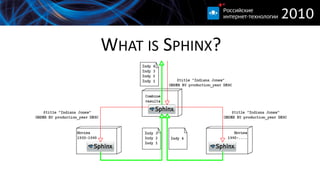
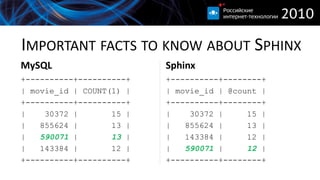
This document discusses improving MySQL application performance with Sphinx. It provides an introduction to Sphinx, describing it as a standalone full-text search engine that can be scaled horizontally and has many features beyond full-text search. It explains that Sphinx indexes data separately from MySQL and must be queried separately, though it can return attribute values to MySQL. The document outlines important facts about MySQL's index usage and limitations, and Sphinx's grouping, attribute storage, and block-based data organization to optimize attribute filtering. It provides an example comparing full-text search performance between MySQL and Sphinx.