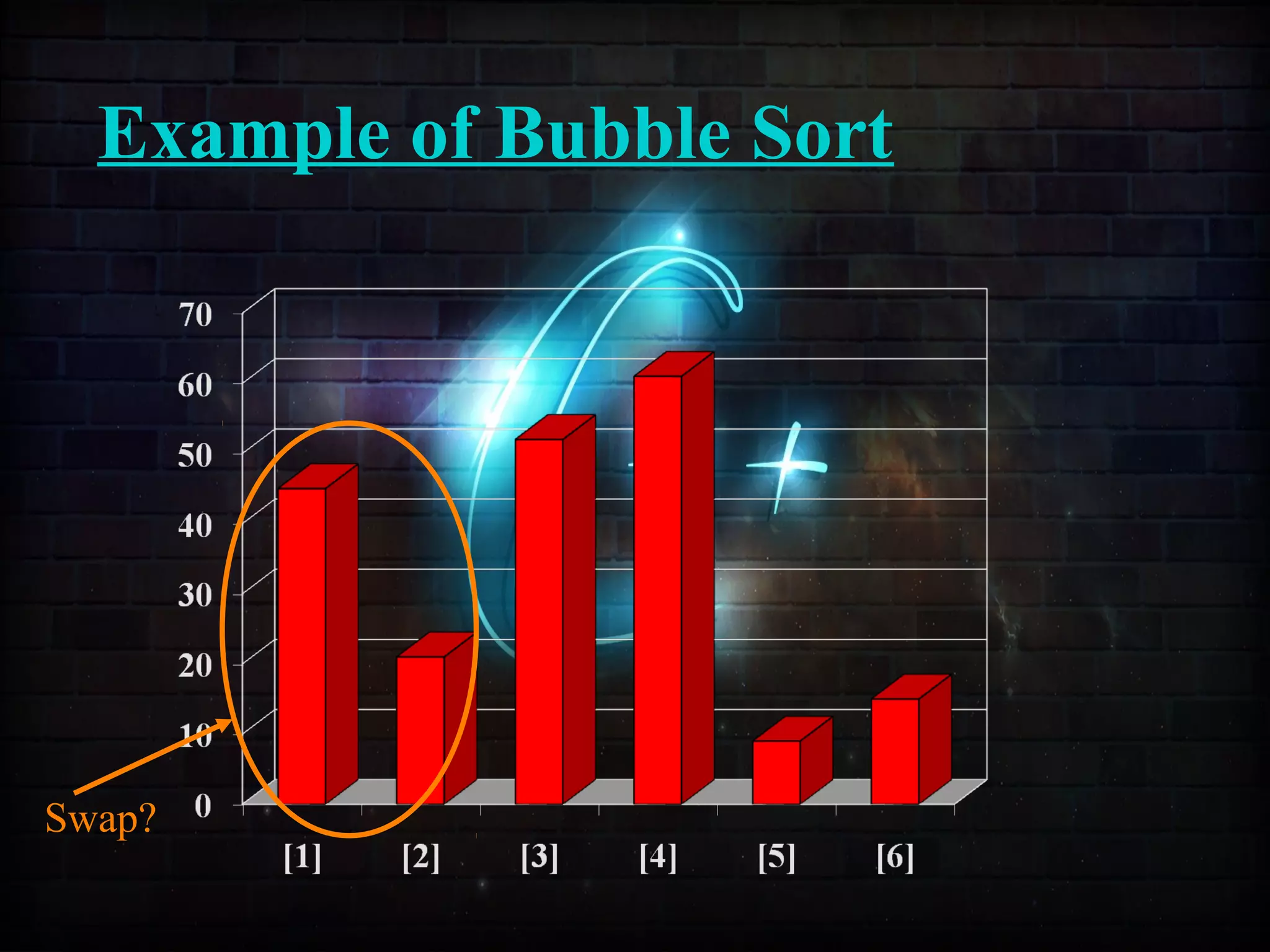
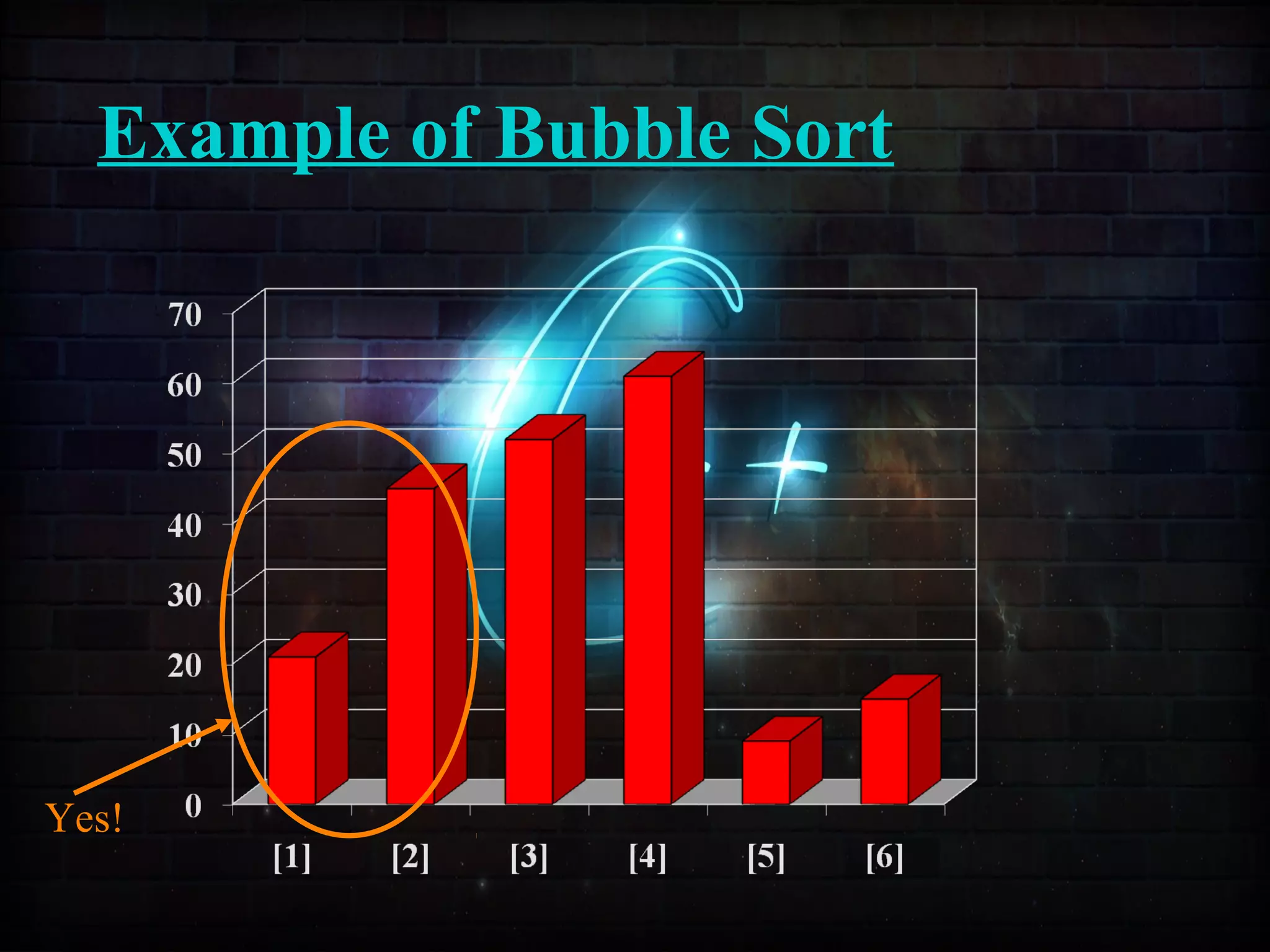
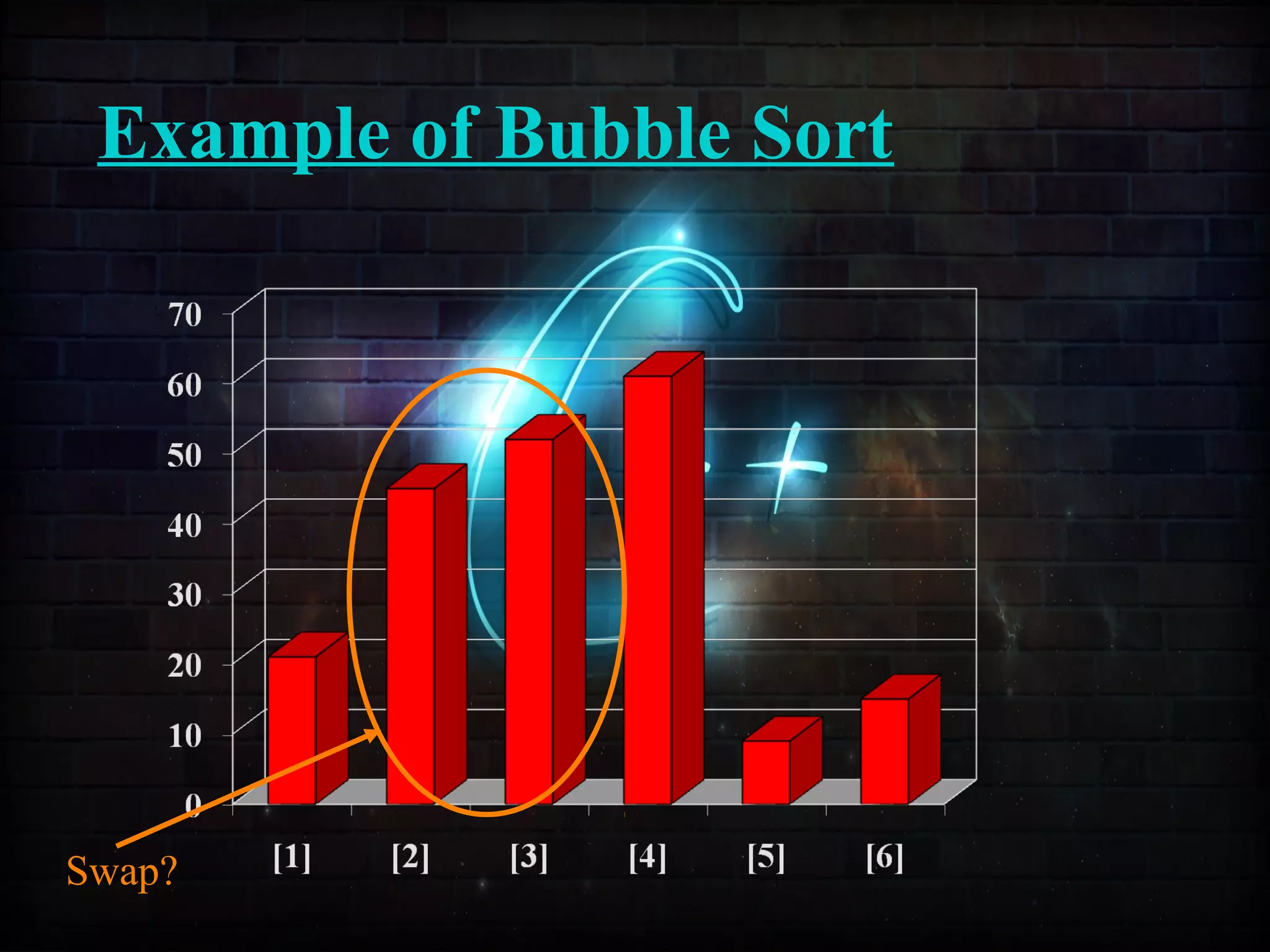
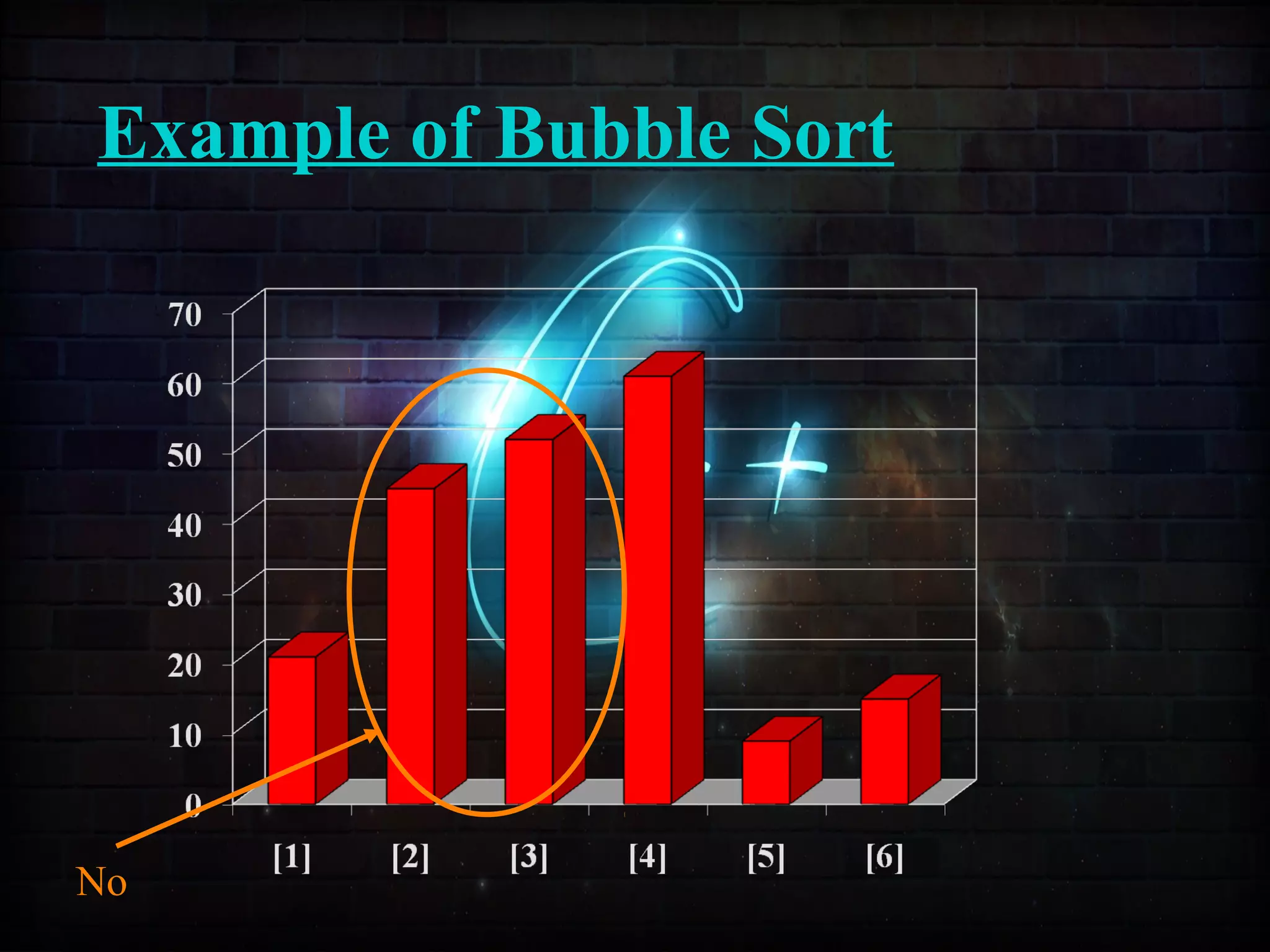
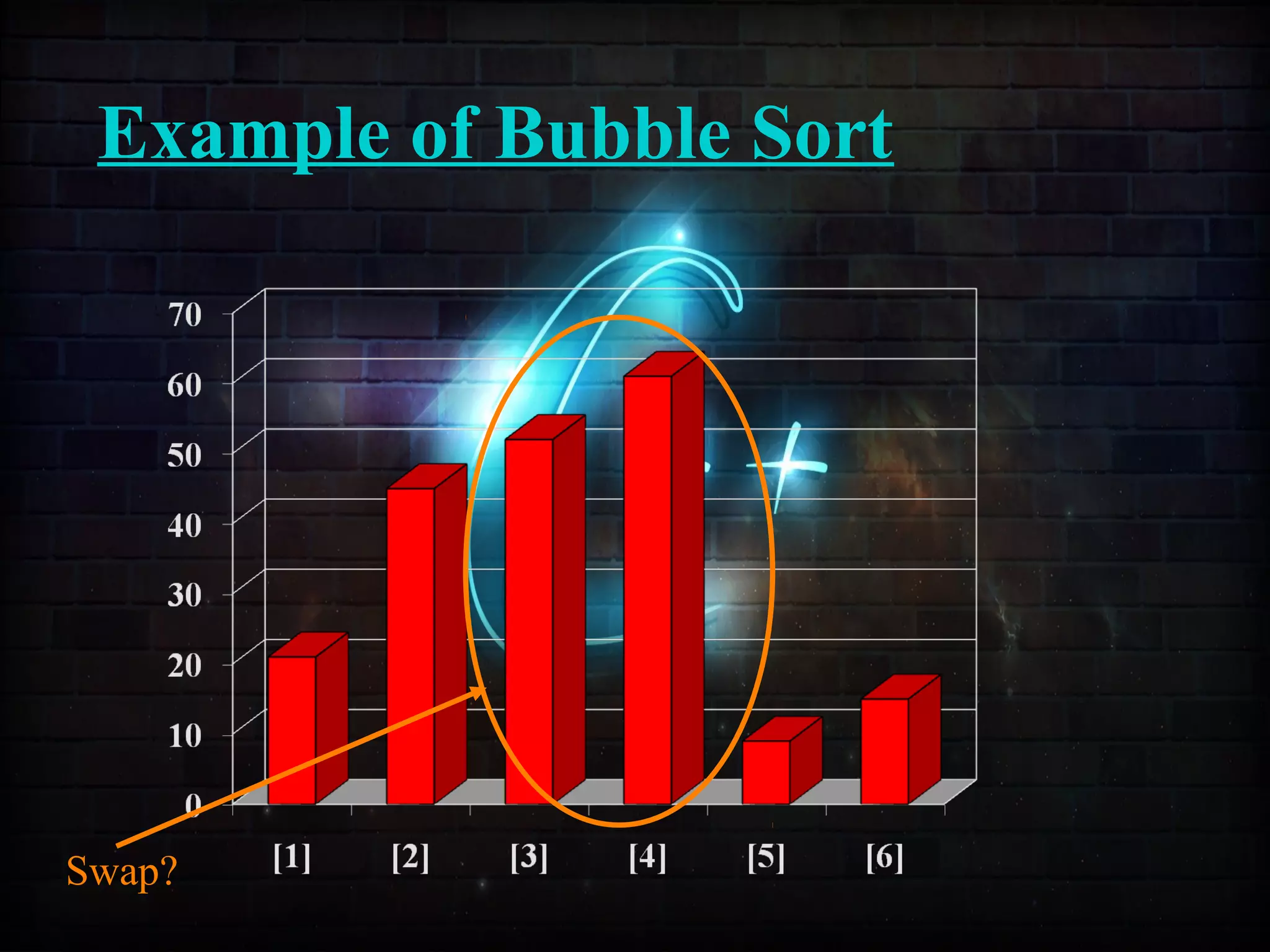
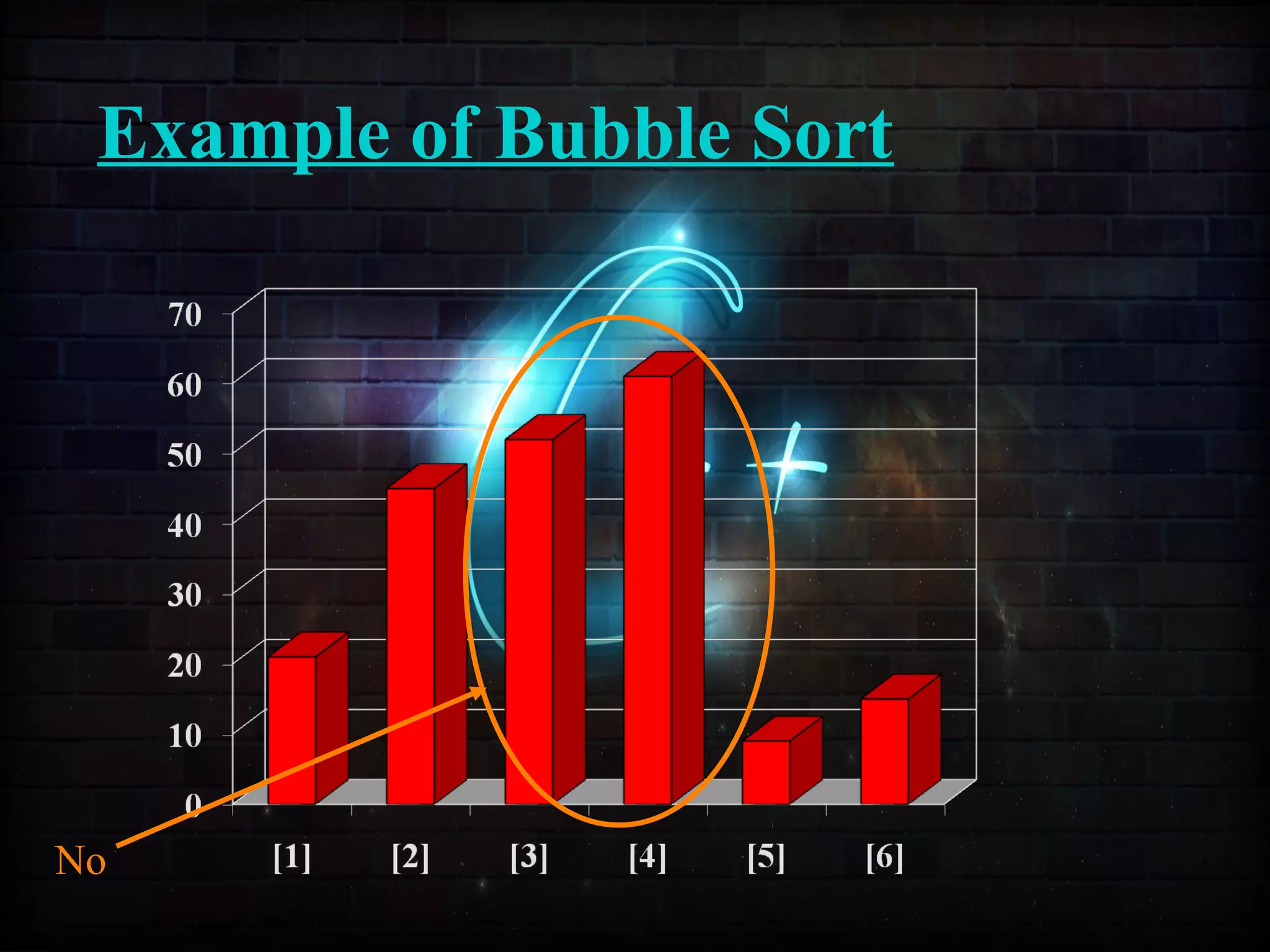
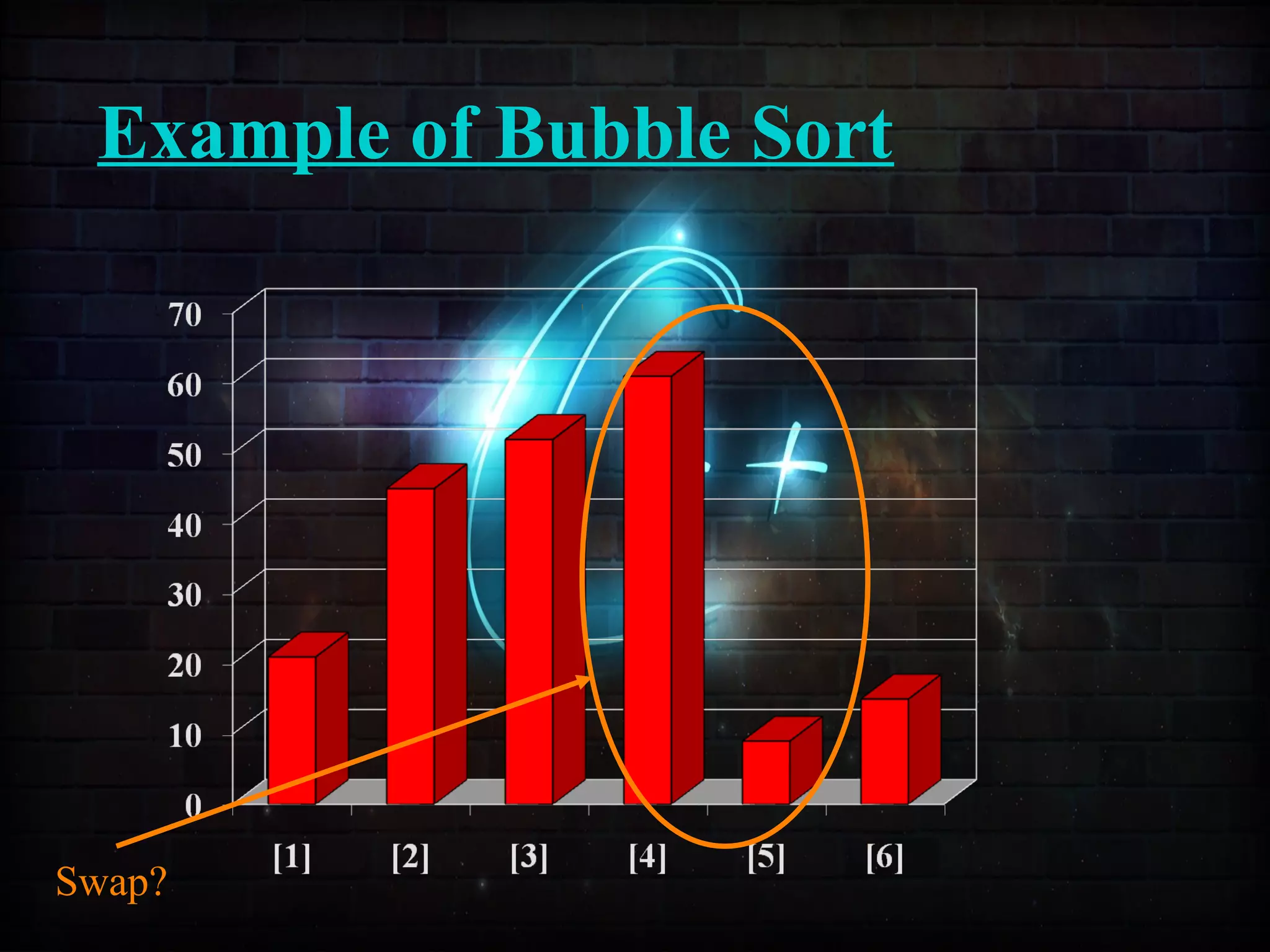
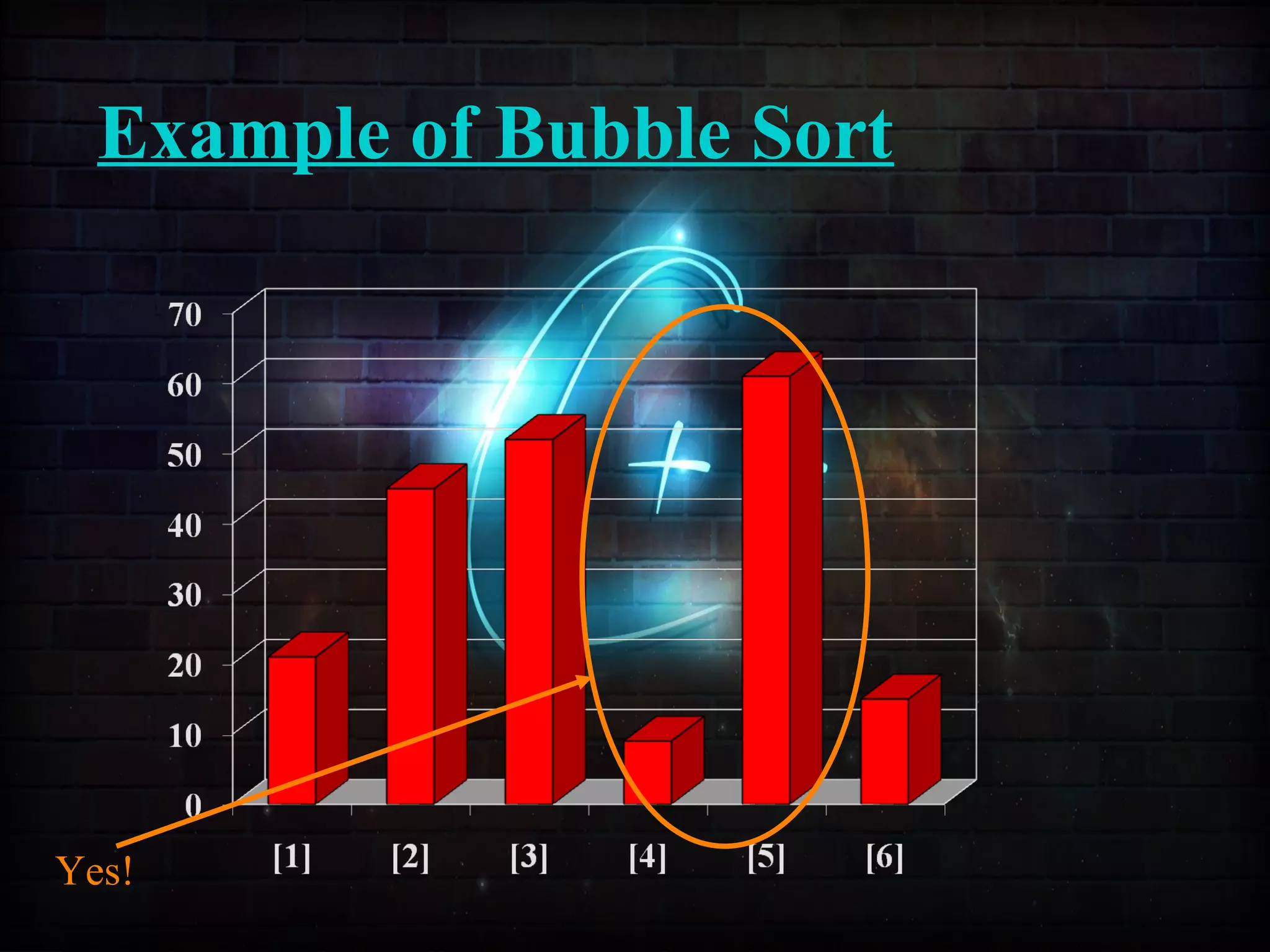
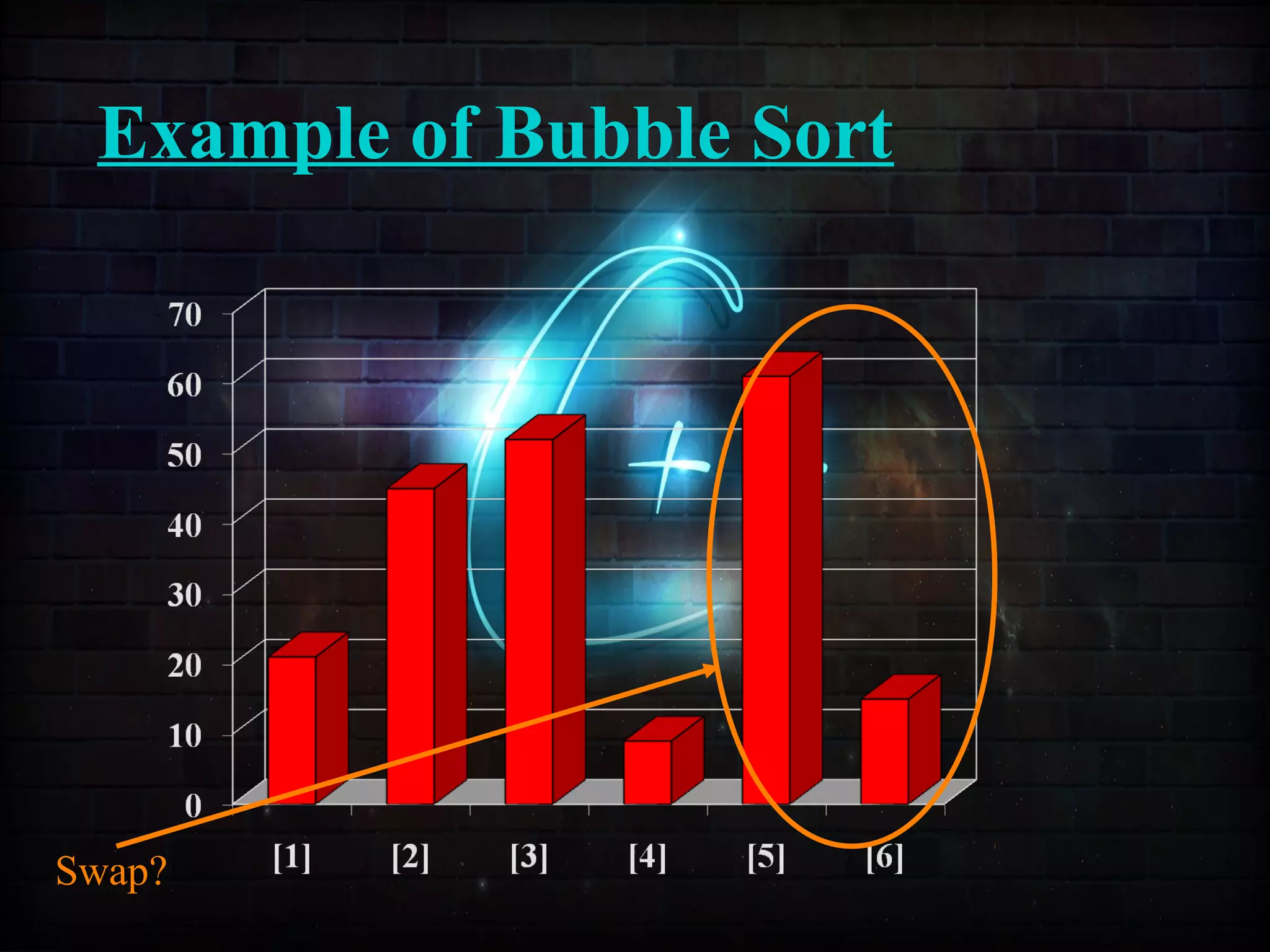
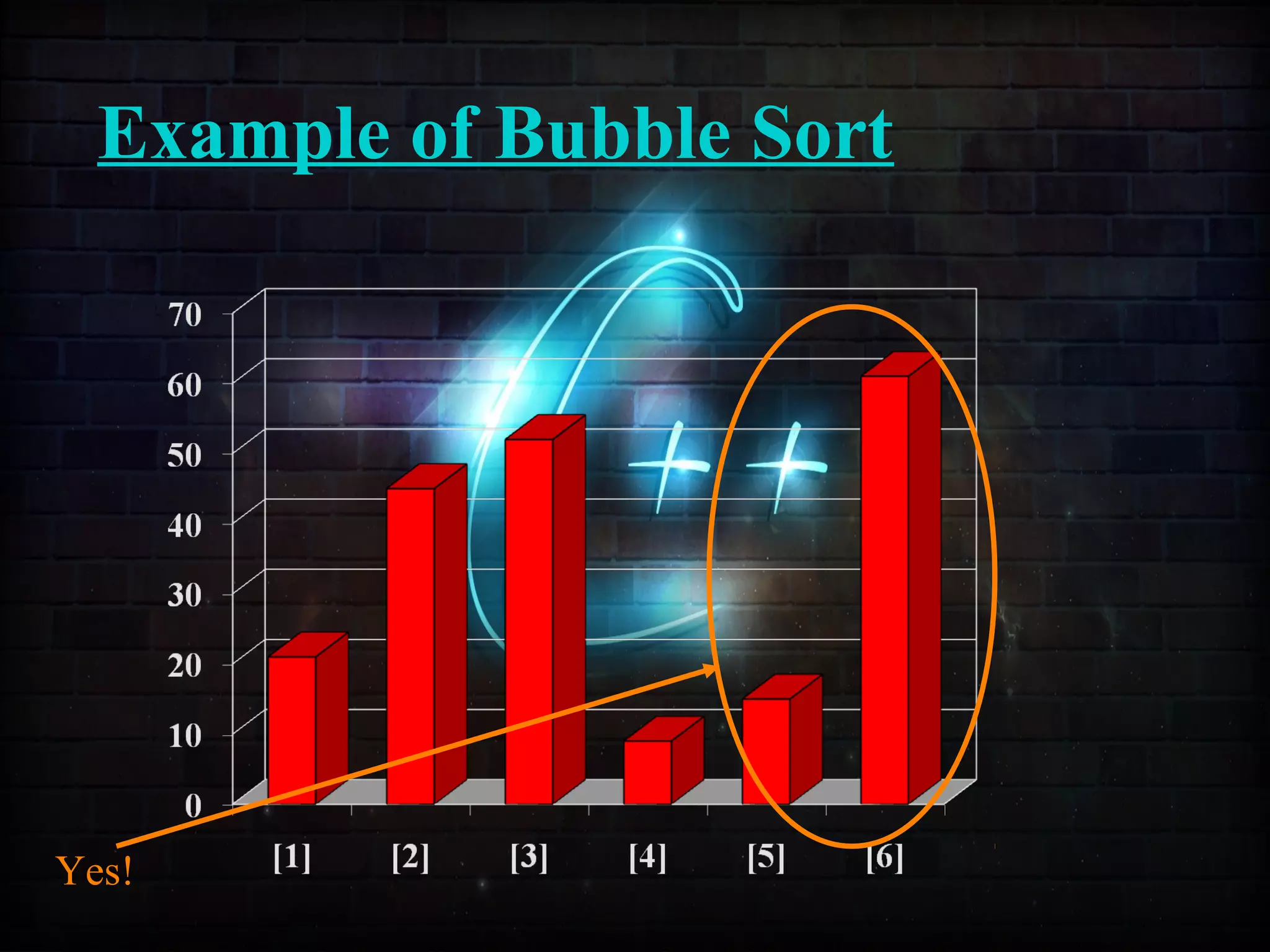
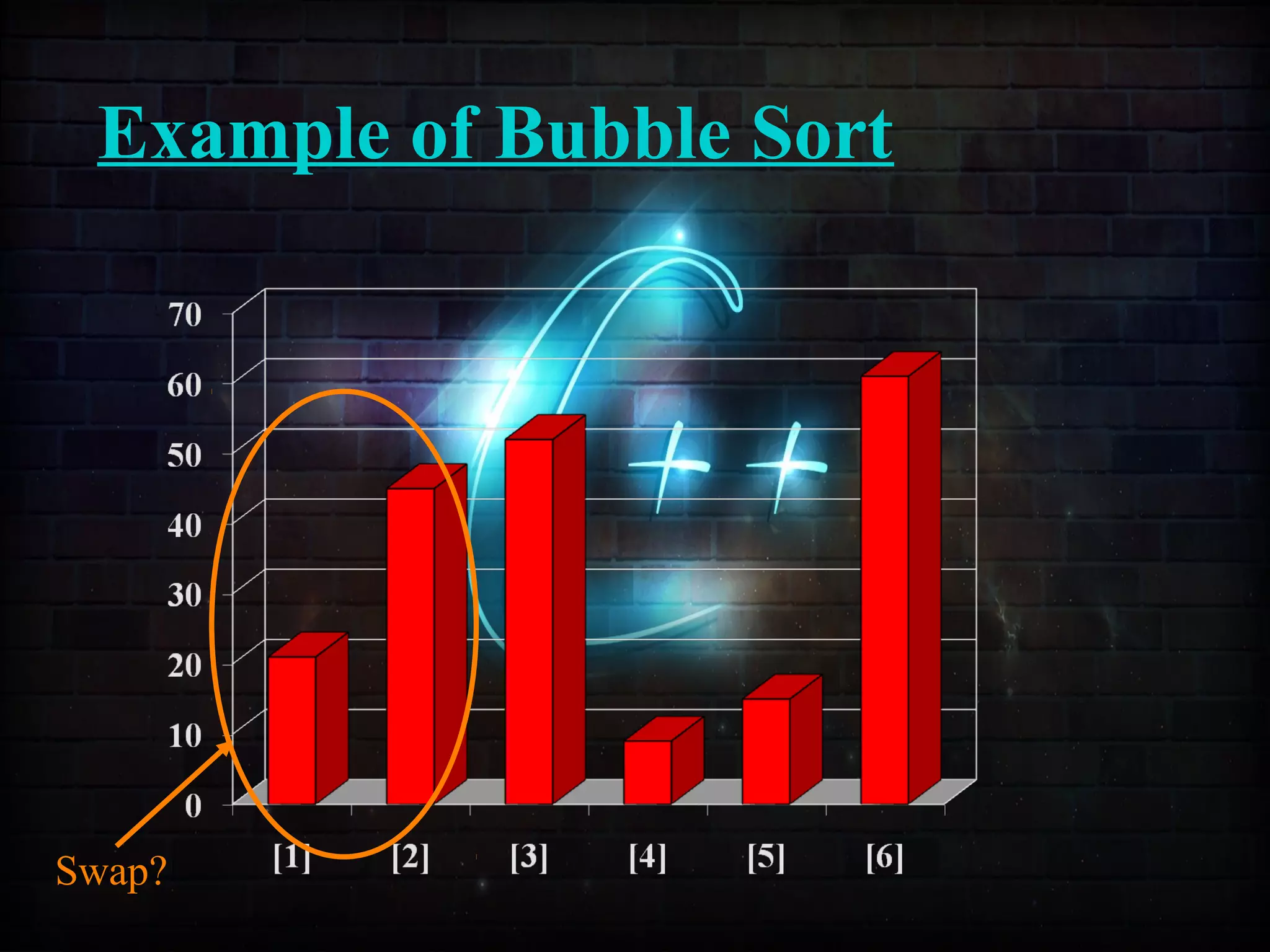
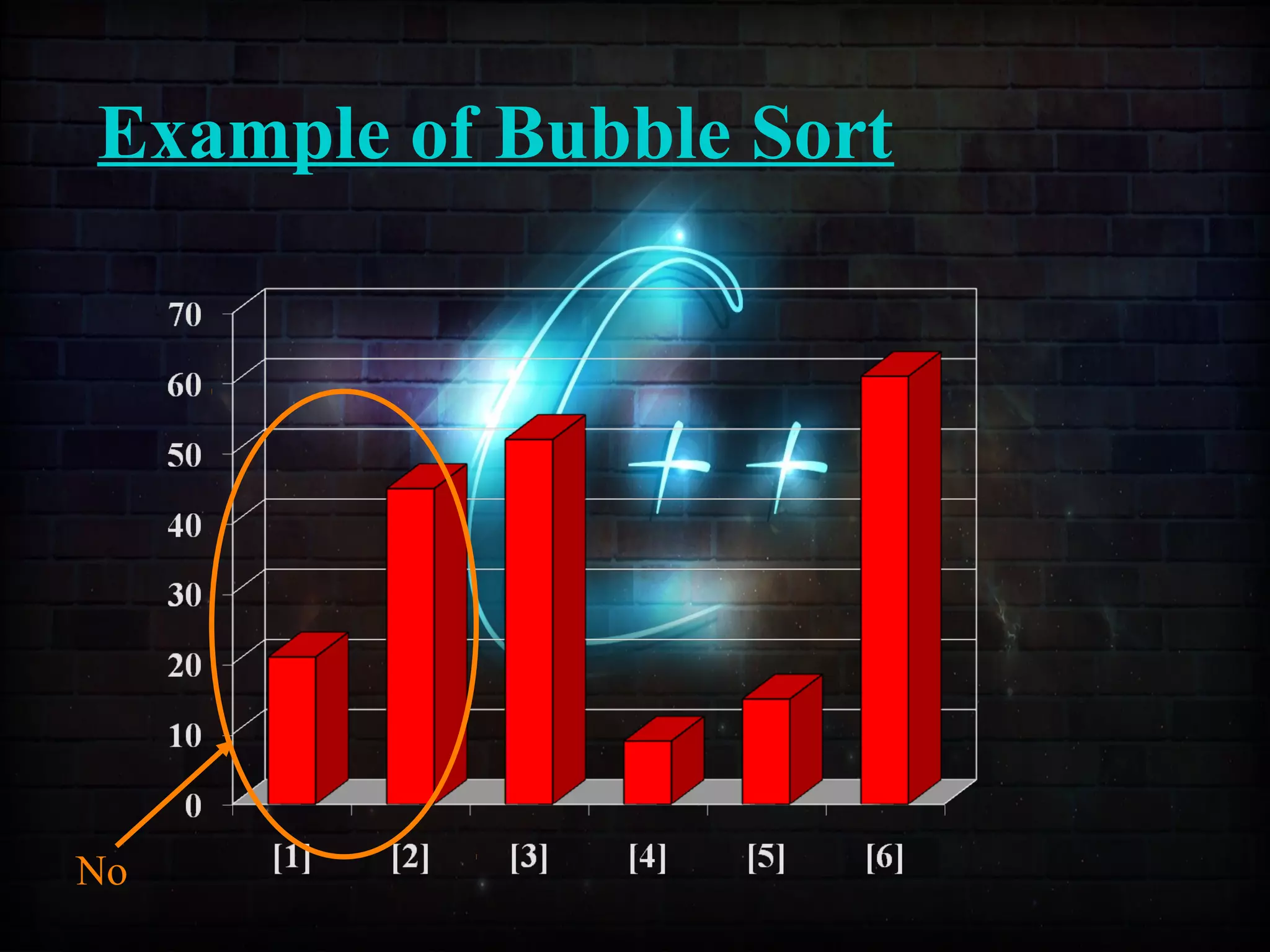
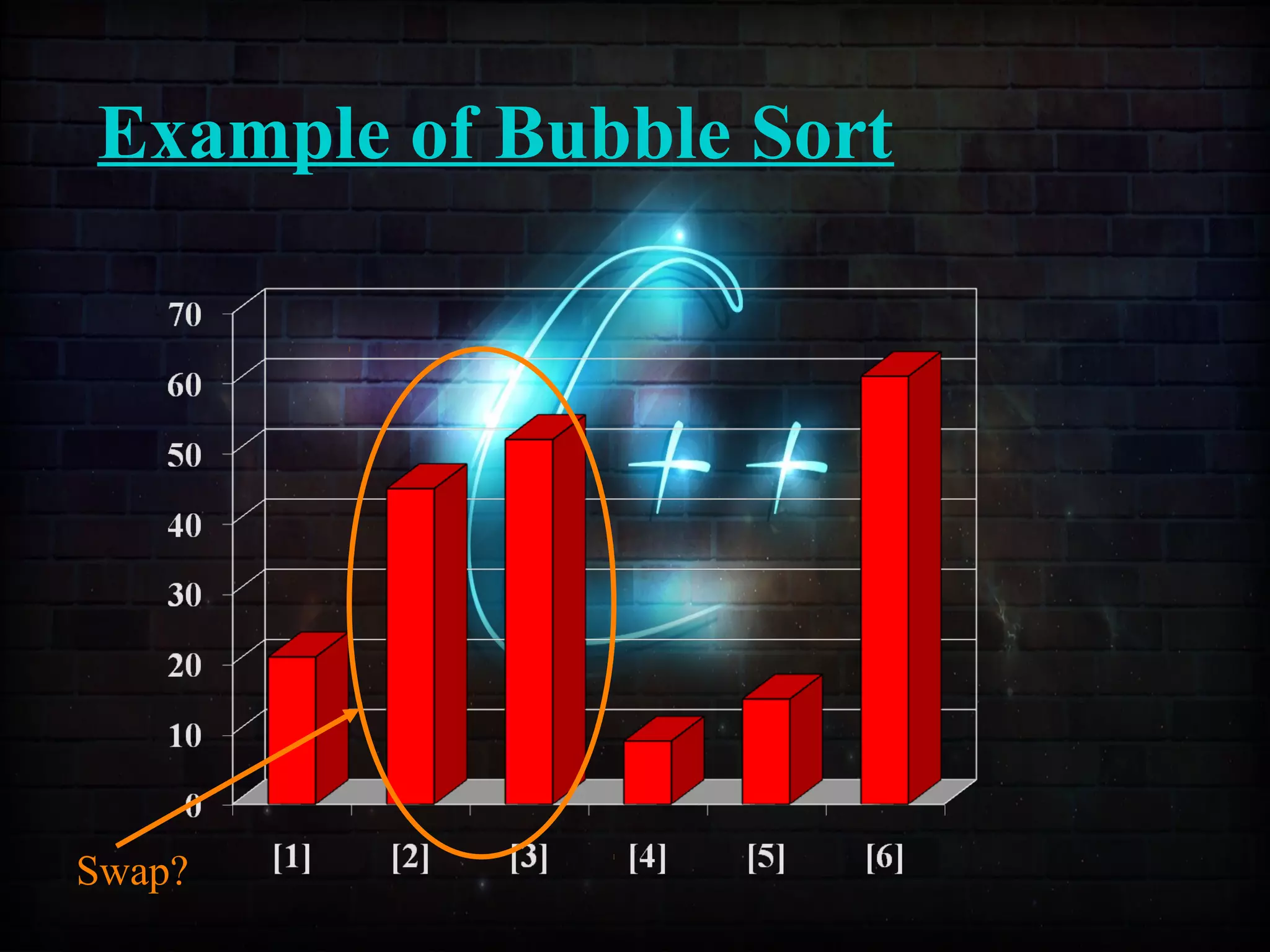
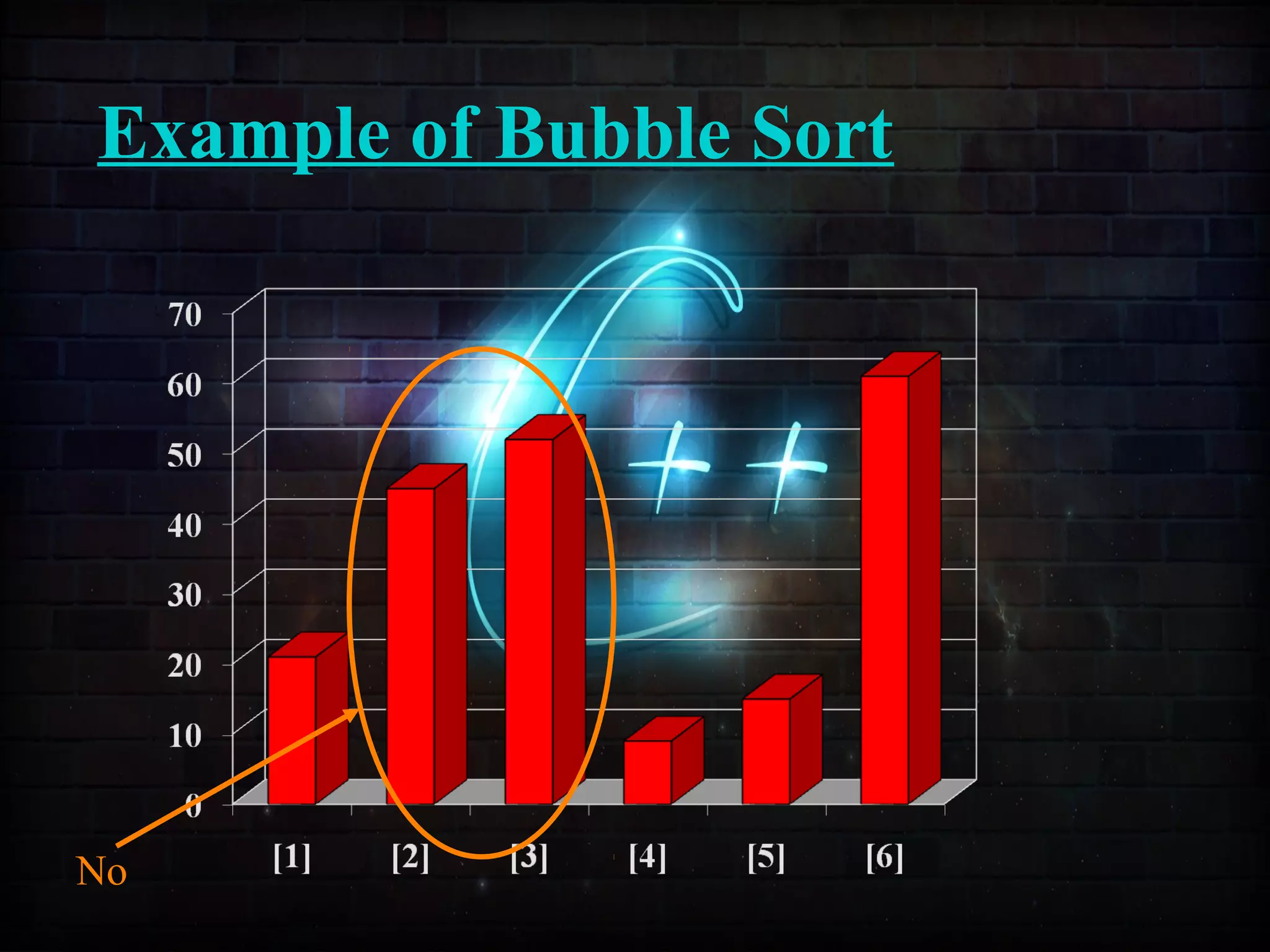
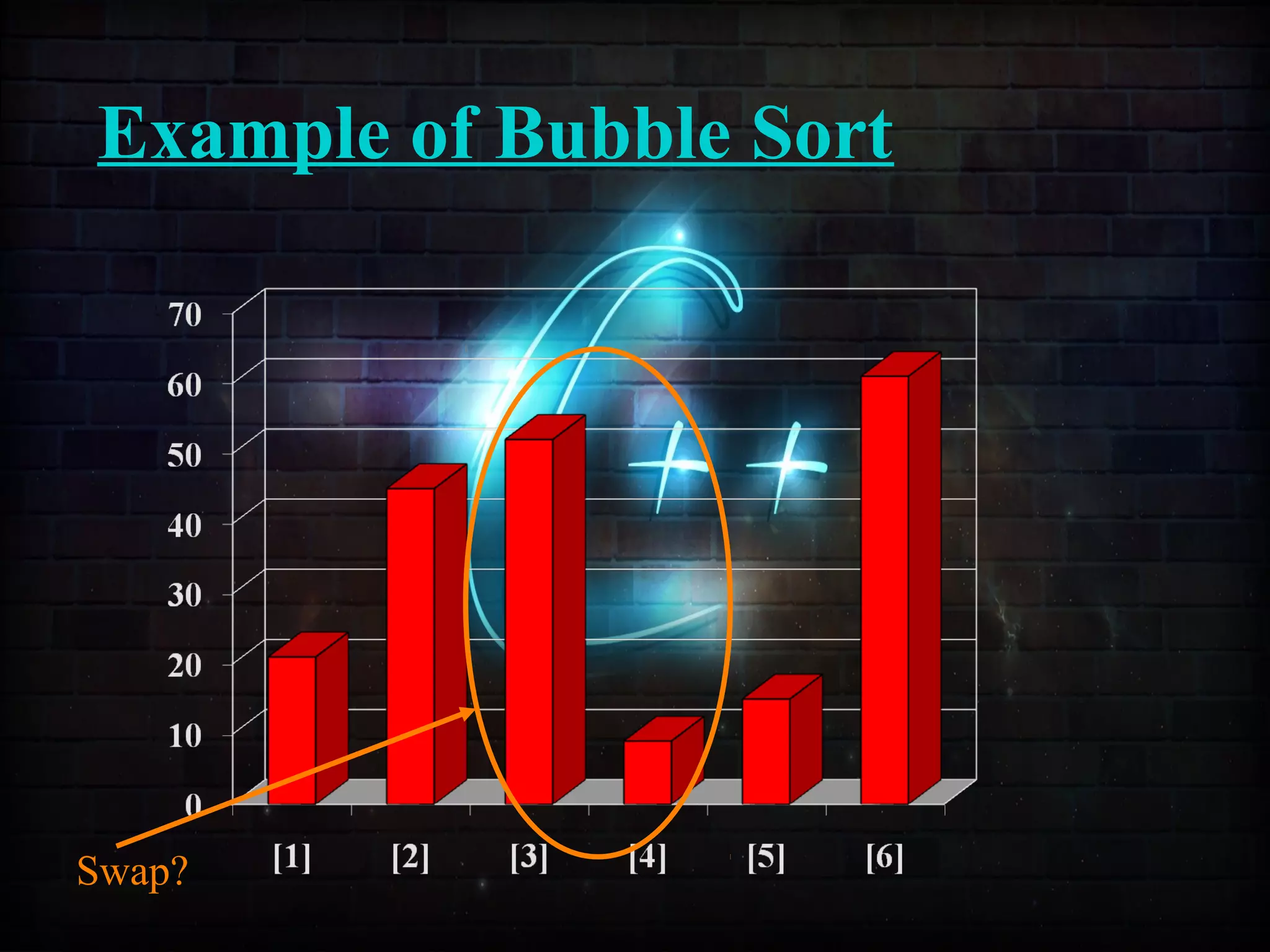
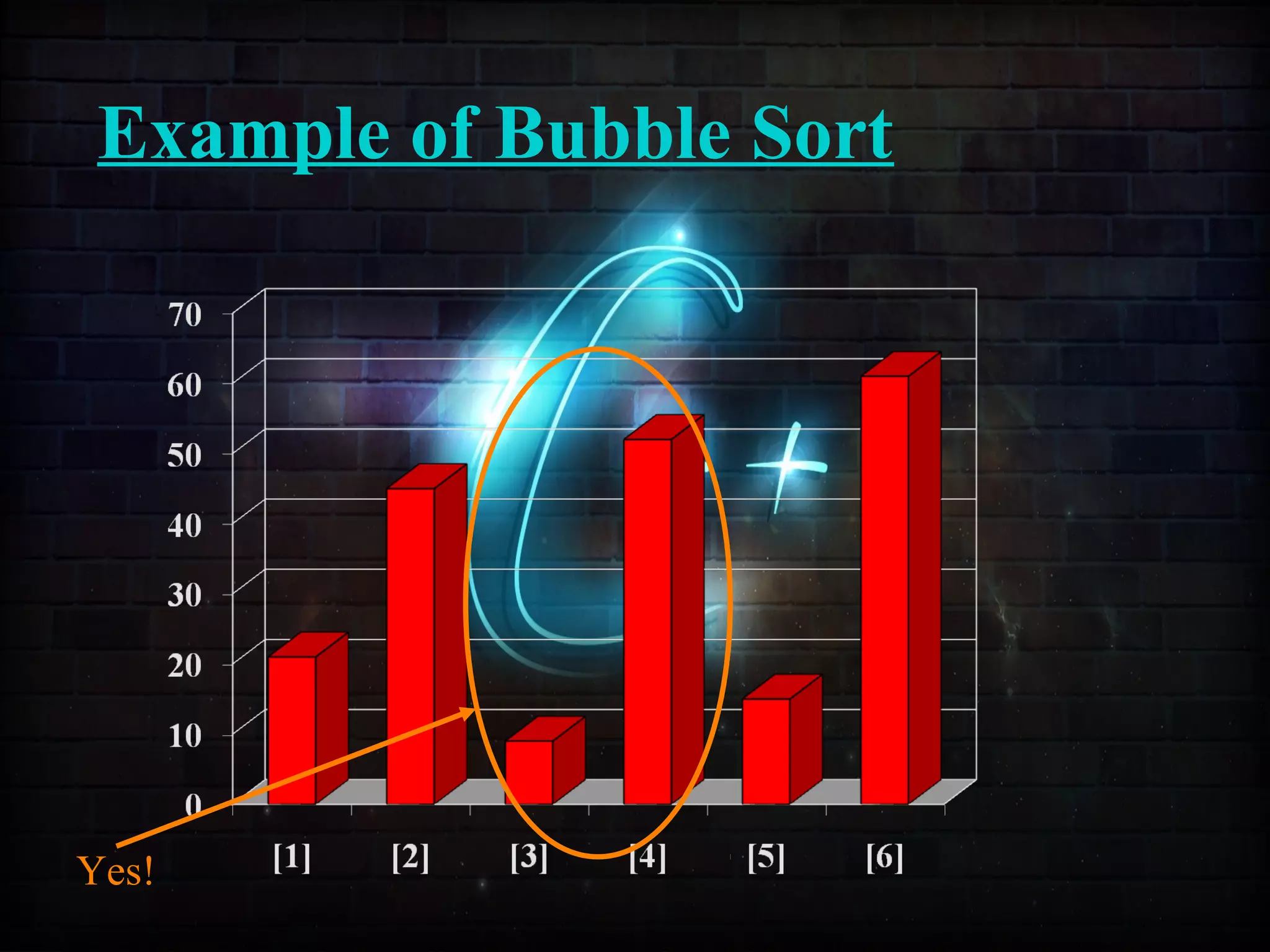
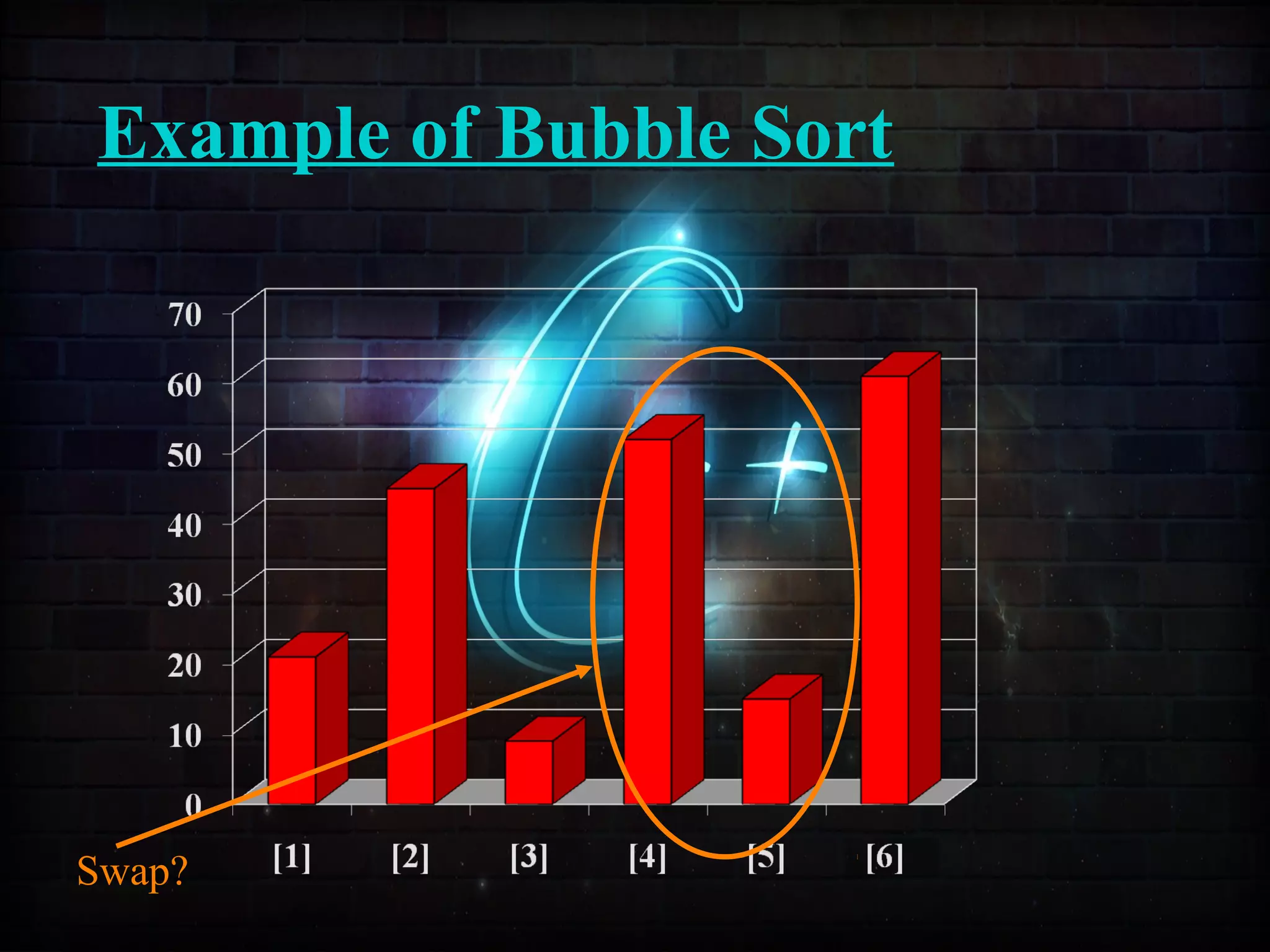
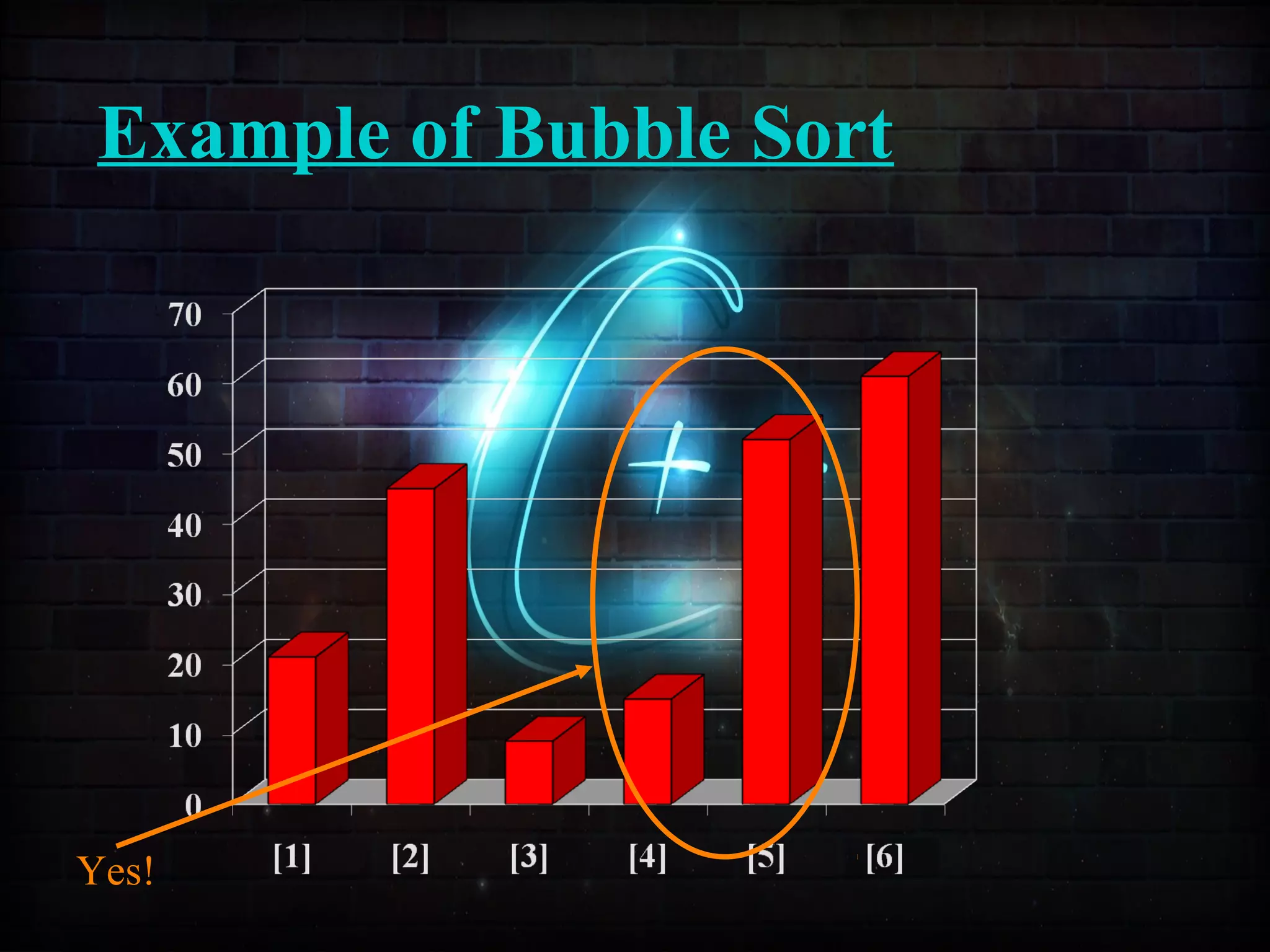
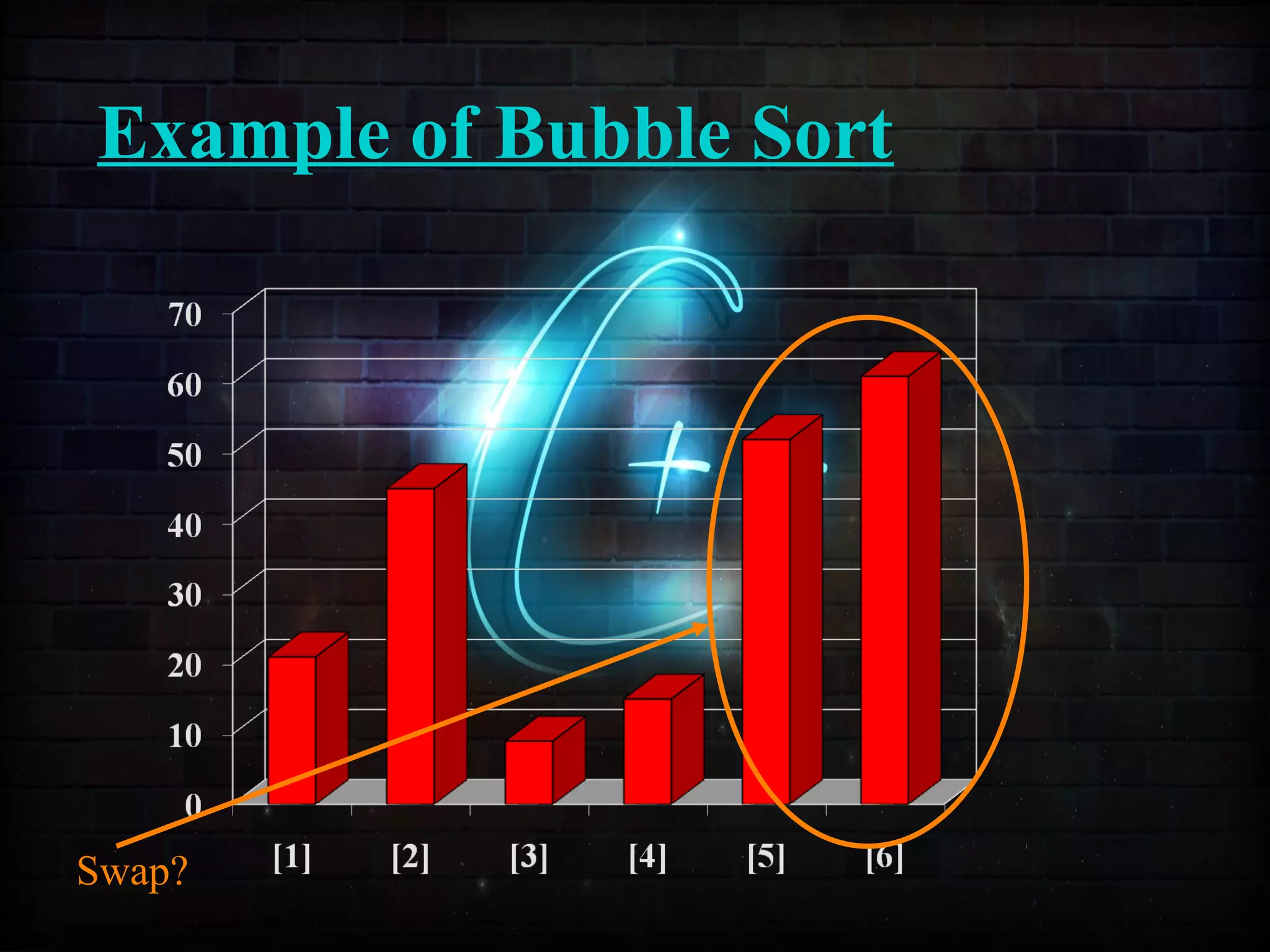
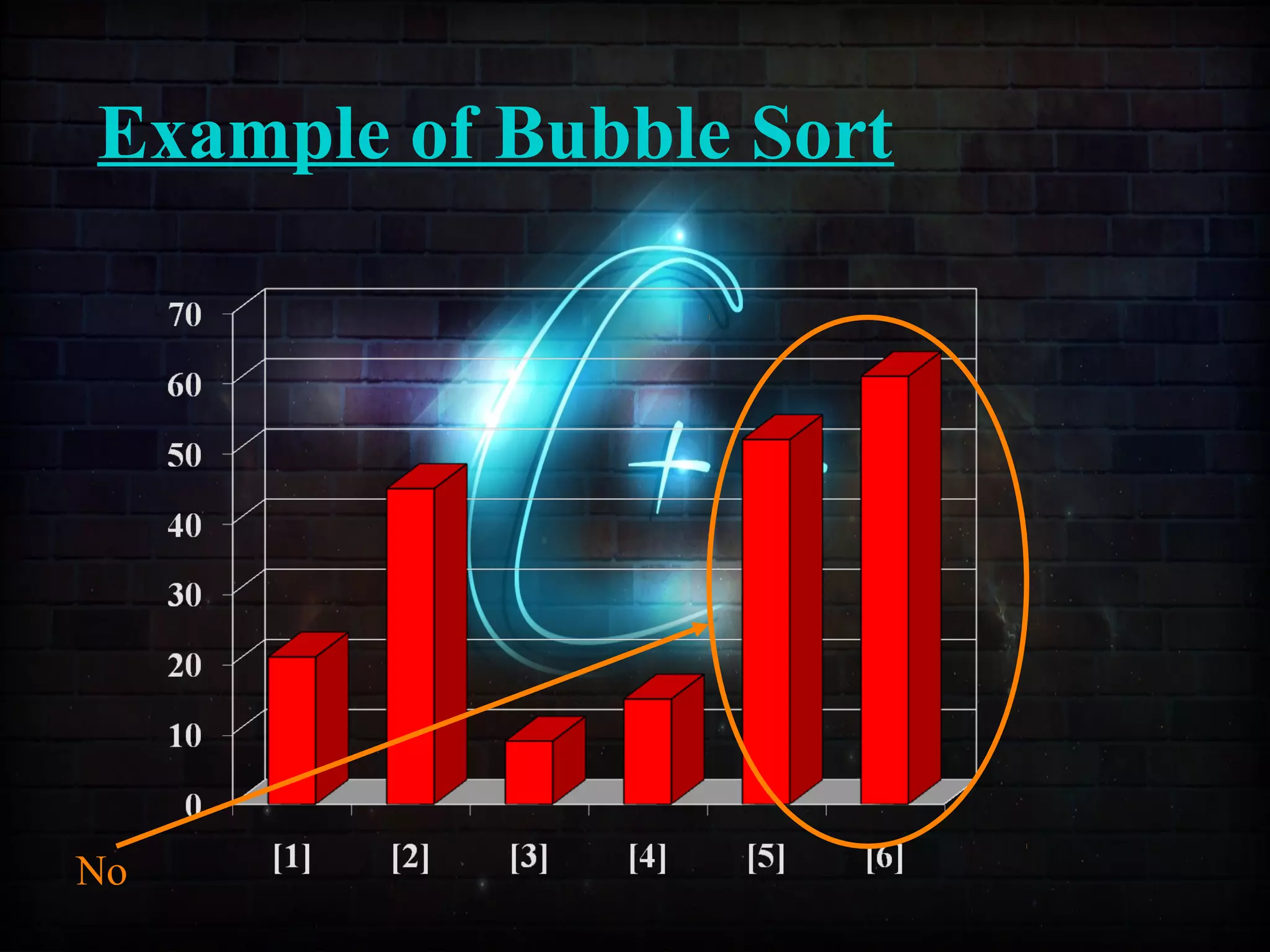
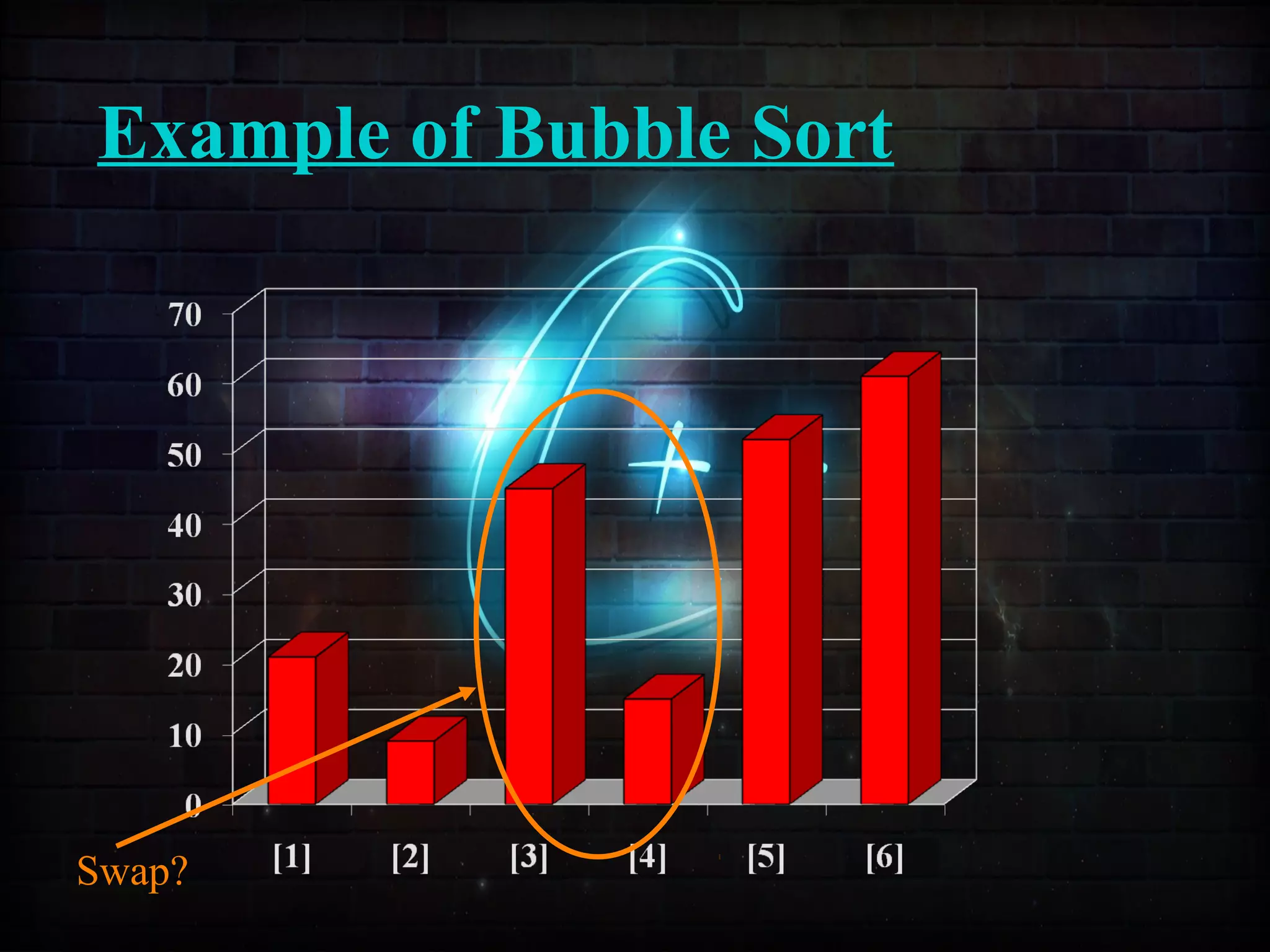
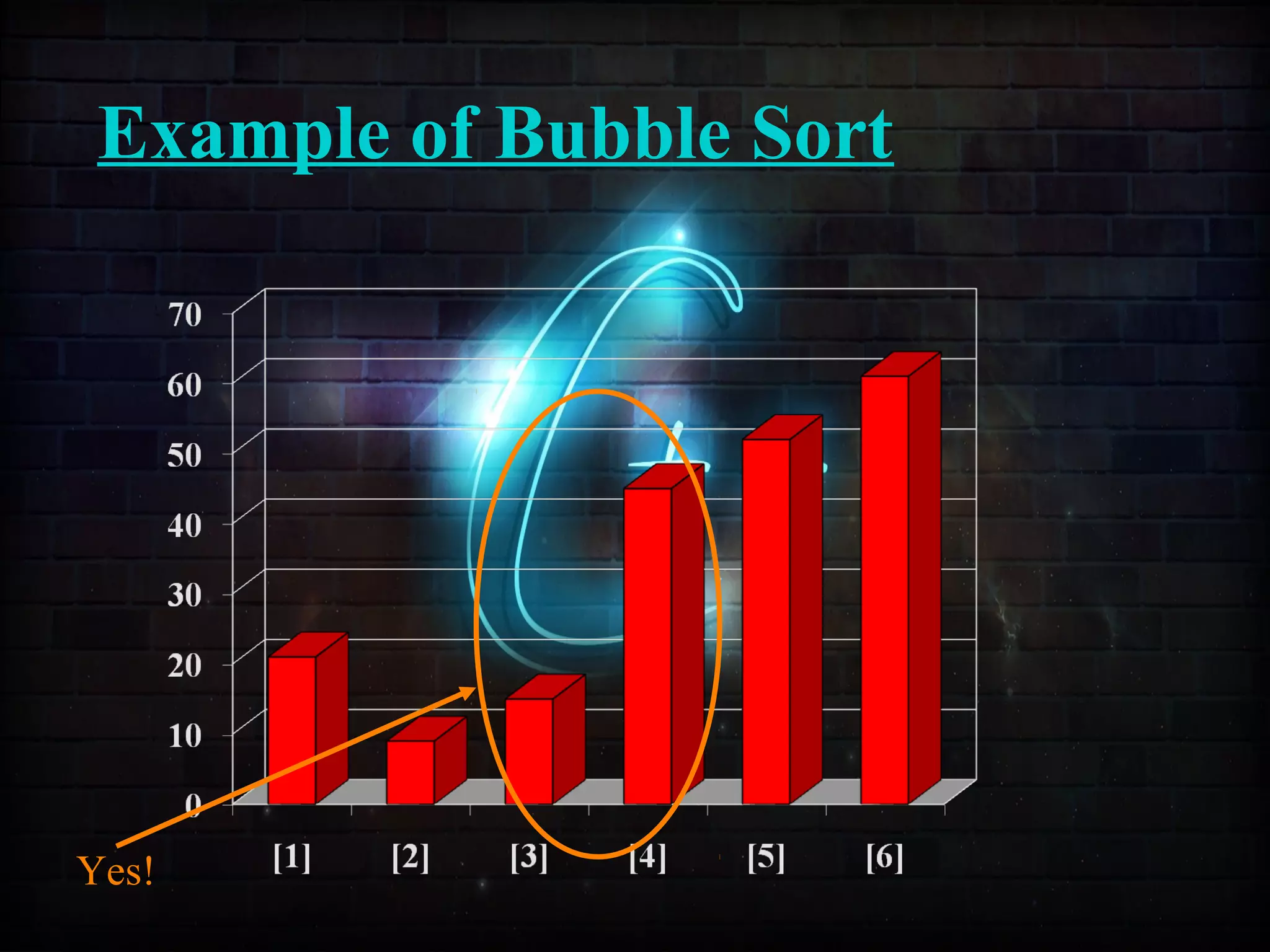
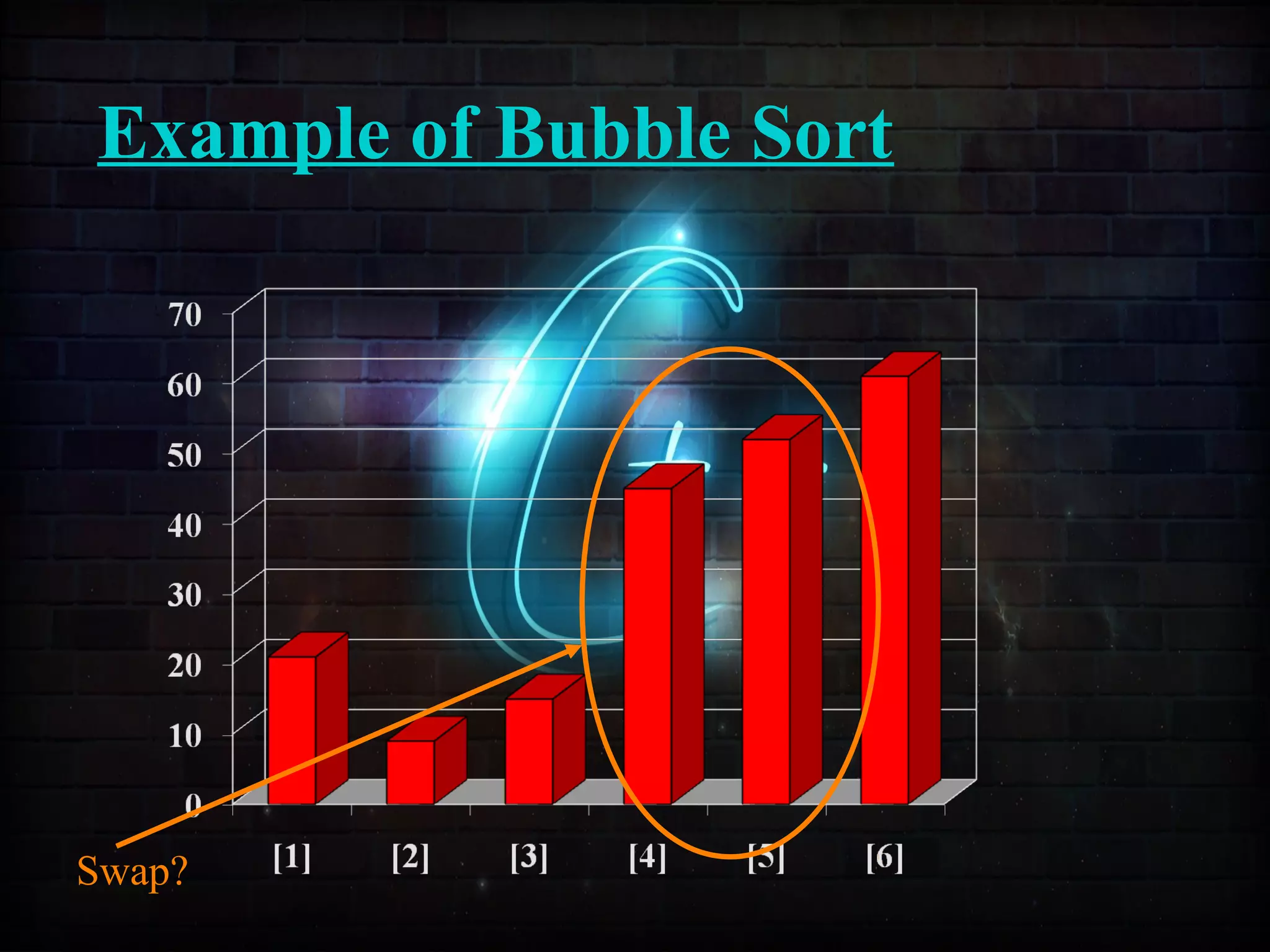
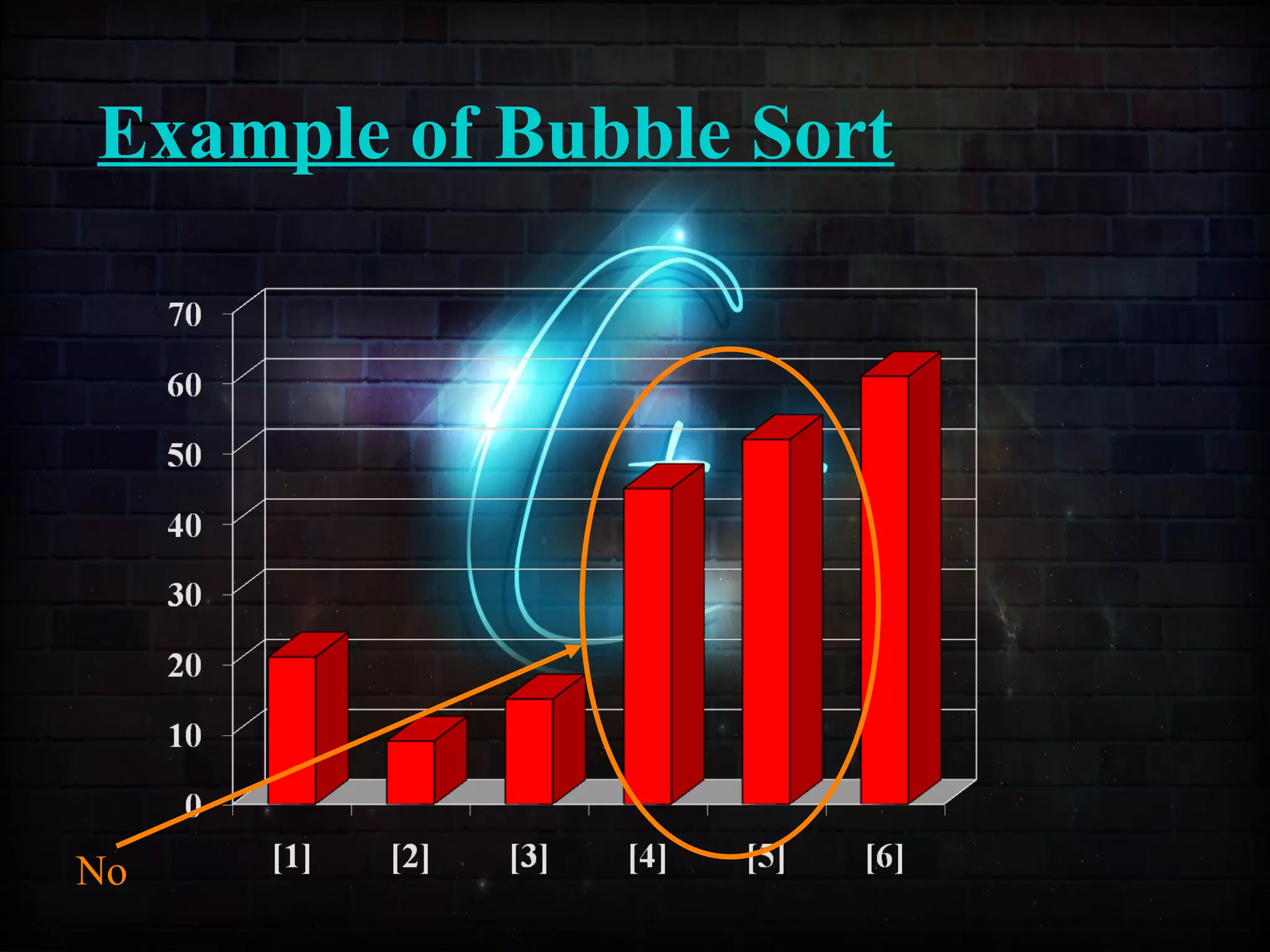
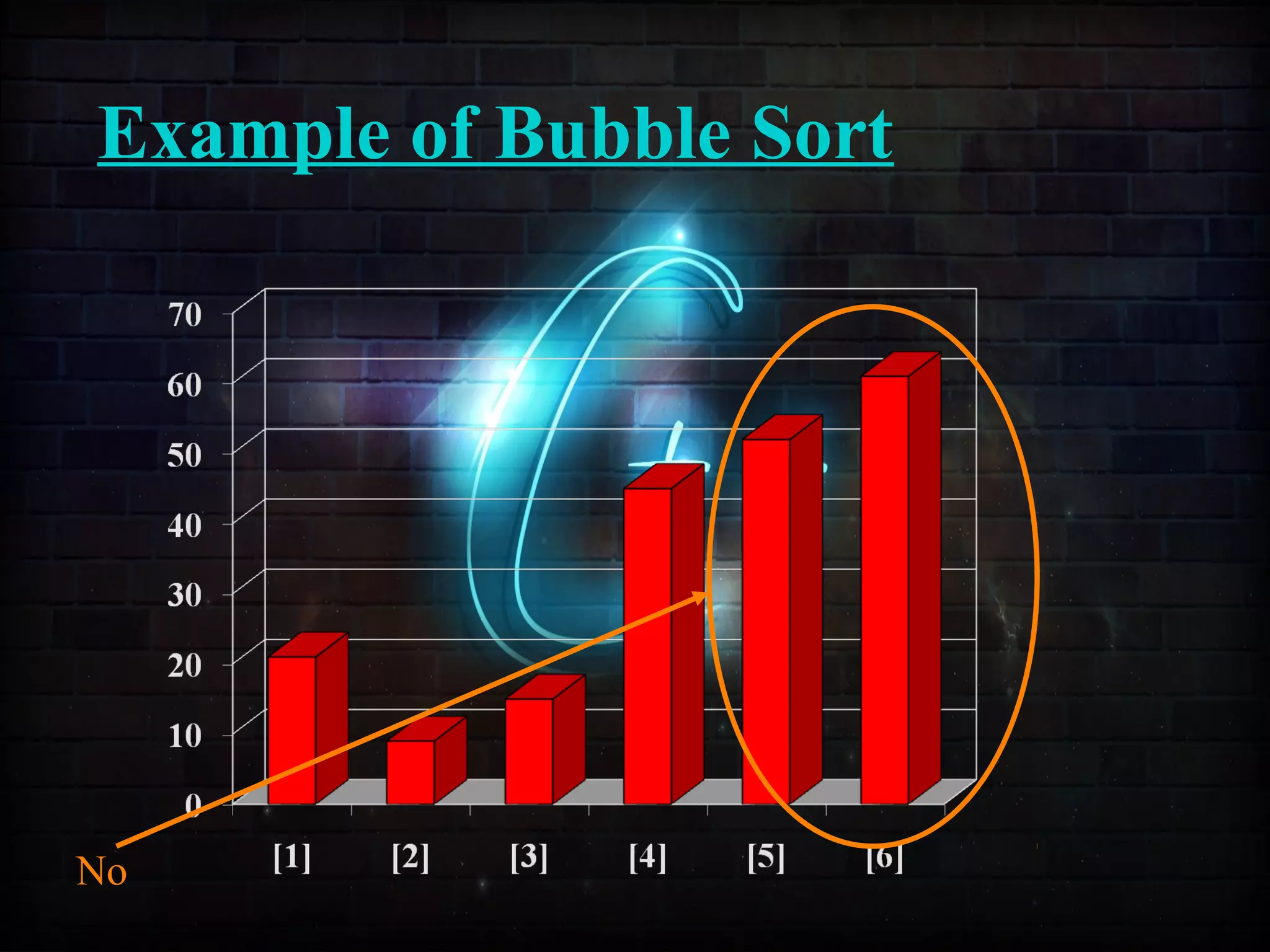
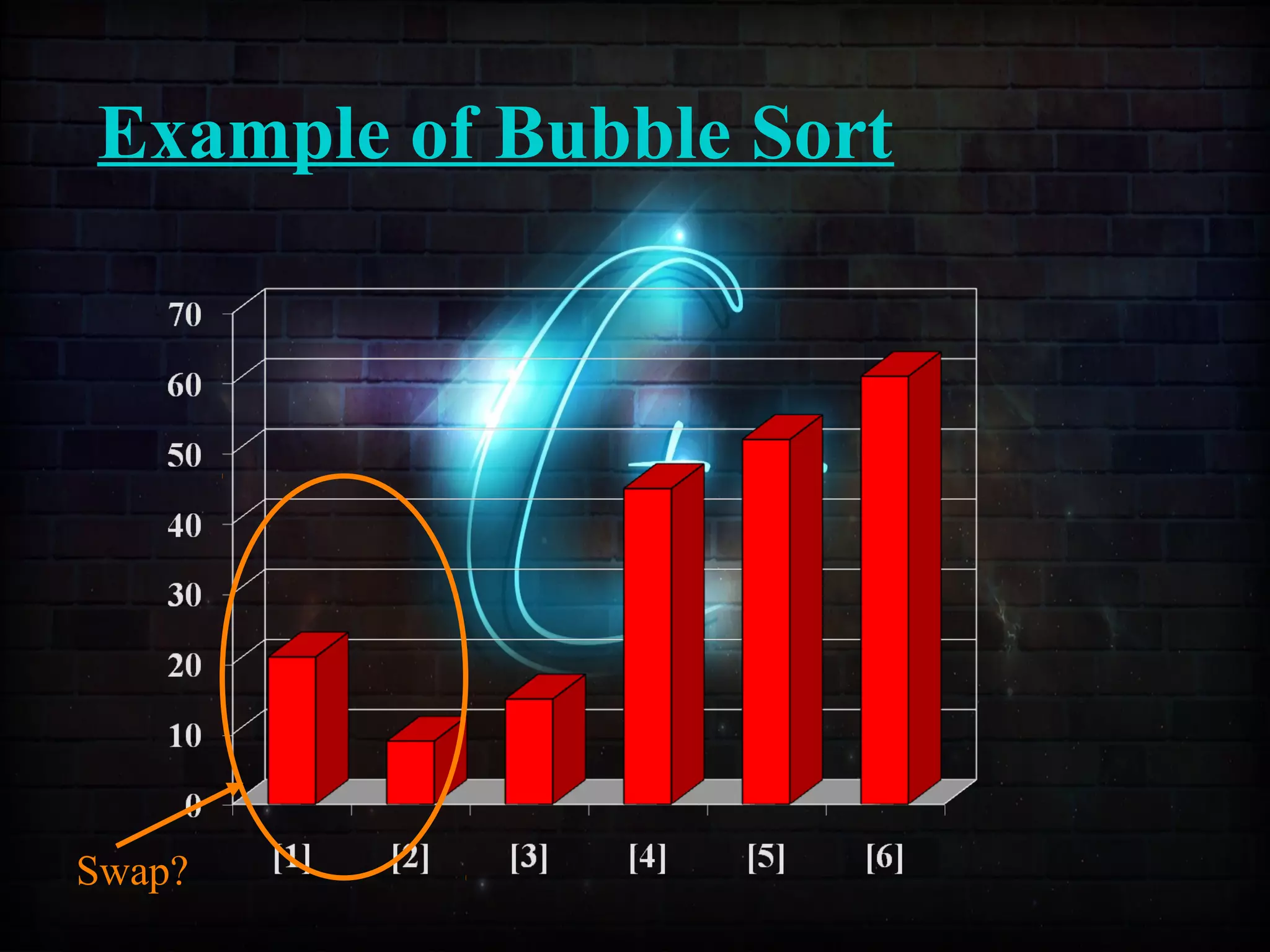
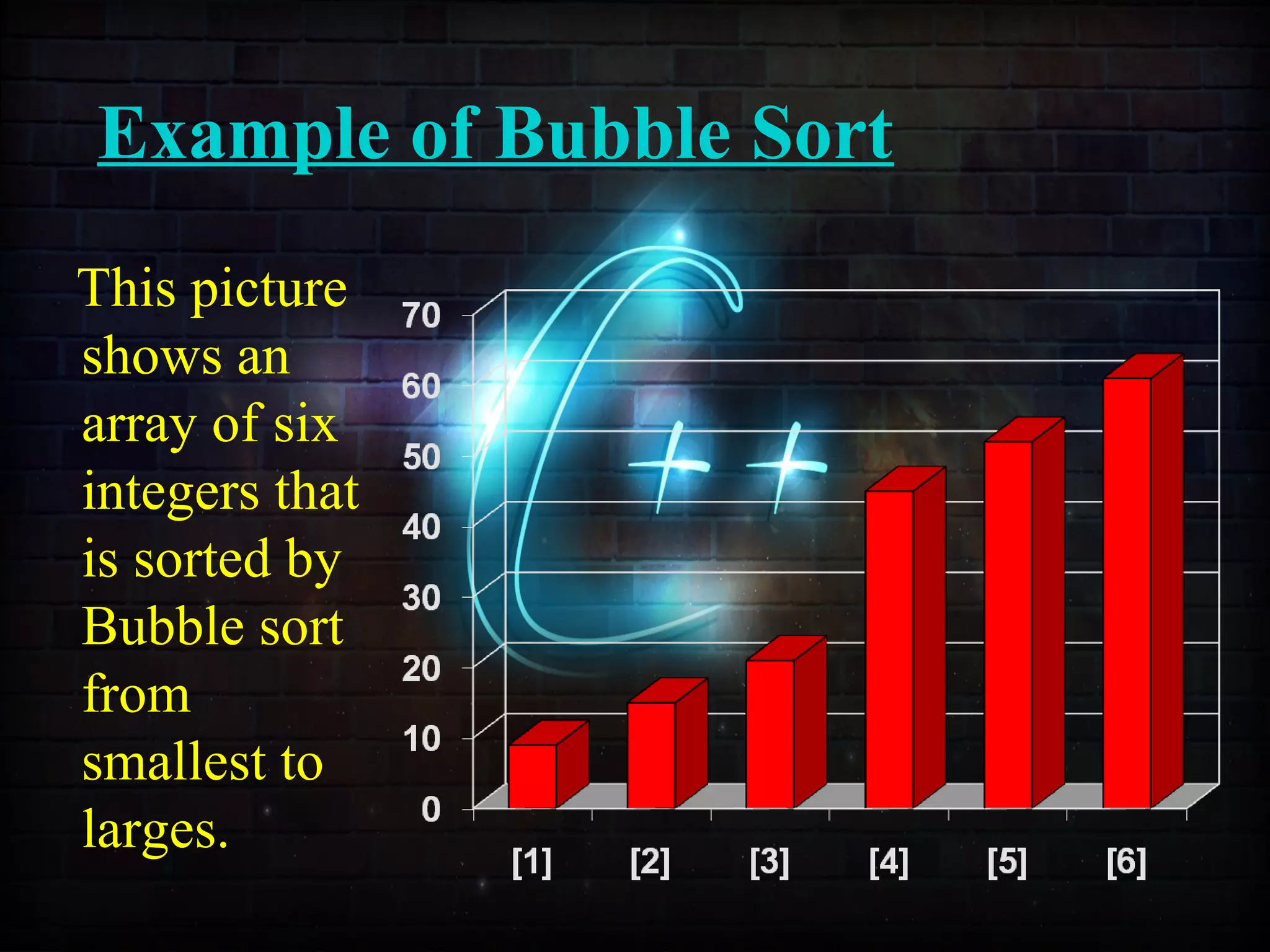
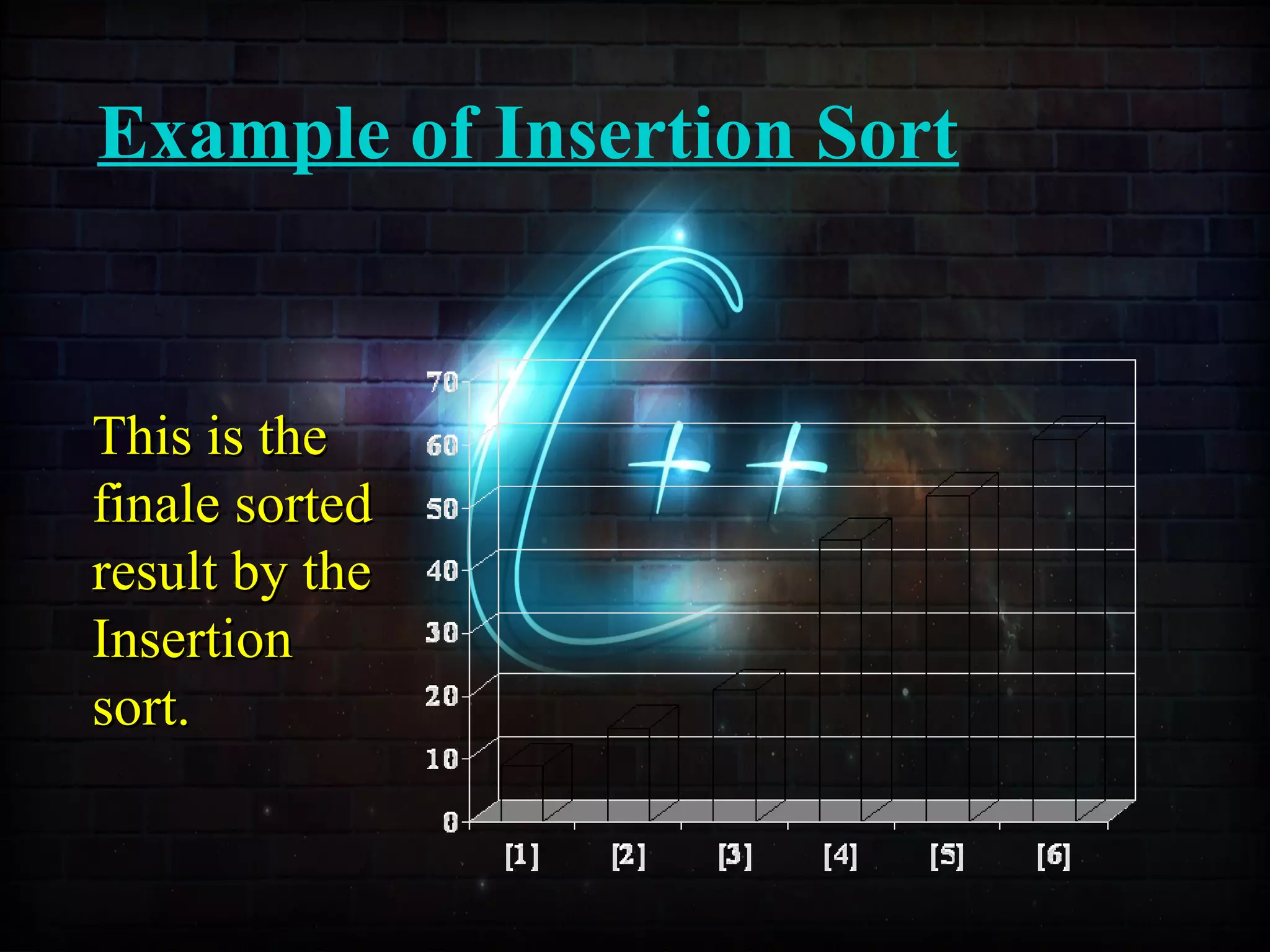
This document discusses a minor project on sorting techniques using functions in C++. It is authored by a group of 4 students and their project guide. The document introduces different sorting algorithms like bubble sort, insertion sort, and selection sort. It provides examples to explain how each algorithm works step-by-step to sort an array of numbers in ascending order. C and C++ are computer programming languages commonly used for software development, and sorting is an important technique to arrange data in a desired order.







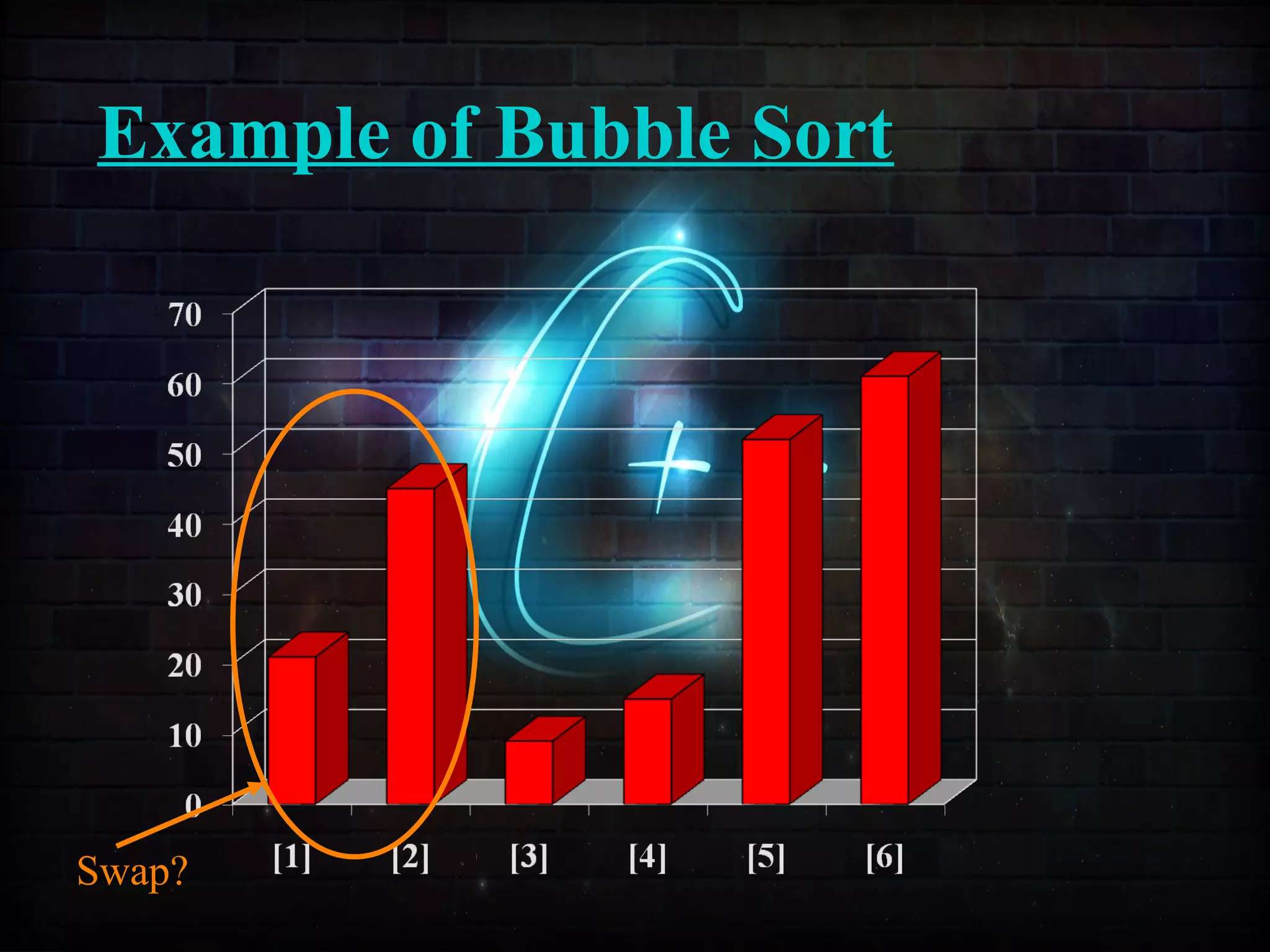
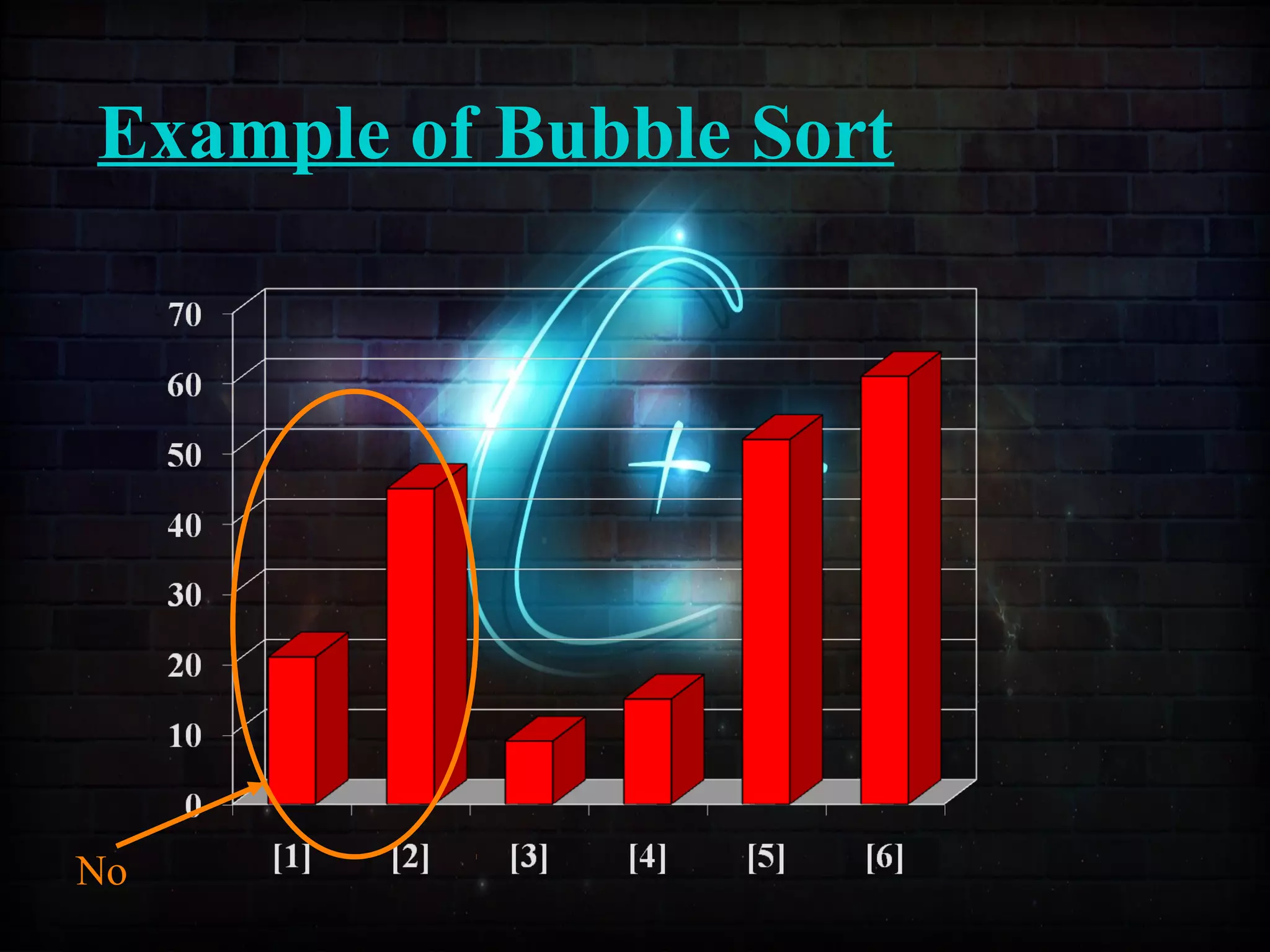
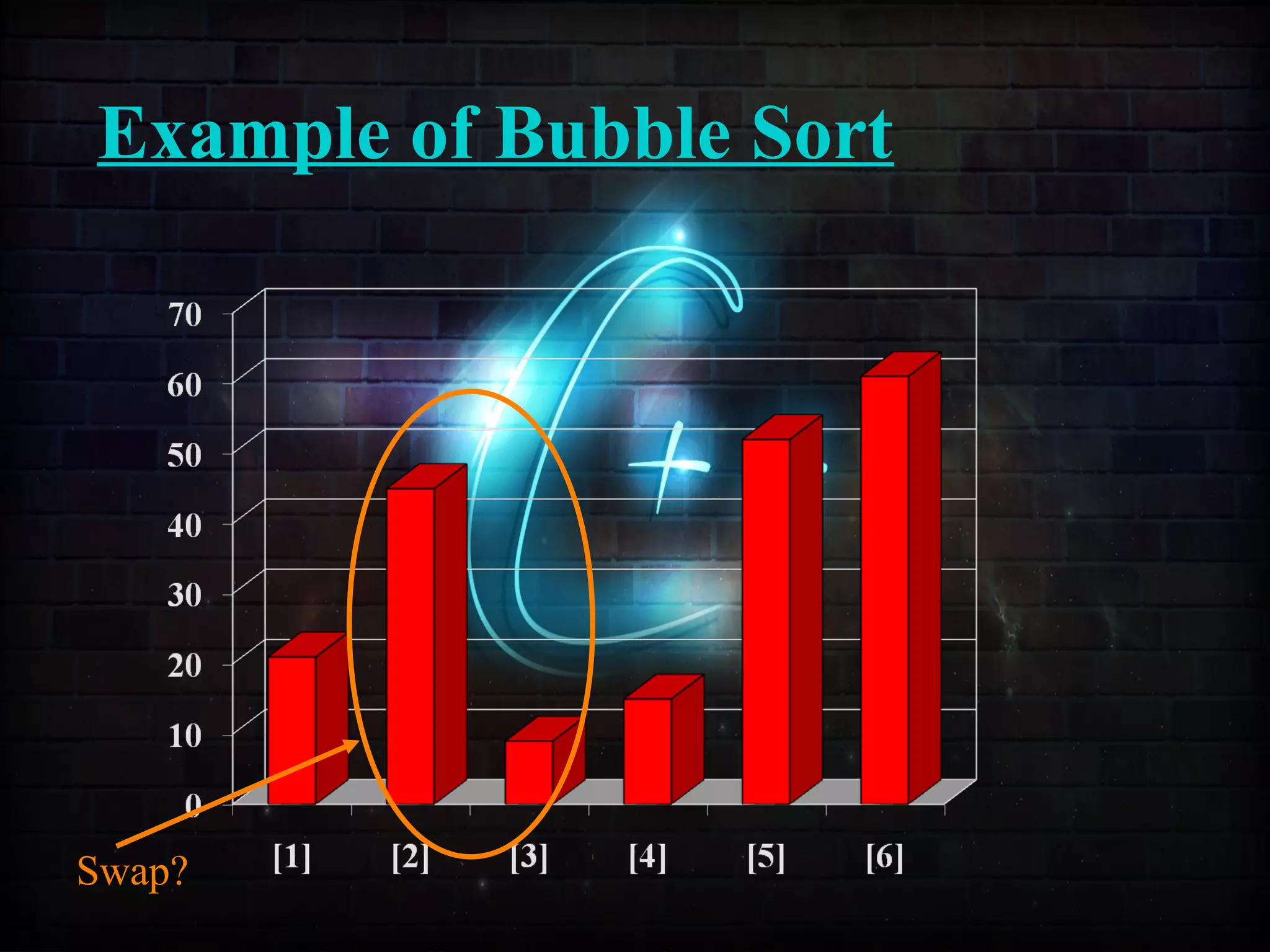
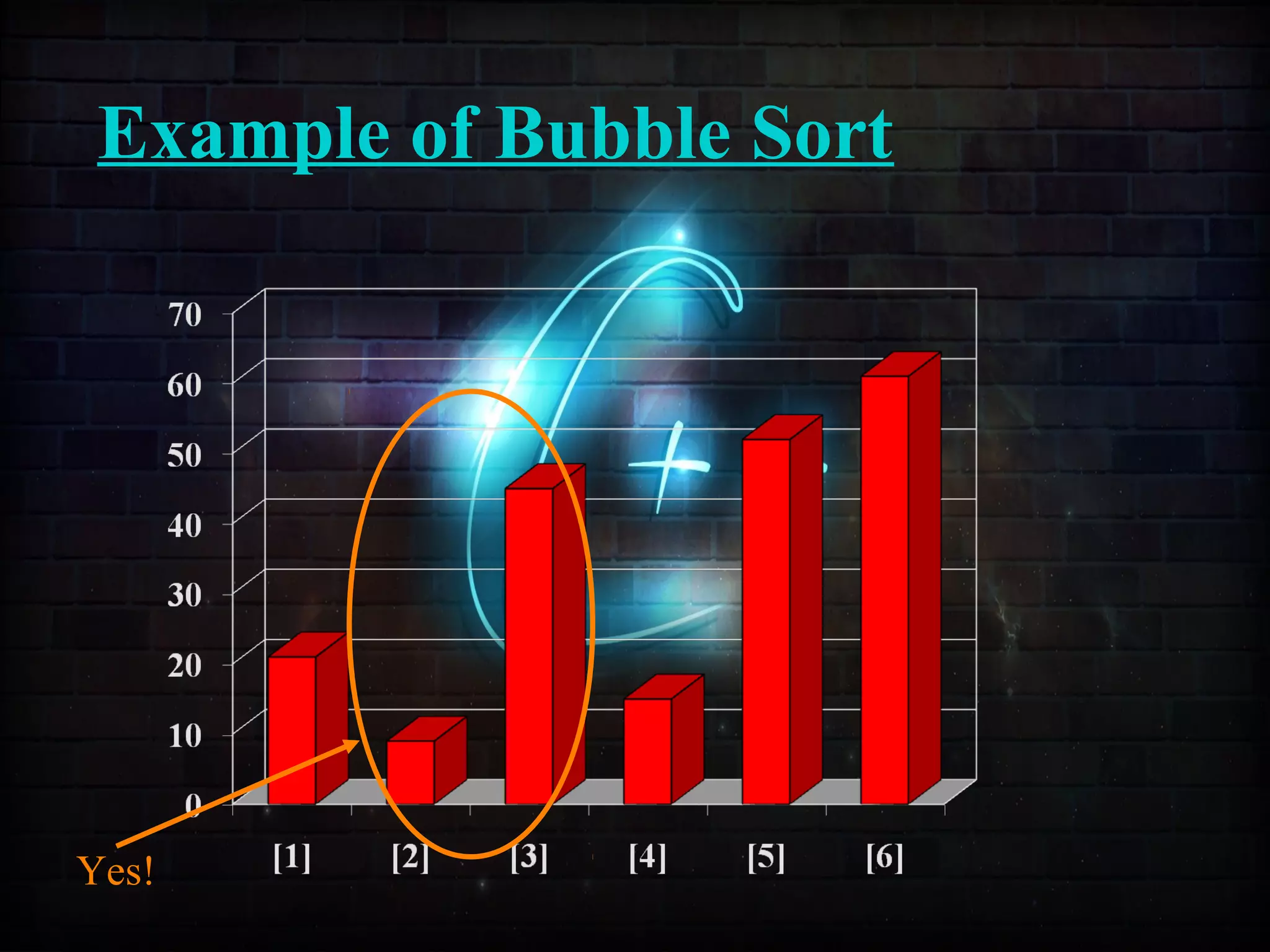


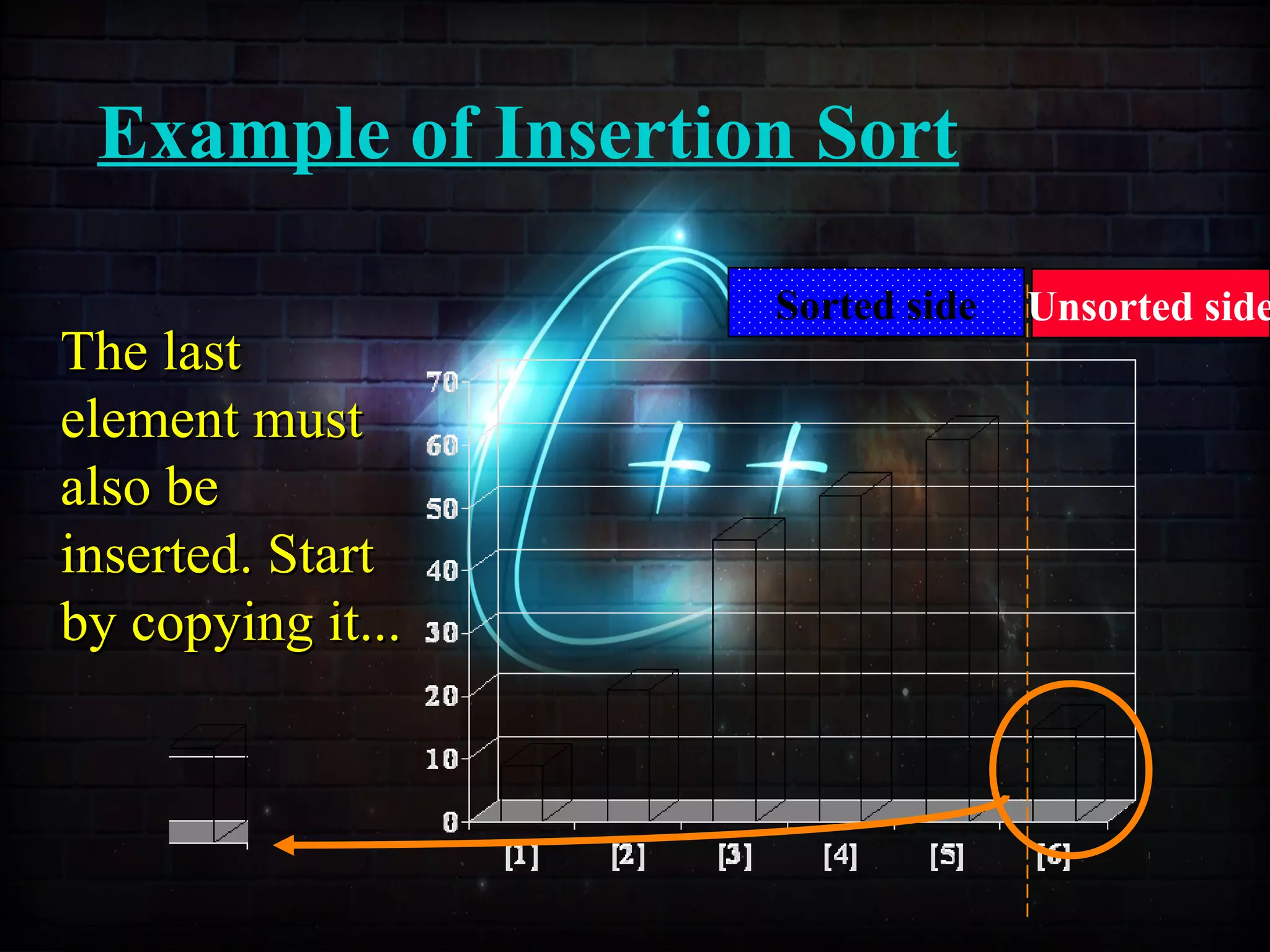
![Example of Insertion Sort
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
These columnsThese columns
or arrays areor arrays are
not sorted.not sorted.
The unsortedThe unsorted
arrays arearrays are
shown in theshown in the
figure.figure.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortingusingfunctionppt-150814134749-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-Techniques-42-2048.jpg)
![Example of Insertion Sort
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
Unsorted sideSorted sideSorted side Unsorted side
The sortedThe sorted
side startsside starts
with just thewith just the
first element,first element,
which is notwhich is not
necessarilynecessarily
the smallestthe smallest
element.element.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortingusingfunctionppt-150814134749-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-Techniques-43-2048.jpg)
![Example of Insertion Sort
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
Sorted side Unsorted side
The sortedThe sorted
side grows byside grows by
taking thetaking the
front elementfront element
from thefrom the
unsortedunsorted
side...side...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortingusingfunctionppt-150814134749-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-Techniques-44-2048.jpg)
![Example of Insertion Sort
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
Sorted side Unsorted side
...and...and
inserting it ininserting it in
the place thatthe place that
keeps thekeeps the
sorted sidesorted side
arranged fromarranged from
small to largesmall to large..](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortingusingfunctionppt-150814134749-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-Techniques-45-2048.jpg)
![Example of Insertion Sort
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
Sorted side Unsorted side
The two
arrays or
column are
sorted in this
figure.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortingusingfunctionppt-150814134749-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-Techniques-46-2048.jpg)
![Example of Insertion Sort
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
In this time
the arrays
are sorted so
we don’t
need to
move any
element.
Sorted side Unsorted side](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortingusingfunctionppt-150814134749-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-Techniques-47-2048.jpg)
![Example of Insertion Sort
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
Sorted side Unsorted sideIn this time,
we also
don’t need
to move the
any array
because
these are
already
sorted.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortingusingfunctionppt-150814134749-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-Techniques-48-2048.jpg)
![Example of Insertion Sort
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
Sorted side Unsorted side
Copy theCopy the
newnew
element toelement to
a separatea separate
location.location.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortingusingfunctionppt-150814134749-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-Techniques-49-2048.jpg)
![Example of Insertion Sort
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
ShiftShift
elements inelements in
the sortedthe sorted
side,side,
creating ancreating an
open spaceopen space
for the newfor the new
element.element.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortingusingfunctionppt-150814134749-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-Techniques-50-2048.jpg)
![Example of Insertion Sort
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
Insert theInsert the
element.element.
Shift elementsShift elements
in the sortedin the sorted
side, creatingside, creating
an open spacean open space
for the newfor the new
element.element.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortingusingfunctionppt-150814134749-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-Techniques-51-2048.jpg)
![Example of Insertion Sort
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
ContinueContinue
shiftingshifting
elements...elements...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortingusingfunctionppt-150814134749-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-Techniques-52-2048.jpg)
![Example of Insertion Sort
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
ContinueContinue
shiftingshifting
elements...elements...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortingusingfunctionppt-150814134749-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-Techniques-53-2048.jpg)
![Example of Insertion Sort
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
...until you...until you
reach thereach the
location forlocation for
the newthe new
element.element.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortingusingfunctionppt-150814134749-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-Techniques-54-2048.jpg)
![Example of Insertion Sort
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
Sorted side Unsorted side
Copy the newCopy the new
element backelement back
into the array,into the array,
at the correctat the correct
location.location.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortingusingfunctionppt-150814134749-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-Techniques-55-2048.jpg)

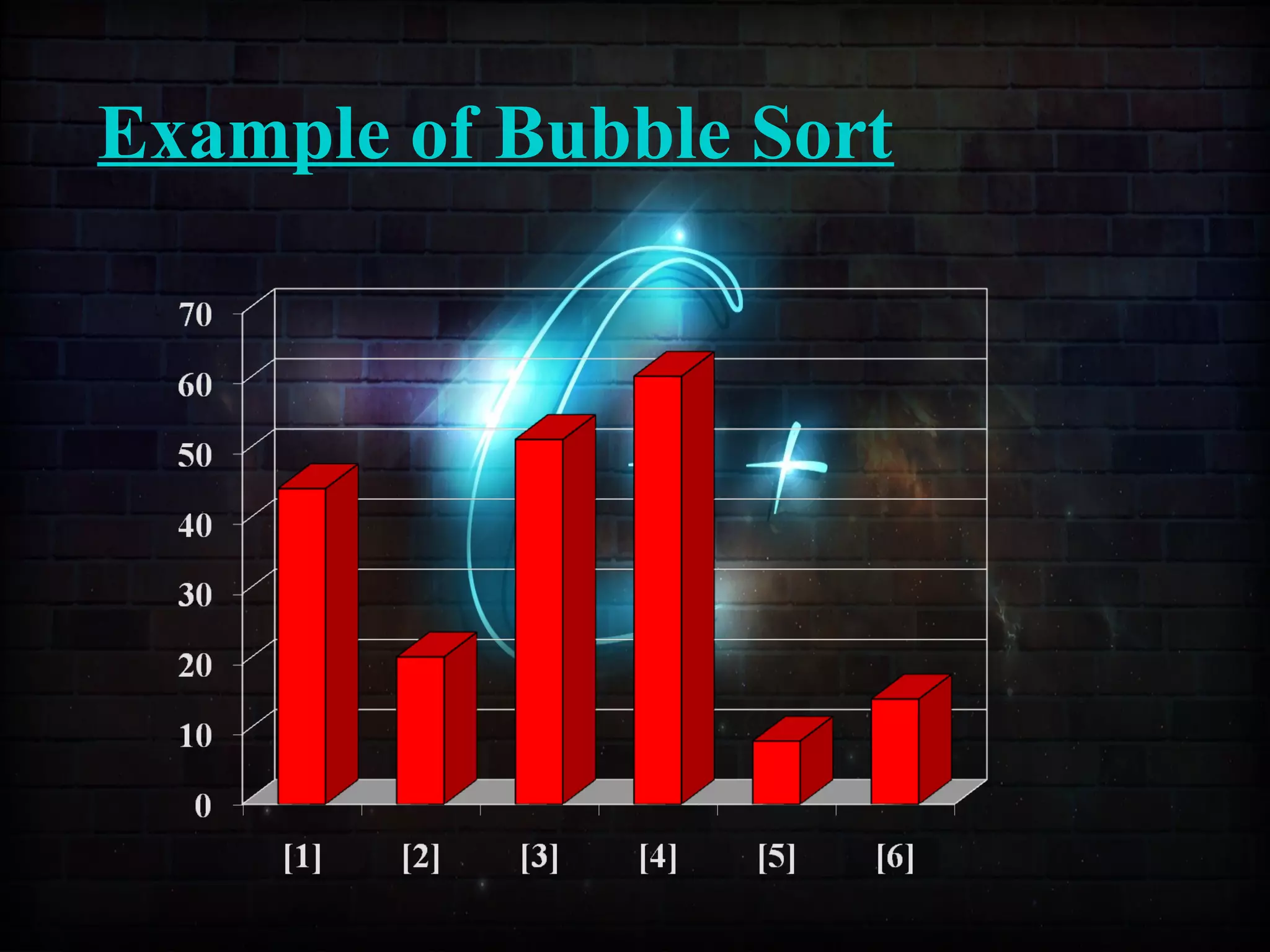
![Example of Selection Sort
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
These columnsThese columns
or arrays areor arrays are
not sorted.not sorted.
The unsortedThe unsorted
arrays arearrays are
shown in theshown in the
figure.figure.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortingusingfunctionppt-150814134749-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-Techniques-59-2048.jpg)
![Example of Selection Sort
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
Start byStart by
finding thefinding the
smallestsmallest
entry.entry.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortingusingfunctionppt-150814134749-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-Techniques-60-2048.jpg)
![Example of Selection Sort
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
Swap theSwap the
smallestsmallest
entry withentry with
the firstthe first
entry.entry.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortingusingfunctionppt-150814134749-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-Techniques-61-2048.jpg)
![Example of Selection Sort
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
Swap theSwap the
smallestsmallest
entry withentry with
the firstthe first
entry.entry.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortingusingfunctionppt-150814134749-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-Techniques-62-2048.jpg)
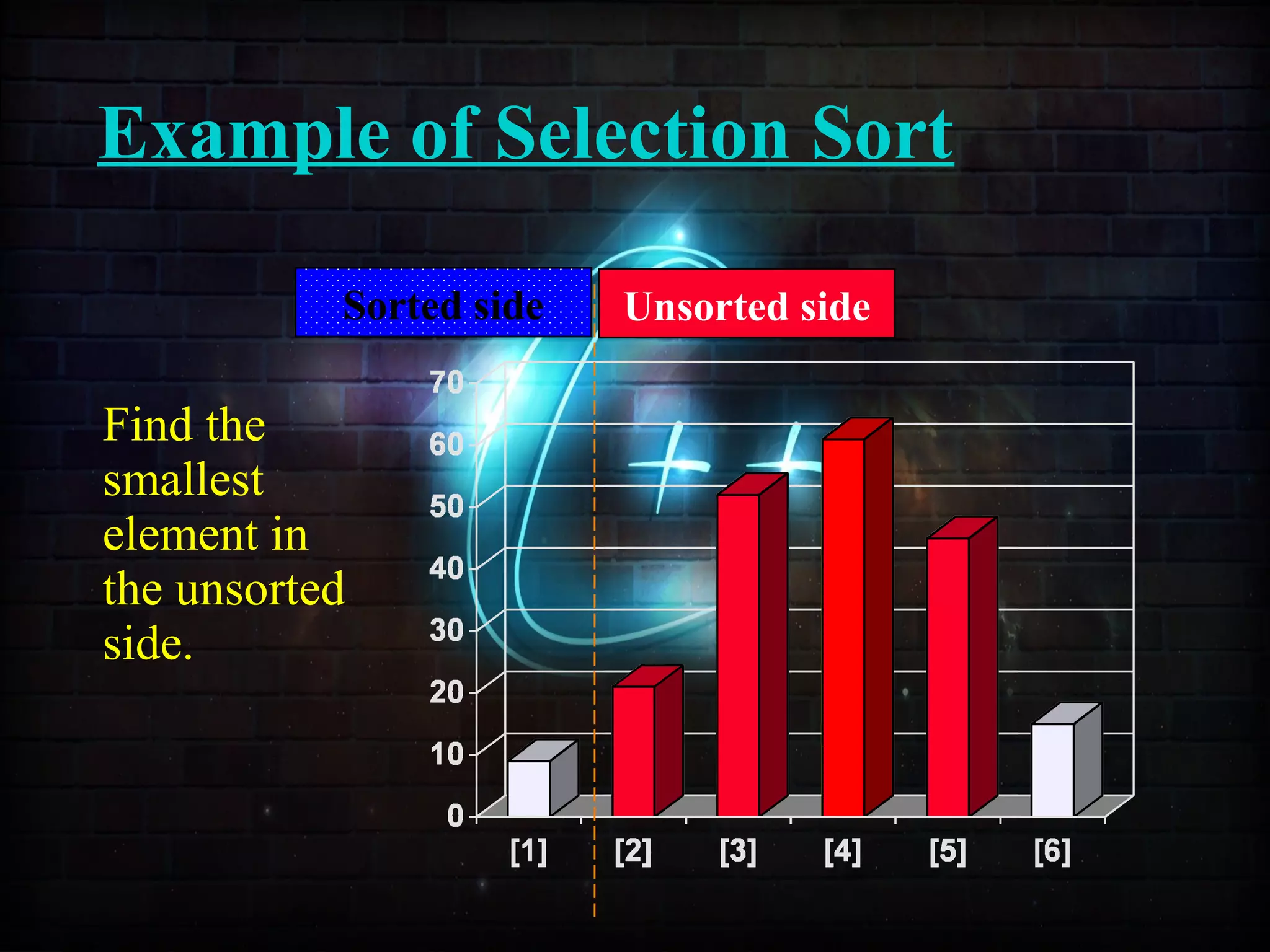
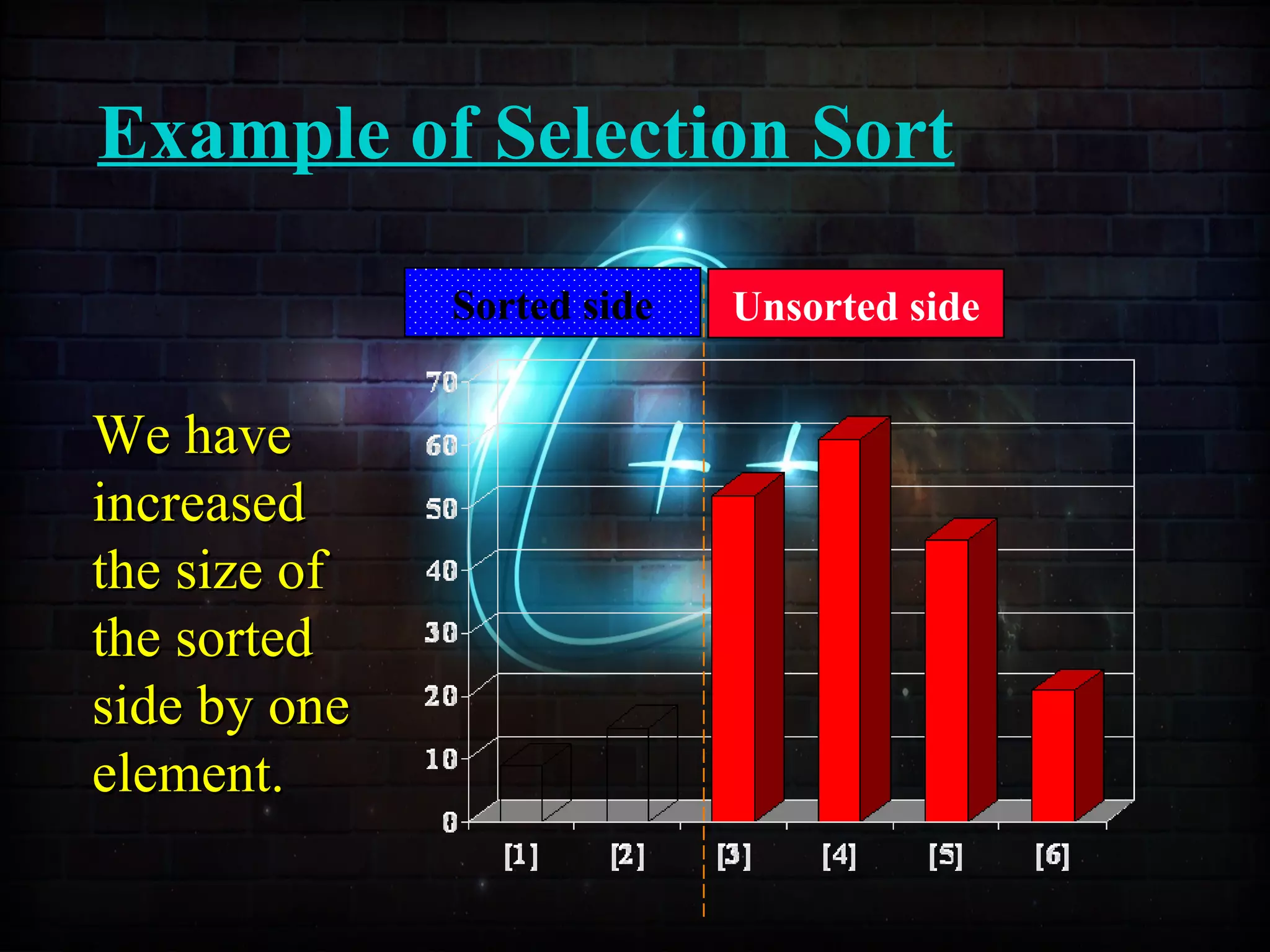
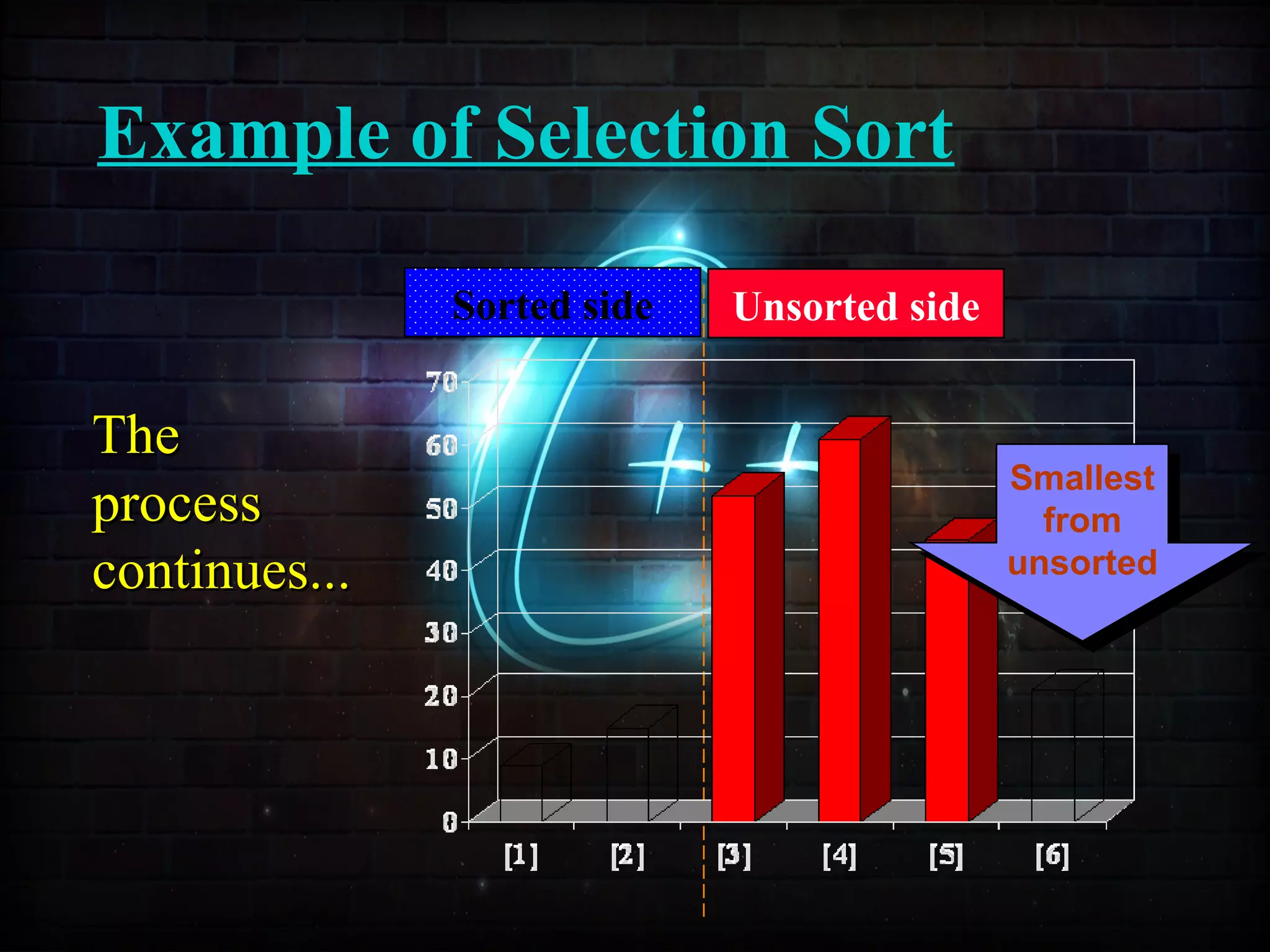
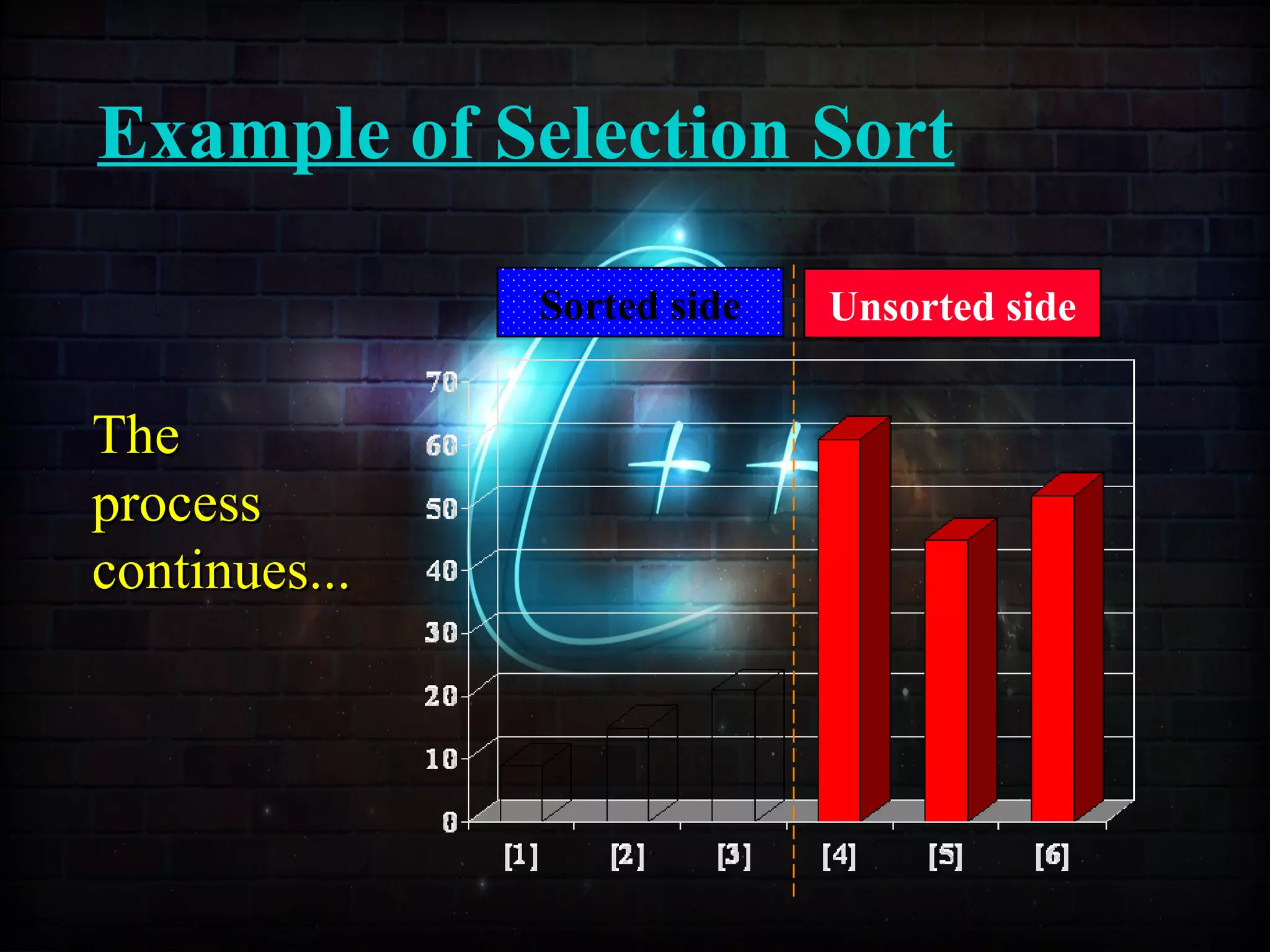
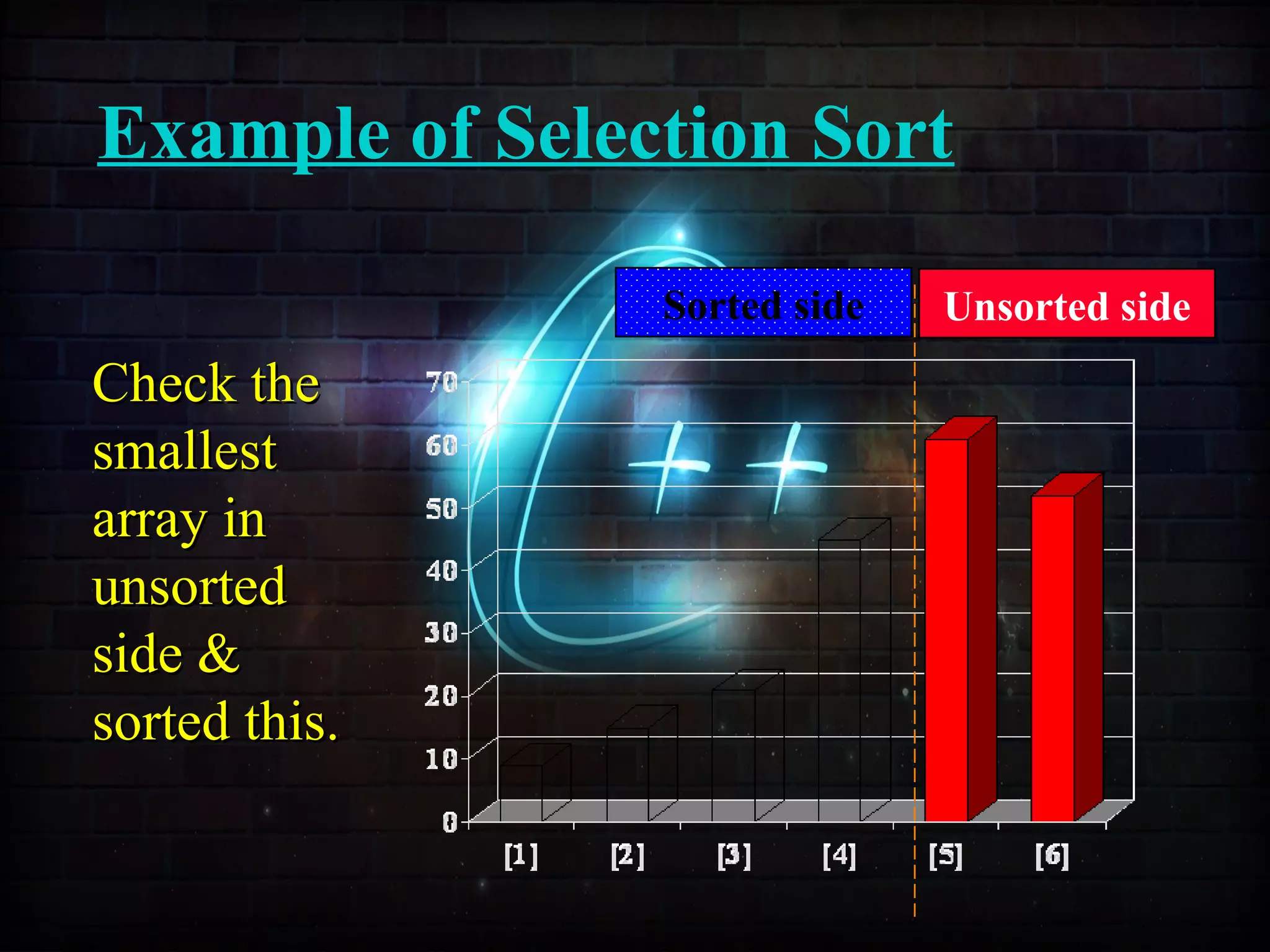
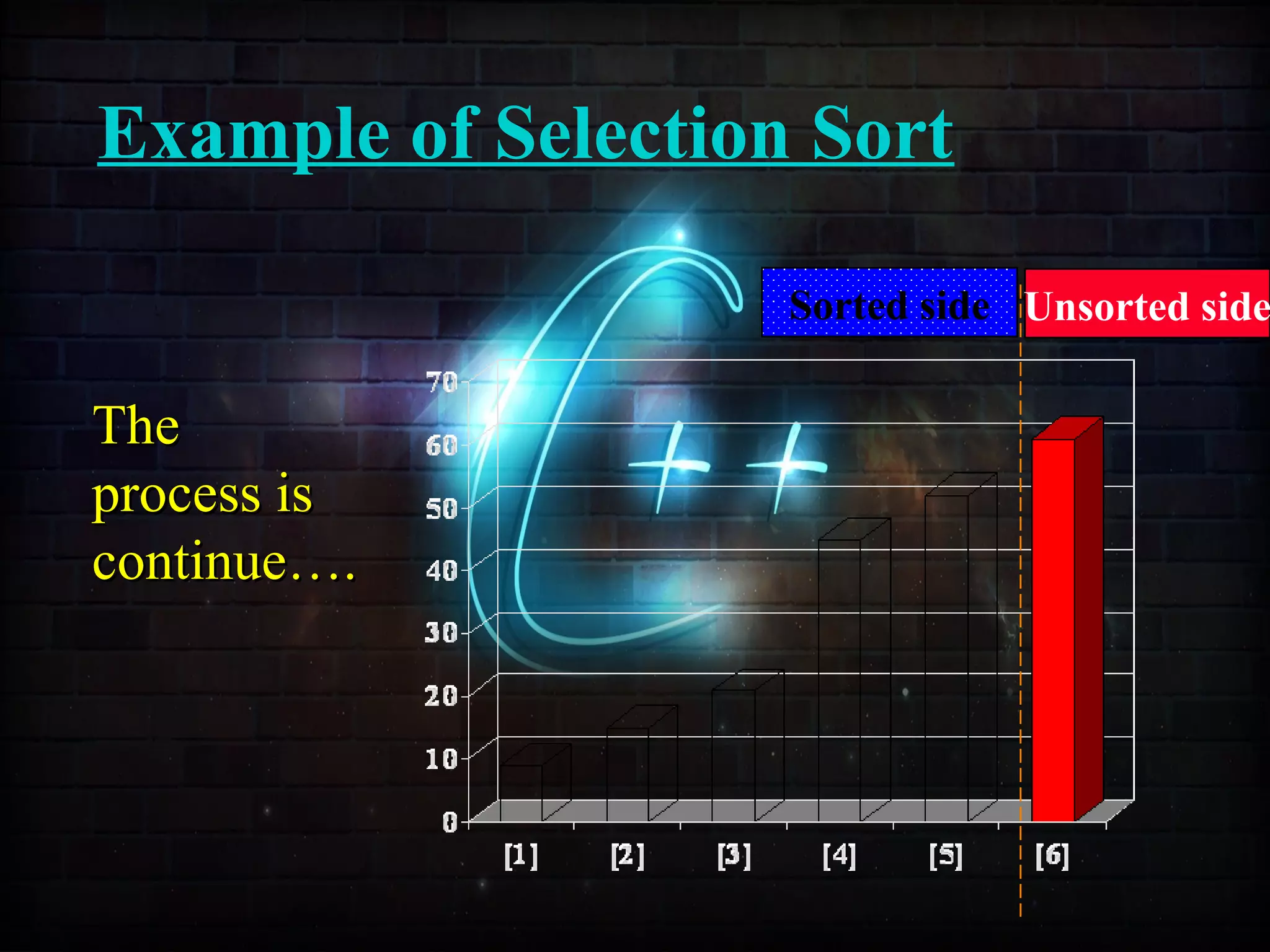
![Example of Selection Sort
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
[1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6]
Sorted side Unsorted side
Part of thePart of the
array isarray is
now sorted.now sorted.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortingusingfunctionppt-150814134749-lva1-app6892/75/Sorting-Techniques-63-2048.jpg)