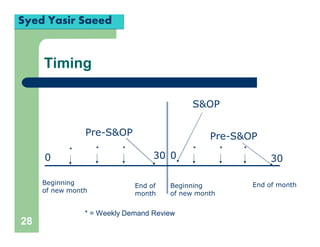
This document provides an overview of the Sales and Operations Planning (S&OP) process in high performing organizations. It describes key elements of the S&OP including integrating demand and supply side plans, using rolling 12-month forecasts and plans, managing risks, and ensuring accountability. It emphasizes that the S&OP process requires collaboration between various business functions like sales, marketing, and operations to align around a single business plan.