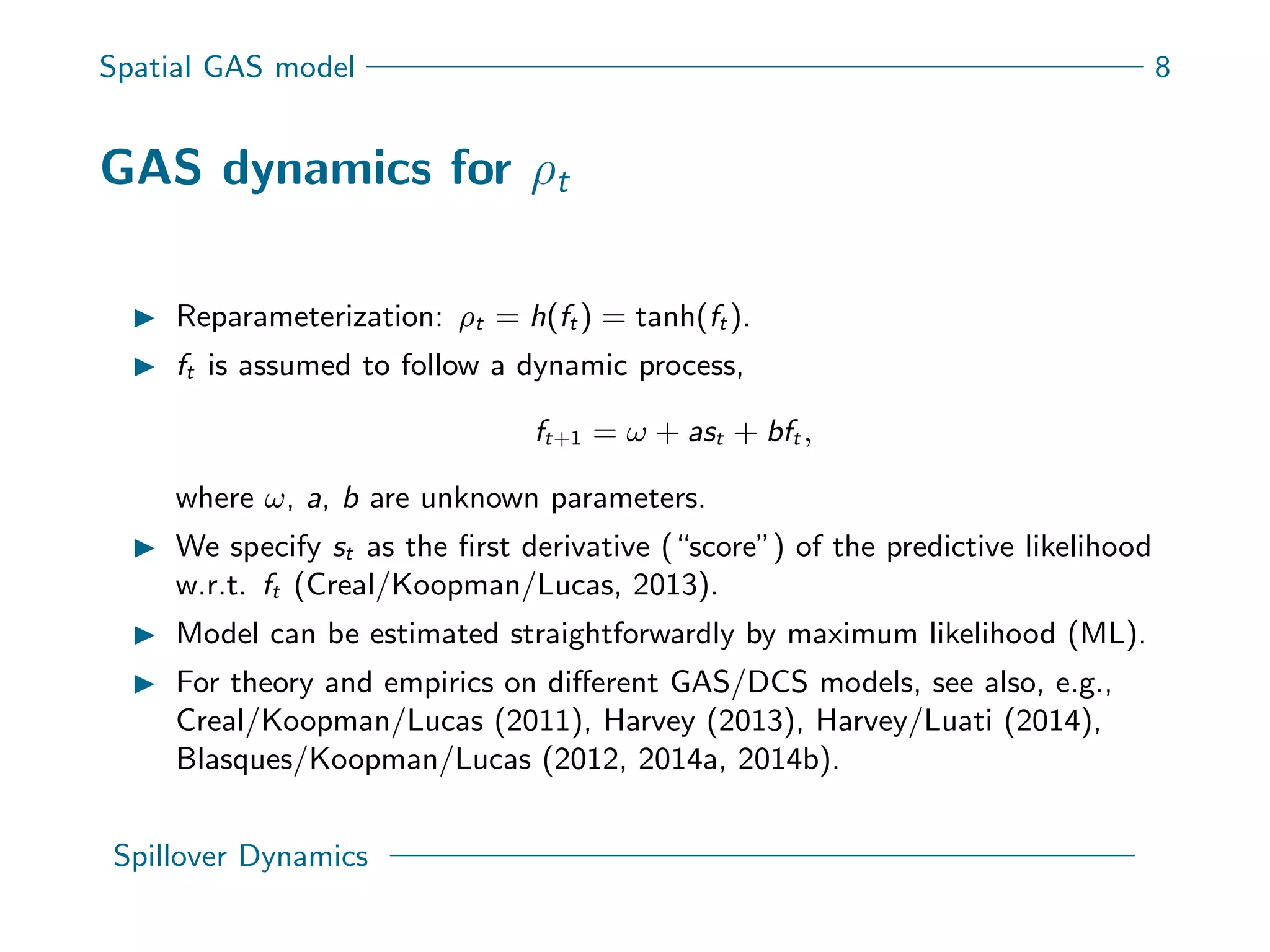
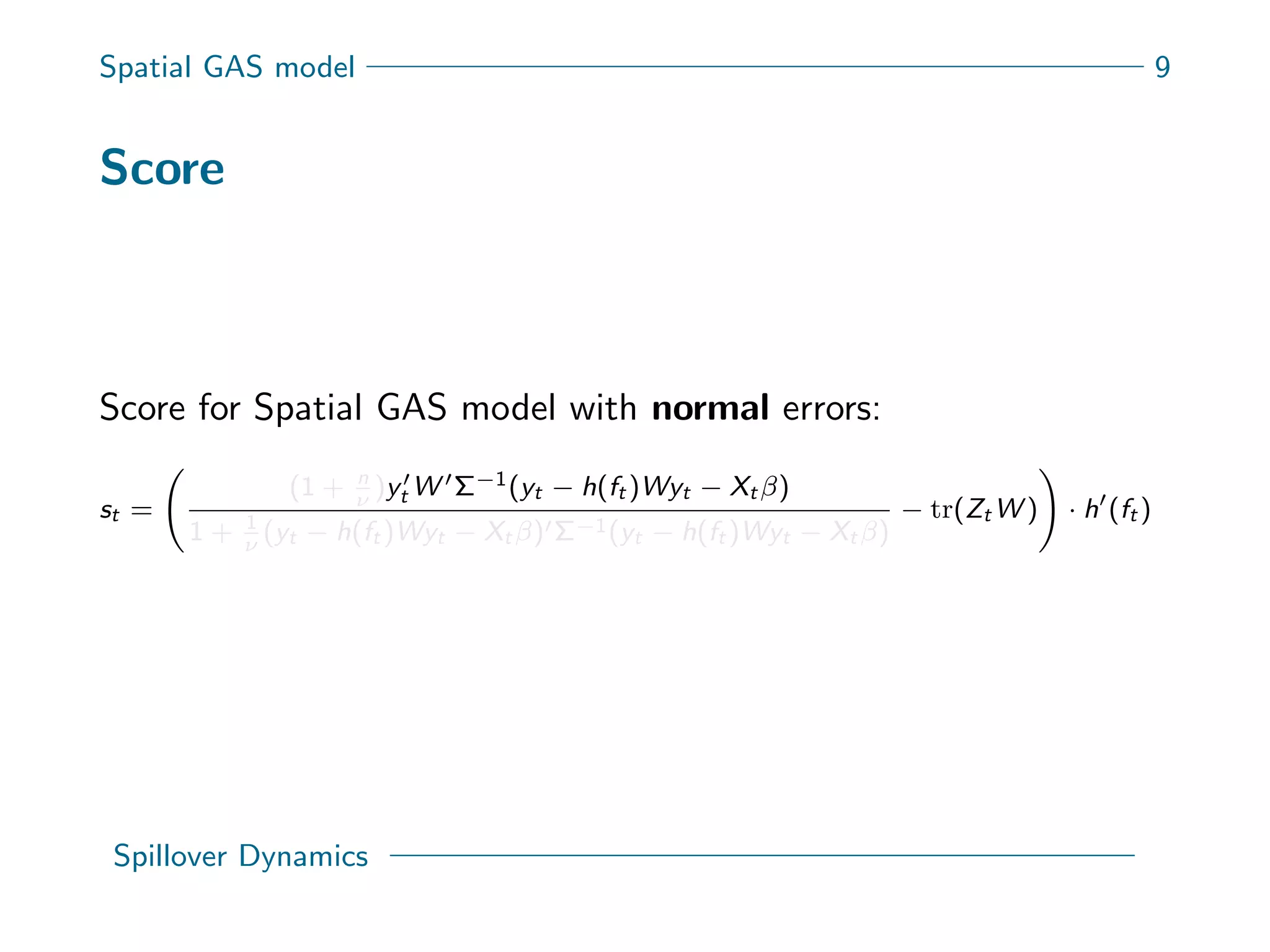
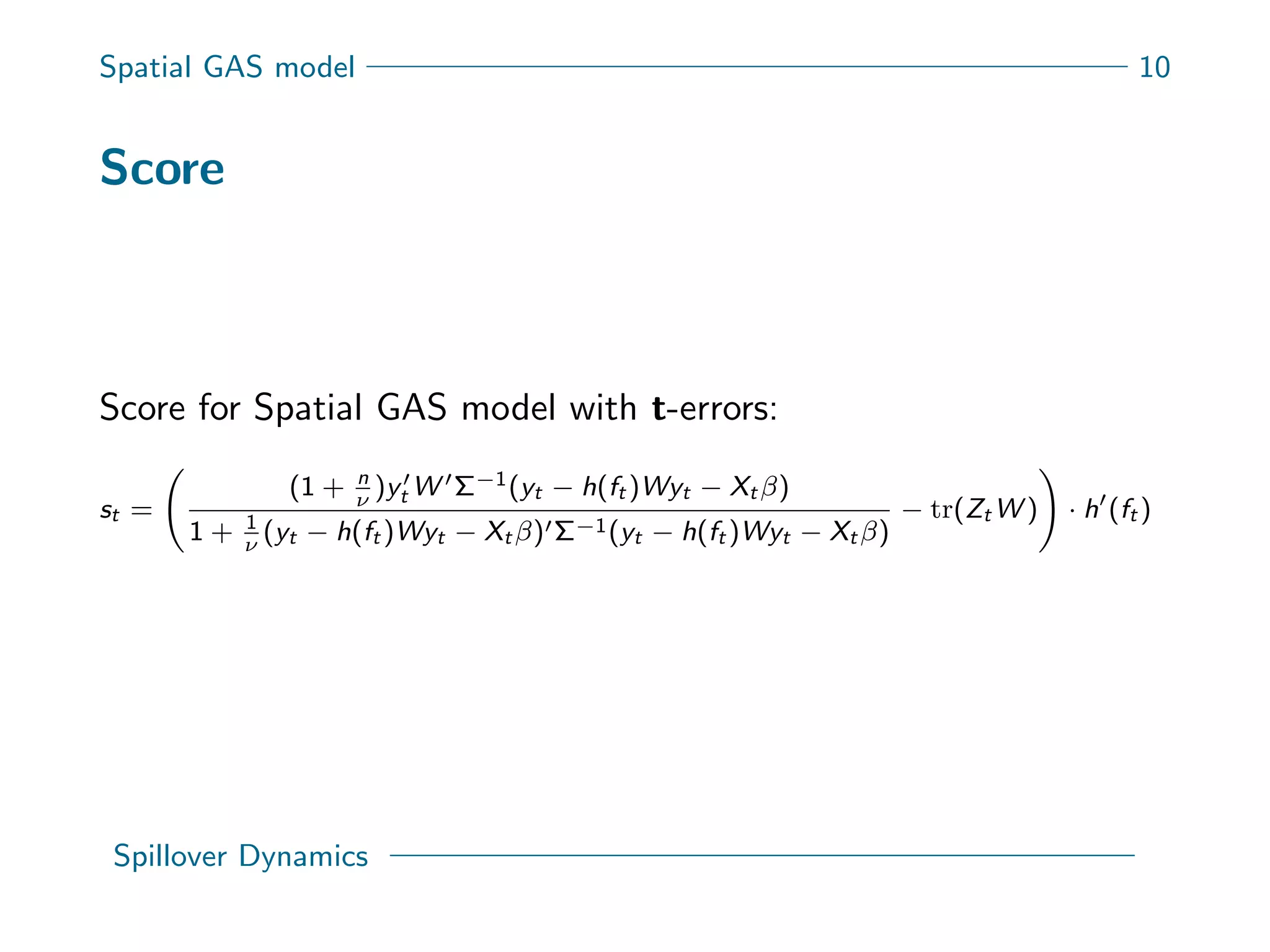
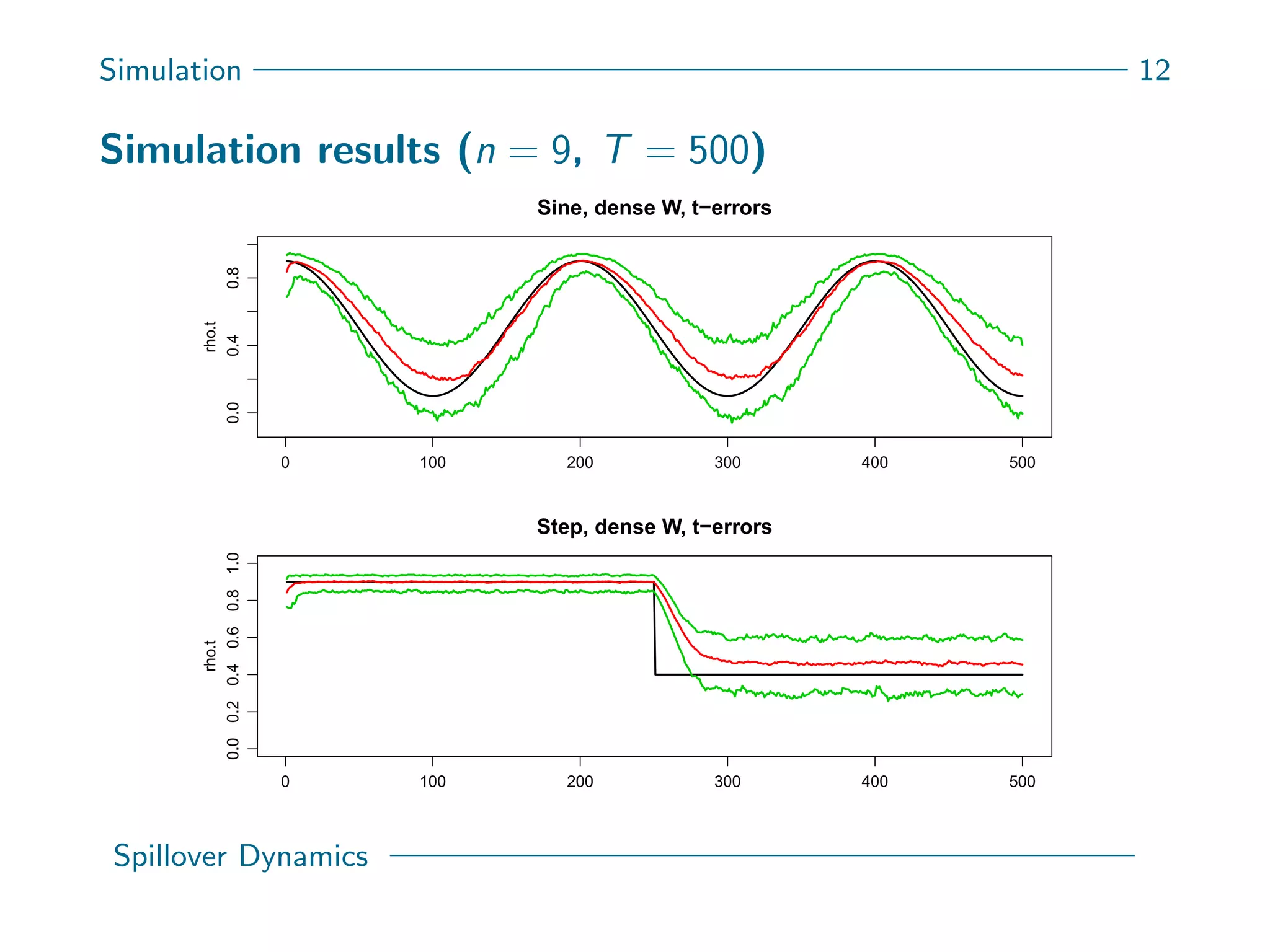
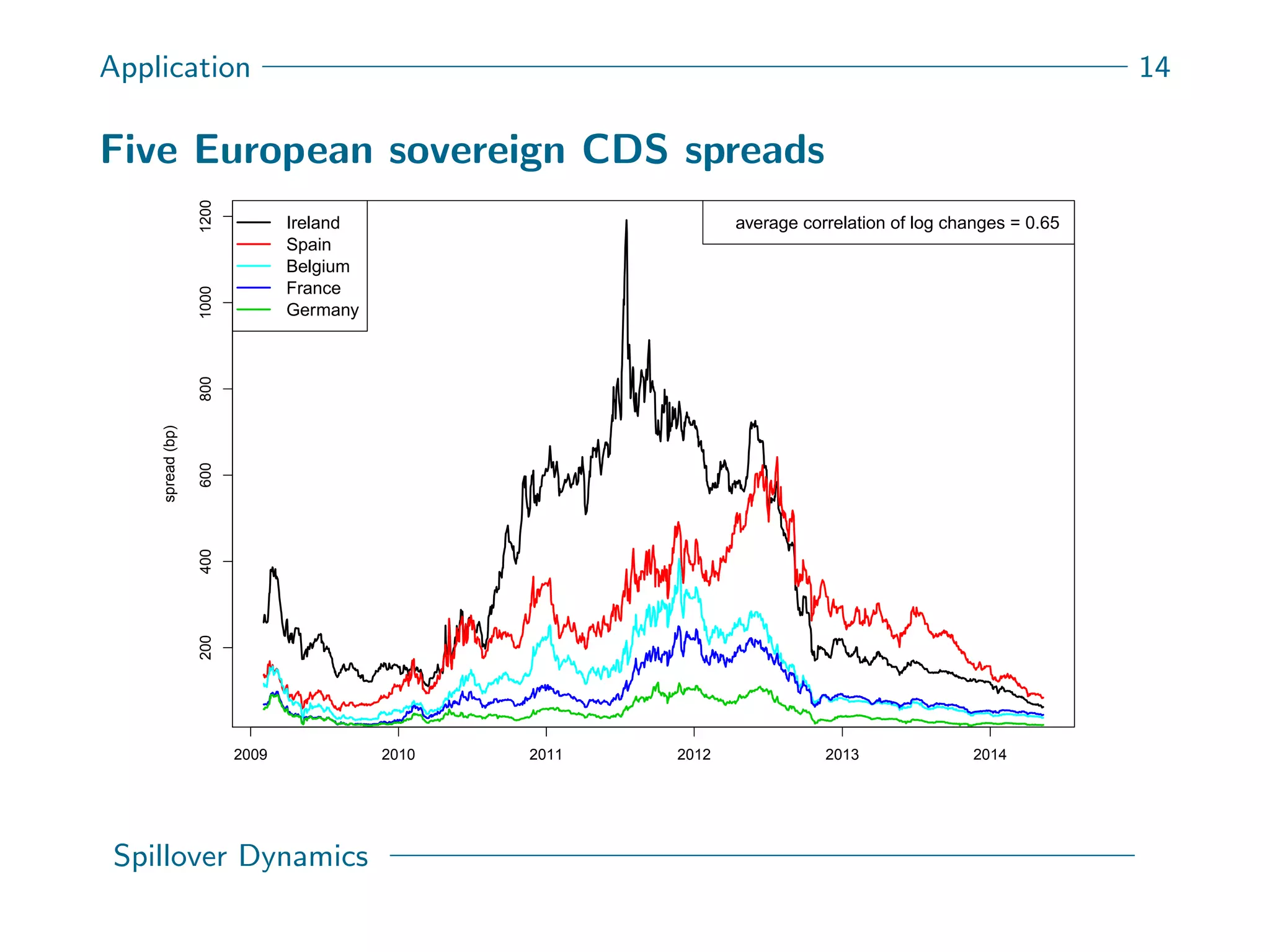
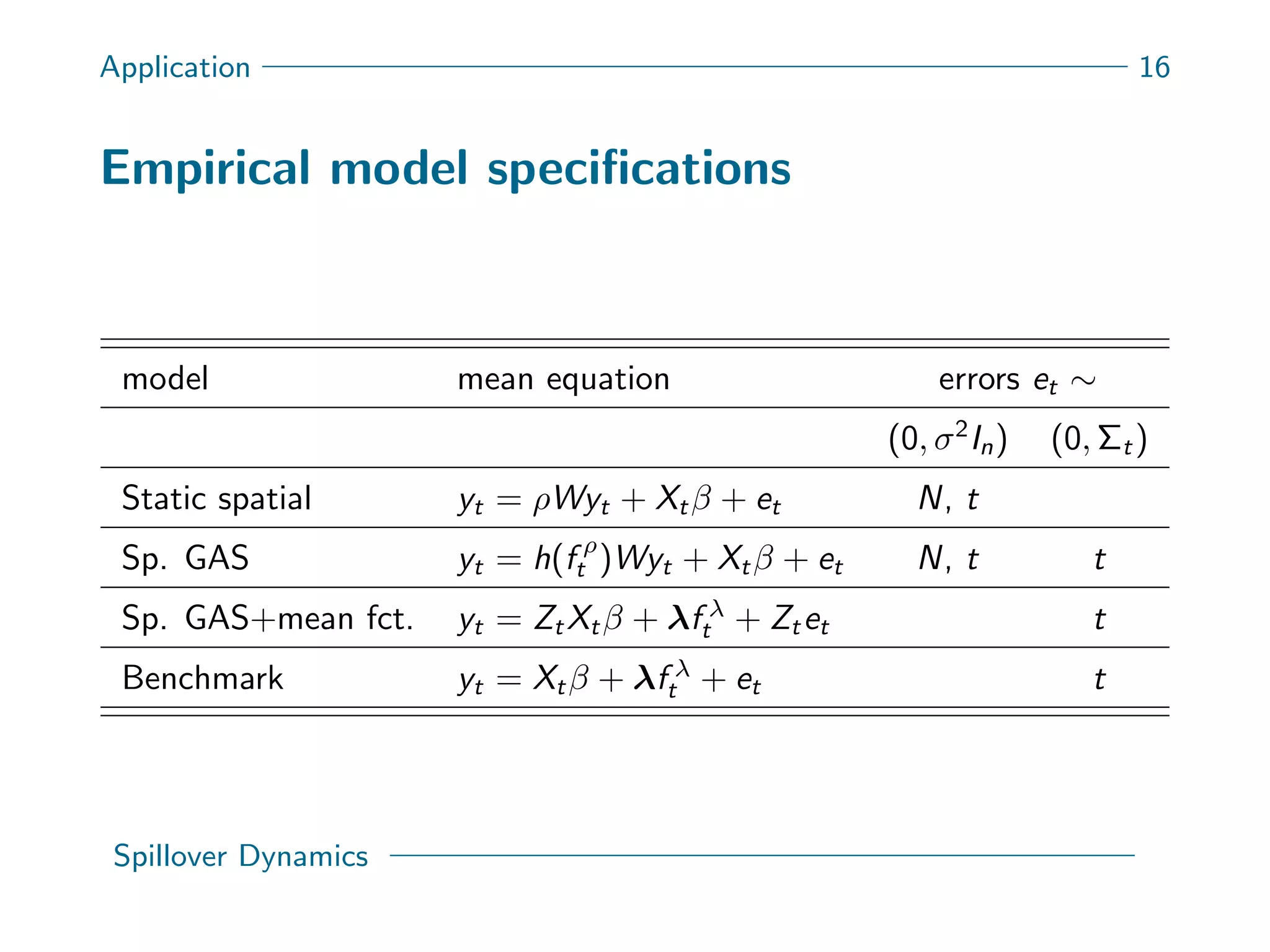
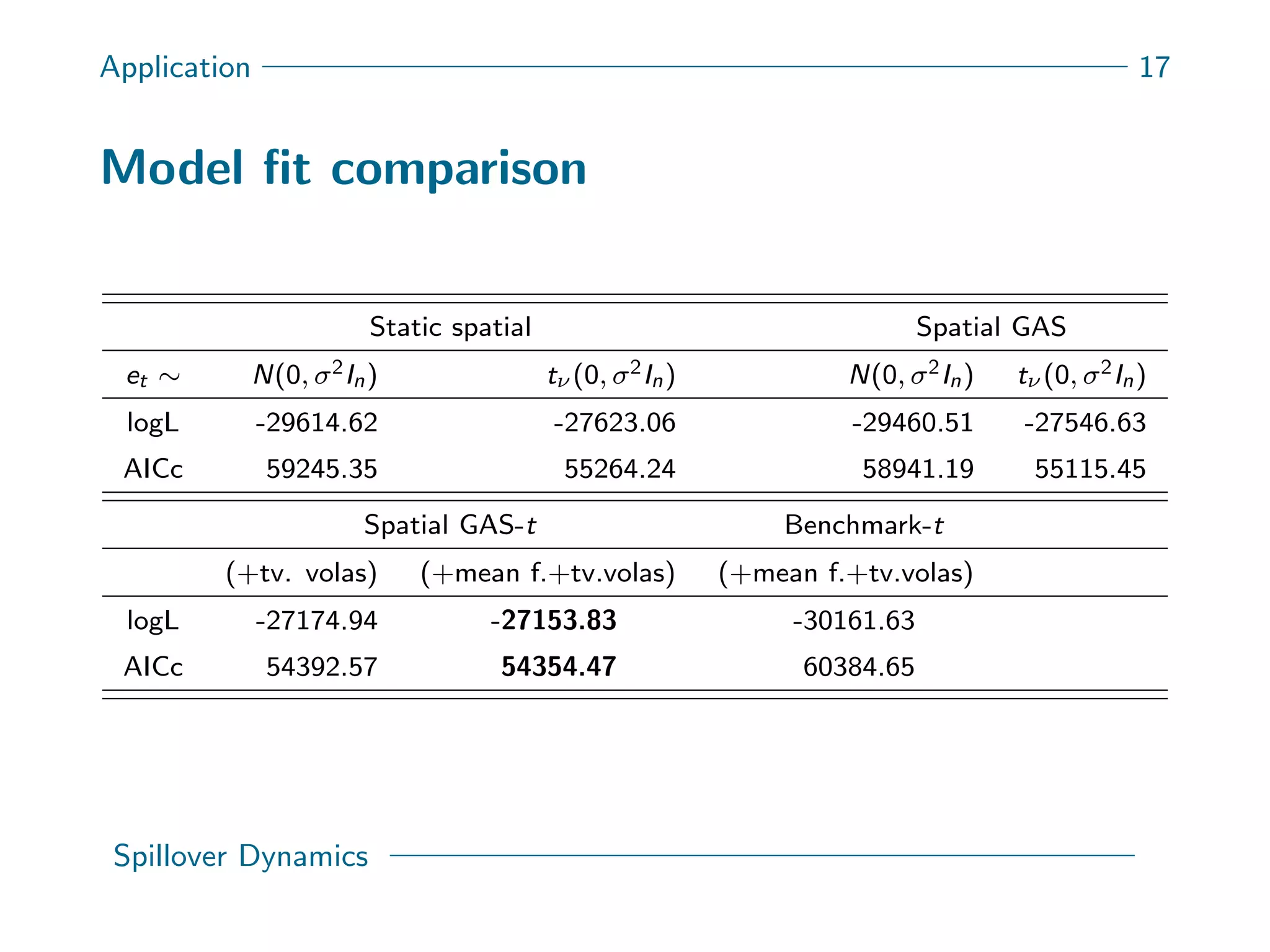
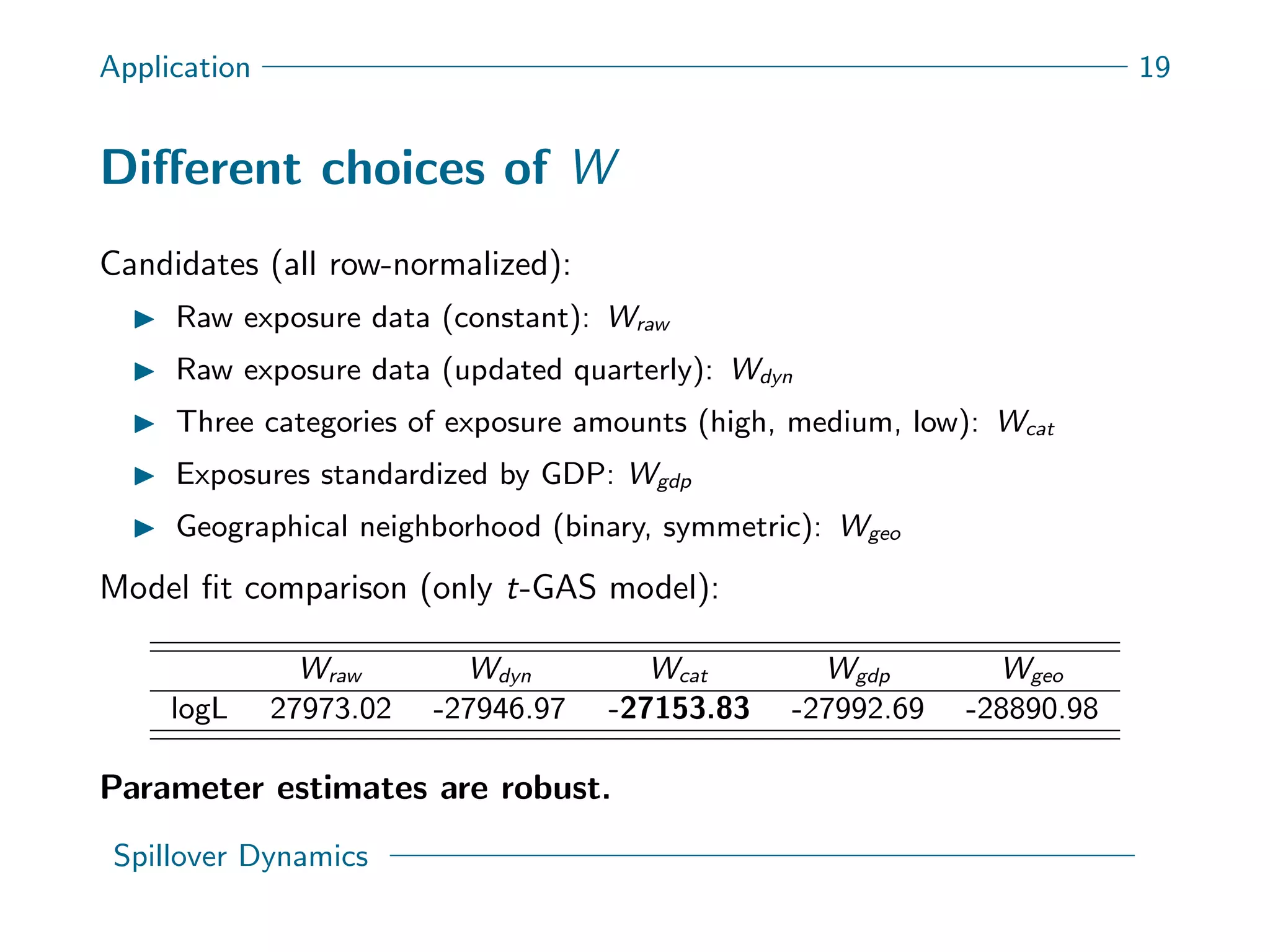
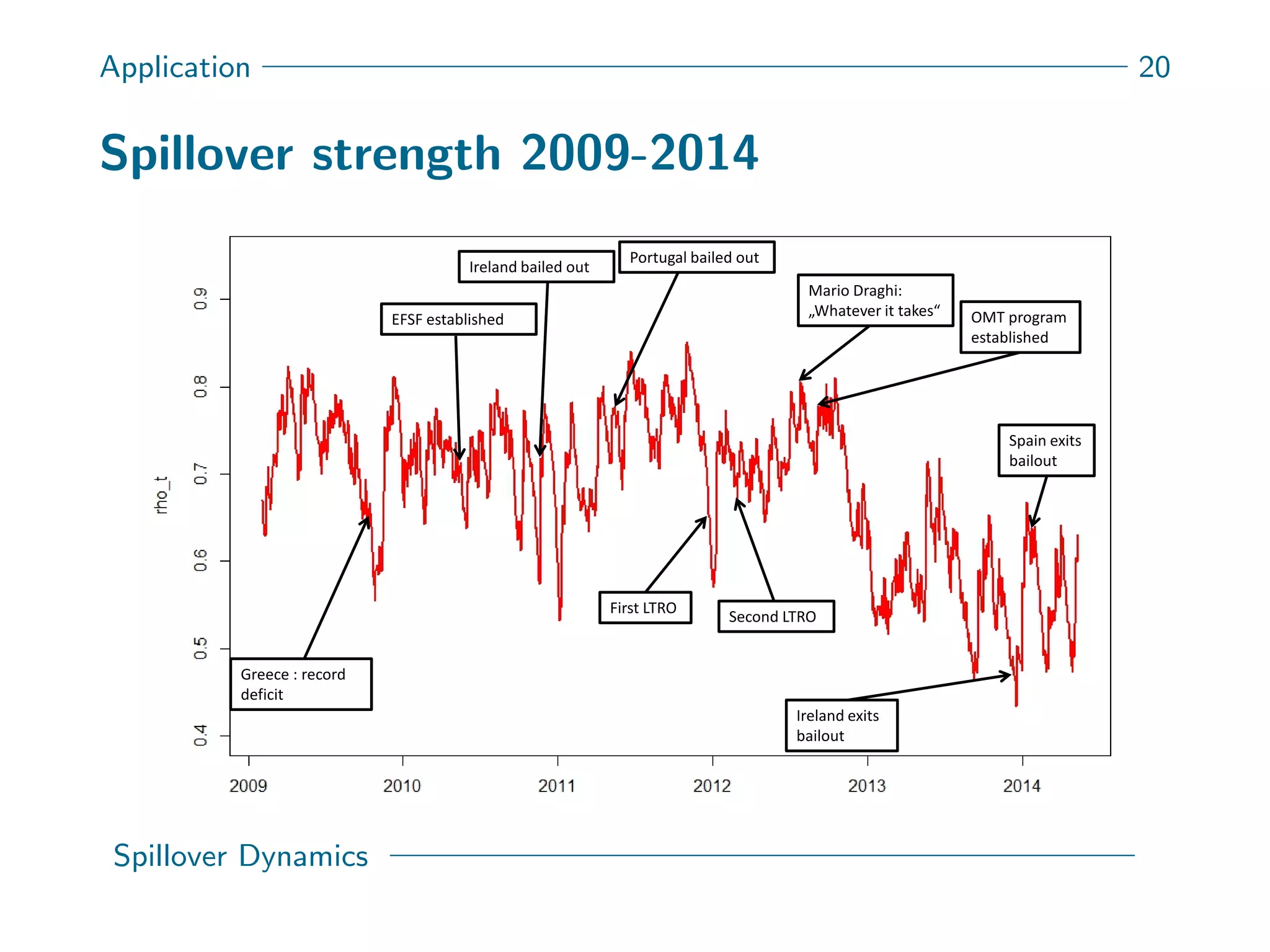
This document presents a new spatial gas model to measure systemic risk in European sovereign credit markets, focusing on spillover dynamics of credit spreads from 2009 to 2014. It incorporates time-varying parameters and fat tails to monitor the effects of policy interventions in the context of financial interconnectedness among European countries. The findings suggest a significant spatial dependence in credit risks and a decrease in systemic risk following government and ECB bailout measures.