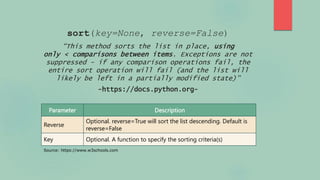
This document discusses the sort() function in Python for sorting lists. It explains that sort() sorts lists in place by default and can sort complex objects like dictionaries and tuples by specifying a key function. The key parameter allows sorting by a specific key or value. The document provides examples of sorting lists of dictionaries by age and tuples by a value, as well as explaining the differences between in-place and non-in-place sorting methods.




![Sorting Complex Object
The sort() function can also be used to sort complex
objects, such as dictionaries and tuples, by specifying a
key function
# Sorting a list of dictionaries by a specific key
people = [{"name": "Alice", "age": 25}, {"name": "Bob", "age": 18}, {"name": "Charlie", "age": 32}]
people.sort(key=lambda x: x["age"])
print(people) # Output: [{'name': 'Bob', 'age': 18}, {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 25}, {'name': 'Charlie',
'age': 32}]
# Sorting a list of tuples by a specific value
inventory = [("apple", 10), ("banana", 5), ("orange", 7)]
inventory.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
print(inventory) # Output: [('apple', 10), ('orange', 7), ('banana', 5)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sortfunctioninpython-230515124156-18163baa/85/Sort-Function-in-Python-pptx-6-320.jpg)

