- The document is a program for a conference on JAX-RS and Java EE 6 held in 2010.
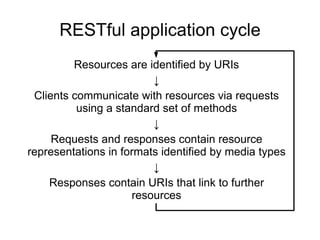
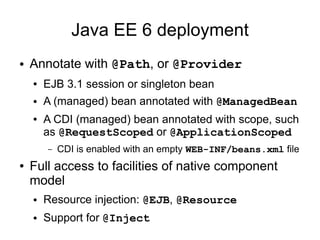
- The keynote speaker Paul Sandoz will give a presentation on JAX-RS, the Java API for RESTful Web Services, and its role in Java EE 6.
- The agenda lists several sessions on topics related to JAX-RS, mobile development, agile practices and more running throughout the day.