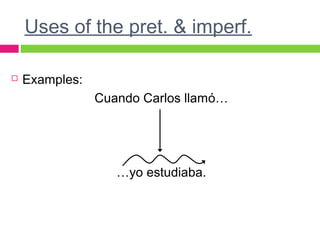
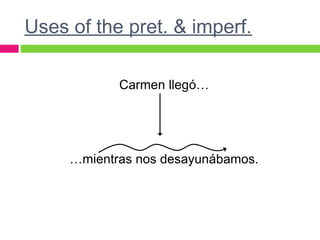
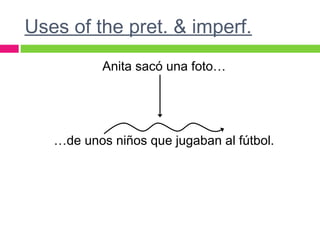
The document discusses the uses of the imperfect and preterite tenses in Spanish. The imperfect is used to describe habitual or repeated past actions, while the preterite describes specific or singular past events. Certain words like "always" or "on Saturdays" indicate the imperfect, while words like "once" or "last Saturday" indicate the preterite. The imperfect also describes ongoing circumstances in the past.