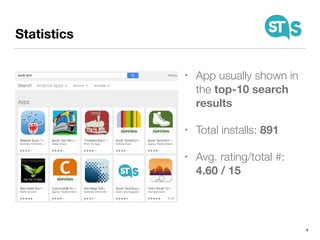
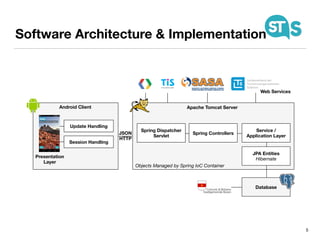
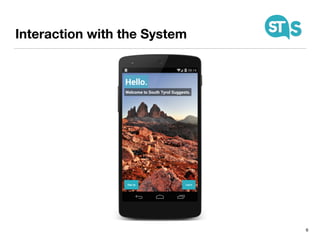
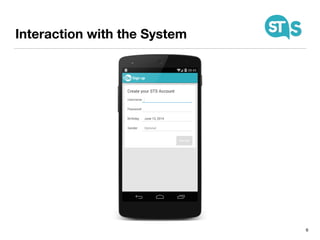
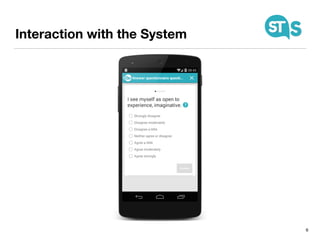
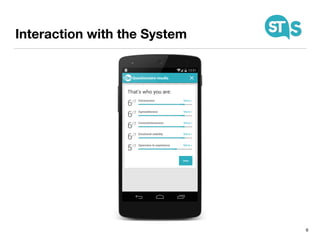
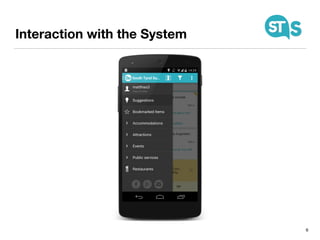
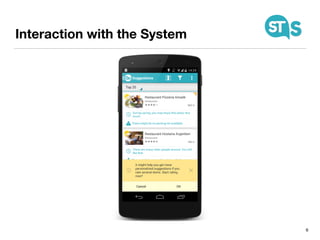
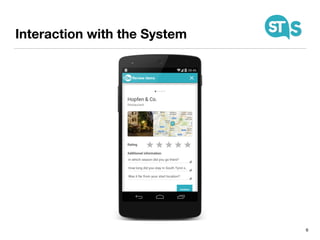
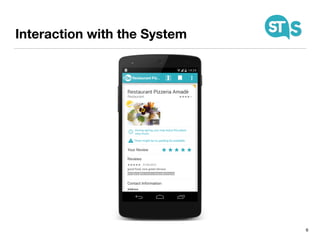
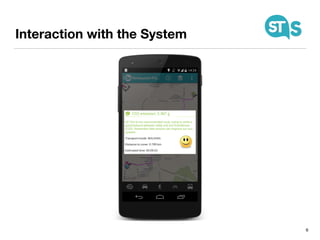
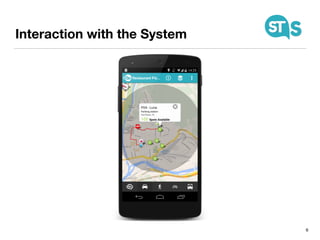
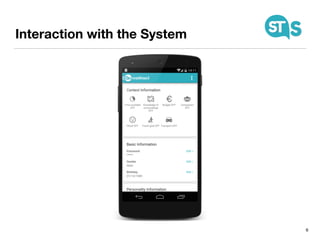
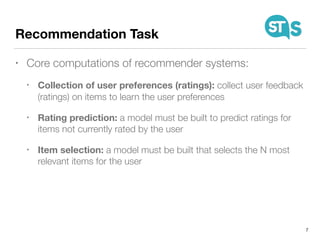
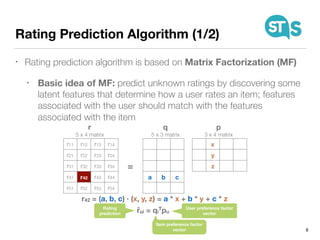
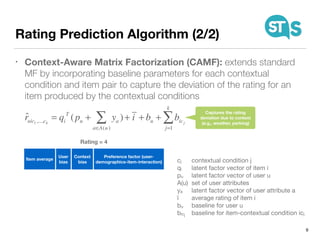
The document details the South Tyrol Suggests app, which provides intelligent recommendations for points of interest (POIs) in South Tyrol based on user context. The app features include eco-friendly routing, user preference elicitation, and utilizes a matrix factorization algorithm for rating predictions tailored to contextual conditions. User studies indicate that the app enhances perceived recommendation quality and user satisfaction, with plans for future feature enhancements such as multimodal routing and integration with wearable devices.