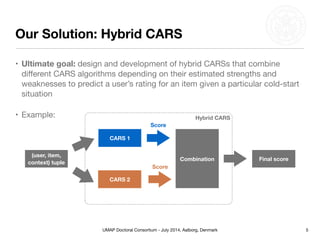
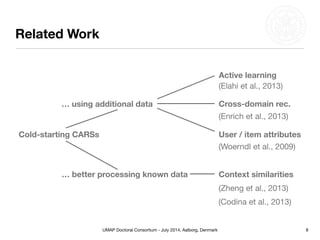
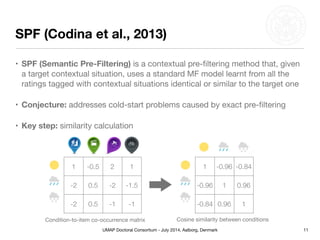
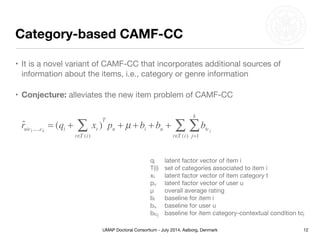
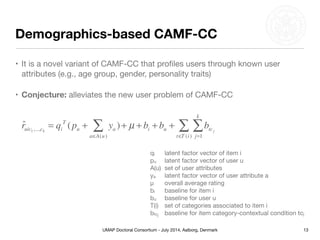
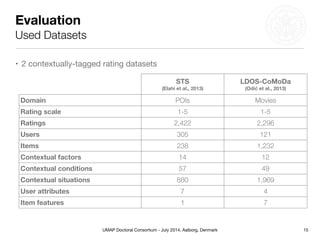
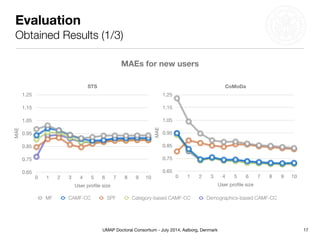
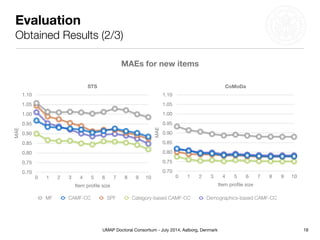
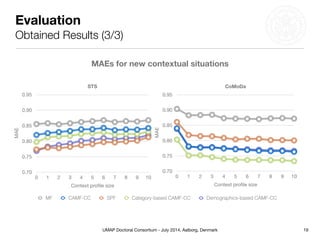
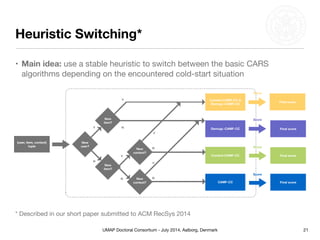
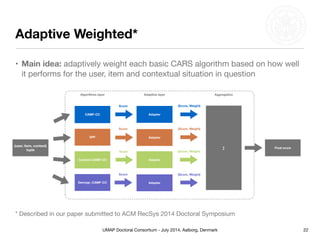
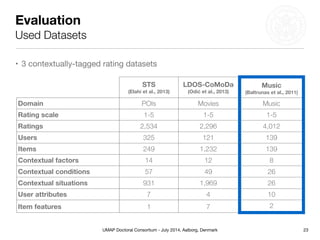
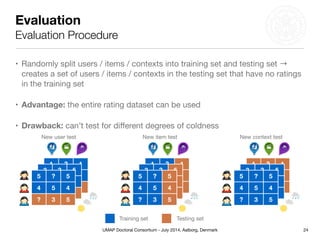
This document summarizes Matthias Braunhofer's doctoral research on addressing the cold-start problem in context-aware recommender systems. It presents basic context-aware rating prediction models like CAMF-CC and SPF, and proposes novel variants that incorporate additional contextual information like item categories or user demographics. It also describes two approaches to building hybrid context-aware recommender systems - heuristic switching and adaptive weighting. An evaluation compares the performance of these models on three datasets in addressing new user, new item, and new context cold-start situations, finding that hybrid models generally outperform basic models.