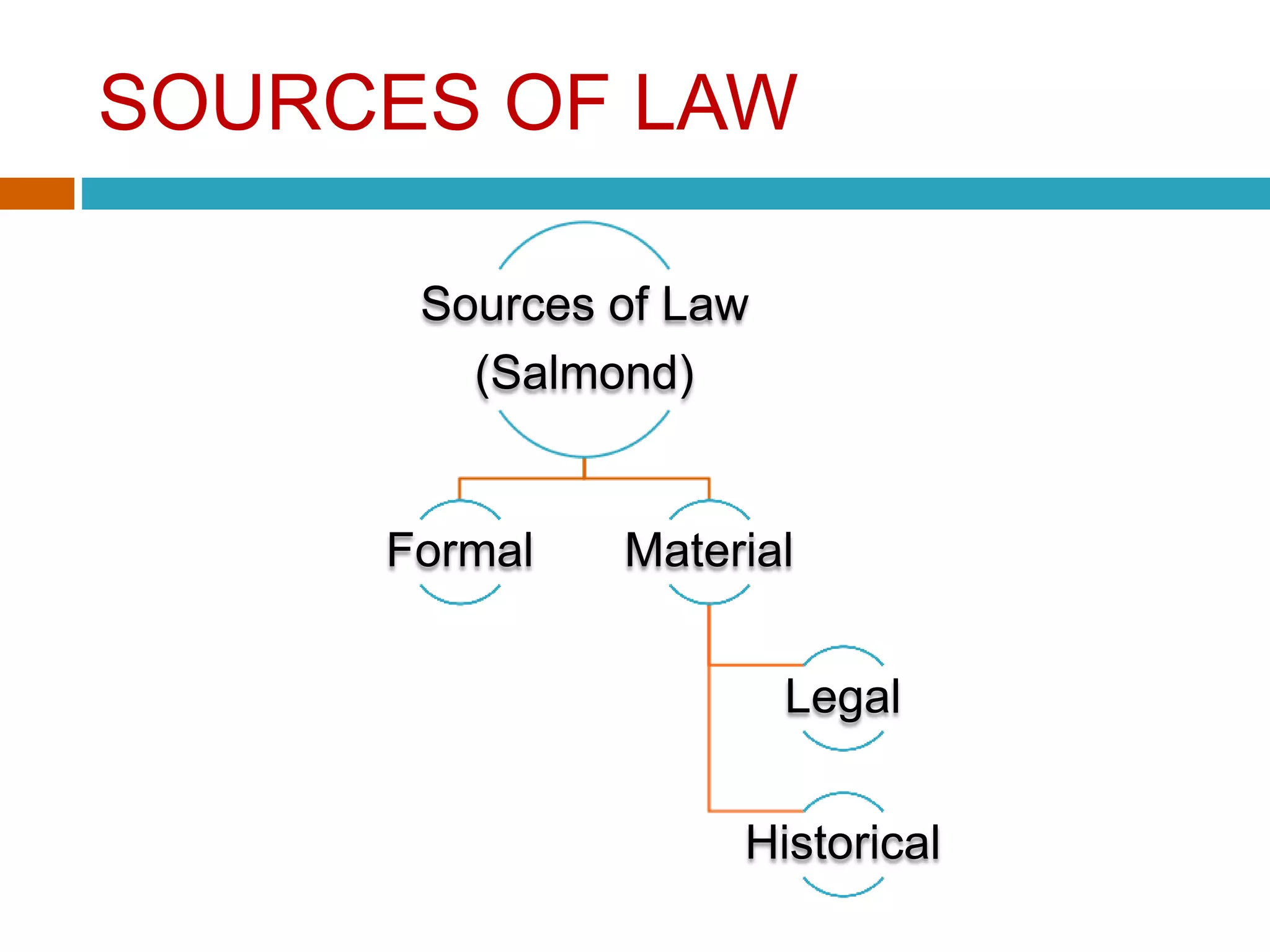
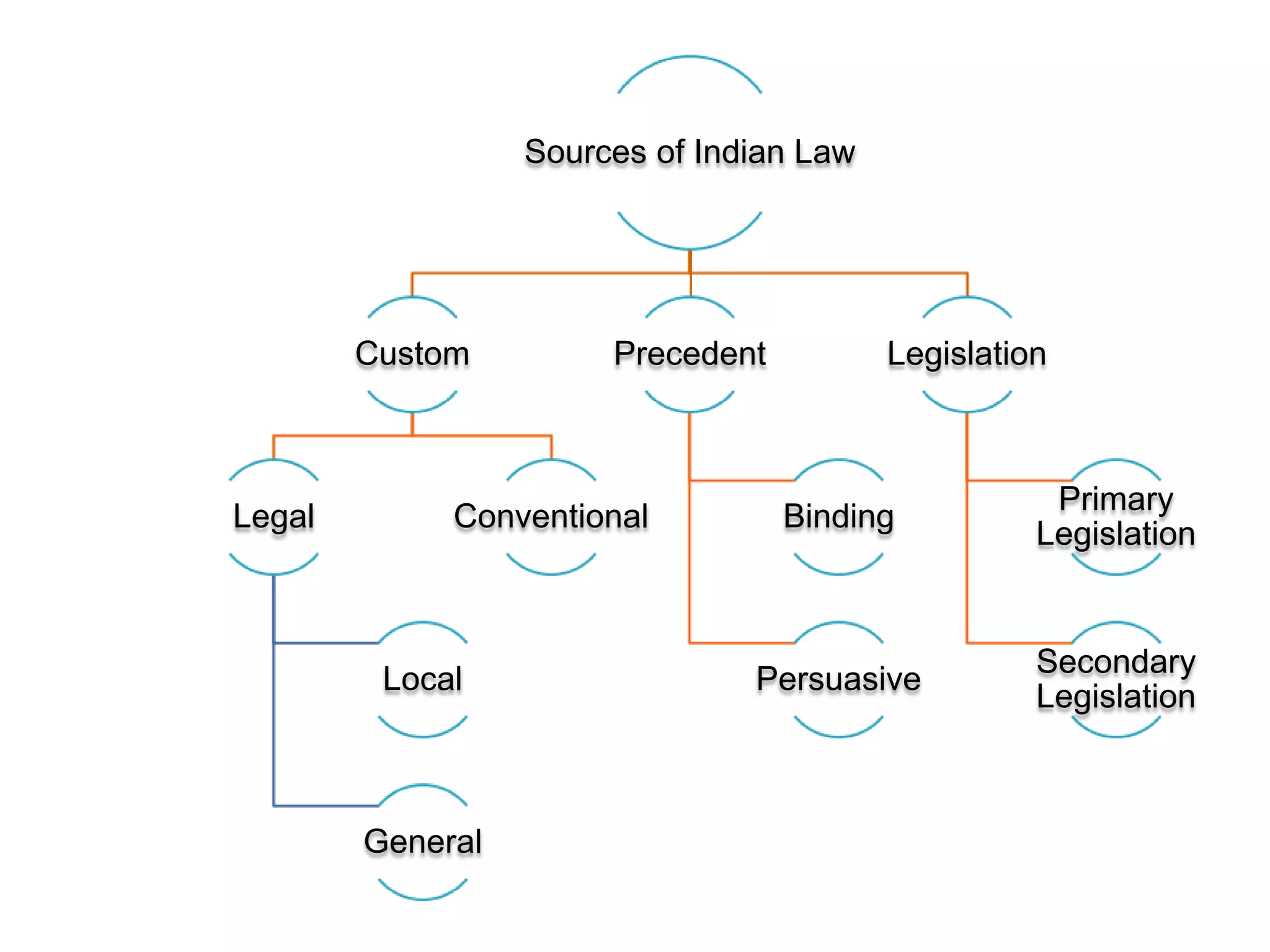
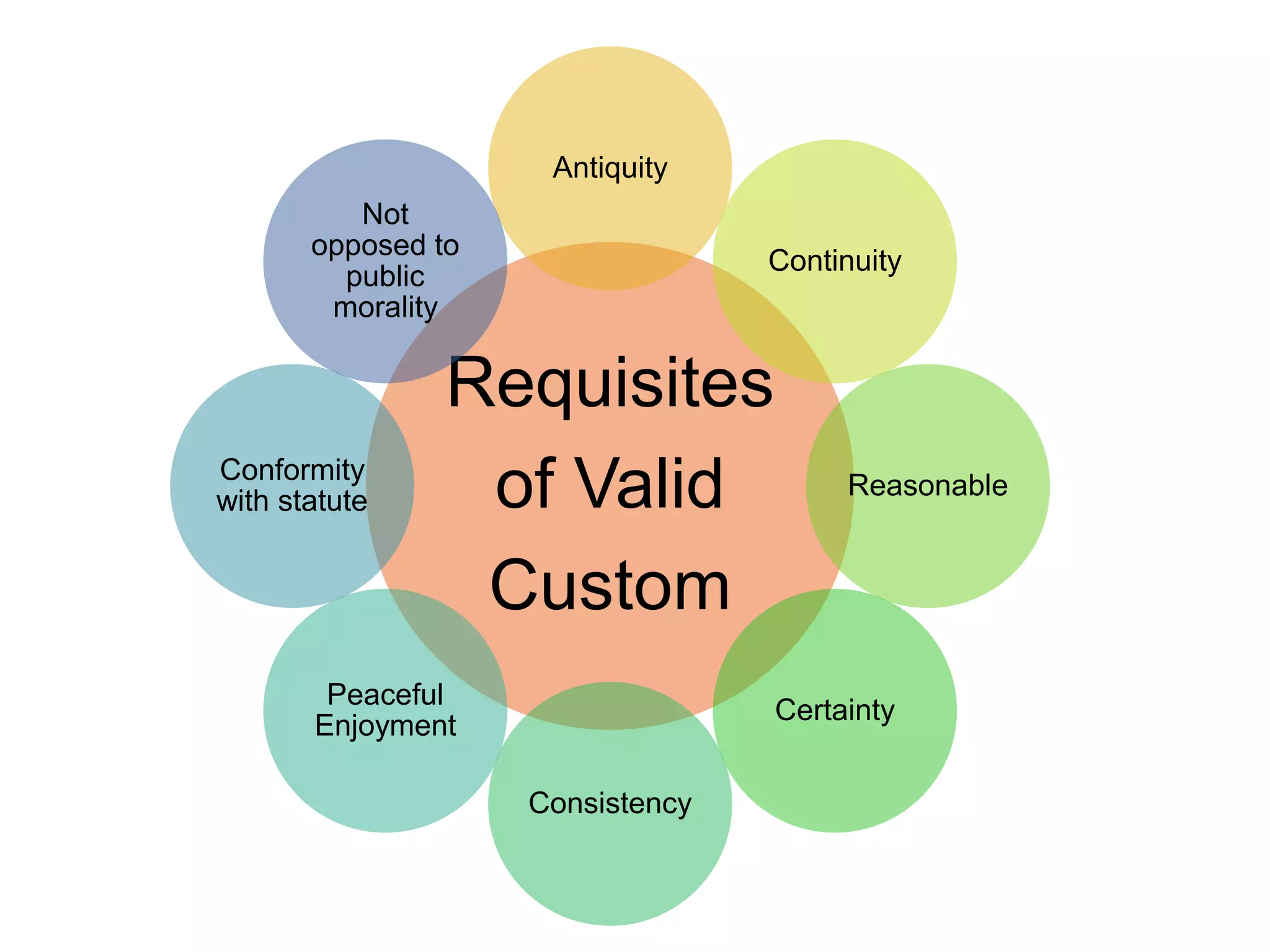
The document discusses the various sources of law in India, including custom, precedent, and legislation. It outlines the requisites for a valid custom, including antiquity, continuity, reasonableness, certainty, consistency, peaceful enjoyment, conformity with statute law, and not being opposed to public morality. It also describes different types of precedents such as original, declaratory, authoritative, and persuasive precedents. Finally, it provides a brief overview of legislation, defining it as laws made by a legislative body and classifying legislation as either supreme or subordinate.